Heppia despreauxii (Mont.) Tuck.
Gen. Lich.: 46, 1872. Basionym: Solorina despreauxii Mont. - Hist. Nat. Isl. Canar., 3: 104, 1840.
Synonyms: Heppia gigantea Egea & Llimona; Heppia paulina Marton; Psora lobatoplicata B. de Lesd.
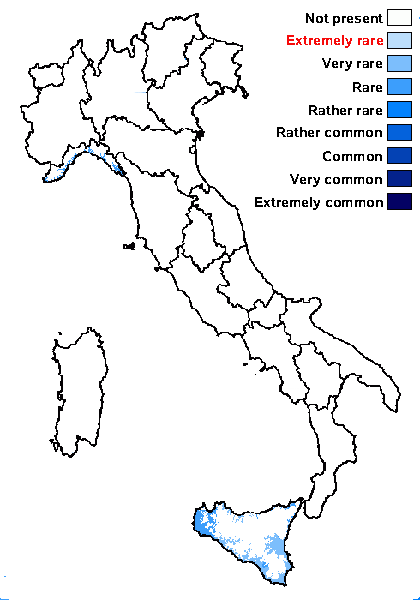
Distribution: N - Lig. S - Si (Grillo & Caniglia 2005).
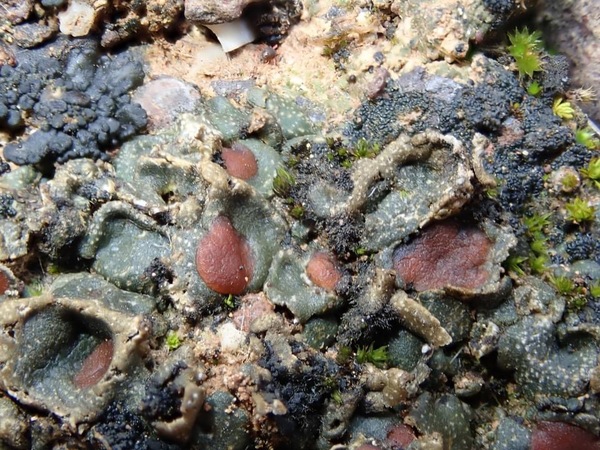
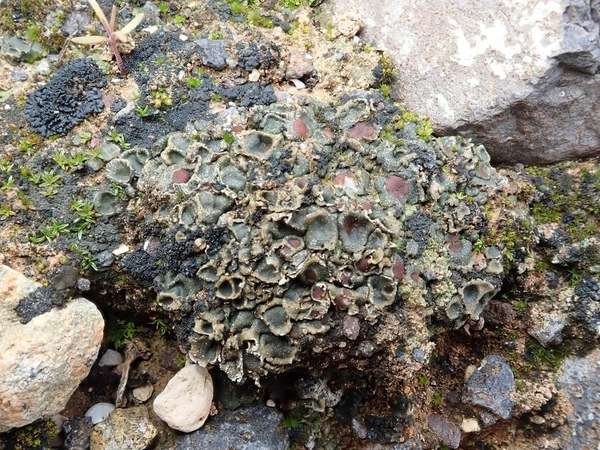
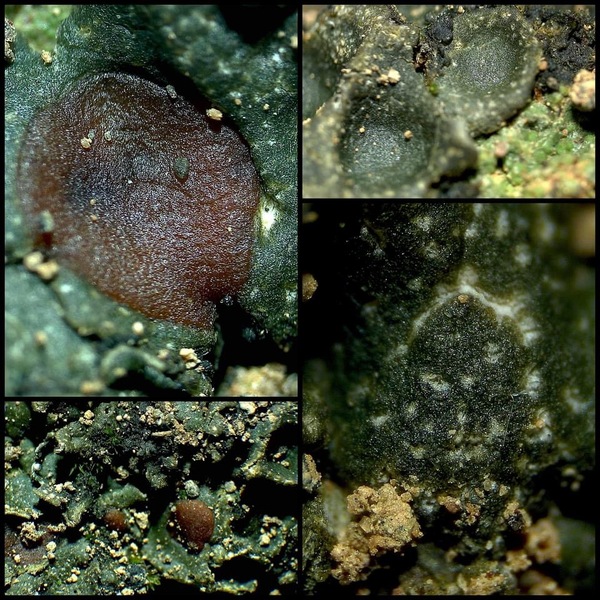
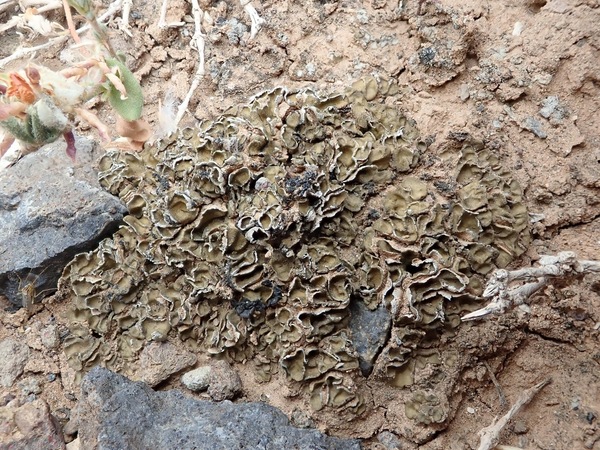
Description: Thallus squamulose, heteromerous, 340-400 µm thick, ochraceous brown, with pale punctiform depressions in a reticulate pattern. Squamules subpeltate, 2.5-7 mm wide, at first flat, then concave, contiguous, with rounded ends and a down-turned edges, attached by a mat of 10-14 µm thick, colourless rhizohyphae, forming 1.4-2.7(-5) cm wide, convex rosettes. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, (25-)50-75 µm thick, covered with a 10-15 µm thick epinecral layer; medulla poorly developed, of anticlinally arranged hyphae; lower cortex absent or restricted to the margins. Apothecia without a thalline margin, semi-immersed in the squamules, 0.5-1.5(-2) mm across, with a dark reddish brown, concave disc, and a thin to indistinct proper margin. Proper exciple very thin, colourless; epithecium brownish, K-; hymenium colourless, 120-180 µm high, I+ blue slowly turning reddish; paraphyses simple, lax, 4-6 µm thick at base, the apical cells 8-10 µm wide; hypothecium colourless, I+ blue. Asci 8-spored, thin-walled, narrowly clavate to subcylindrical, prototunicate. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, thin-walled, (18-)20-29(-31) x (7-)9-12 µm. Pycnidia dark, immersed. Conidia fusiform. Photobiont cyanobacterial, Scytonema-like. Spot tests: all negative. Chemistry: without lichen substances.
Note: the Ligurian record is the northernmost known for this Mediterranean-Macaronesian lichen growing on clay soil in dry, open grasslands. According to Timdal (in litt.) Psora lobatoplicata is a likely synonym of this species.
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: rare
Dry mediterranean belt: very rare
Predictive model
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: rare
Dry mediterranean belt: very rare

Predictive model
 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF







