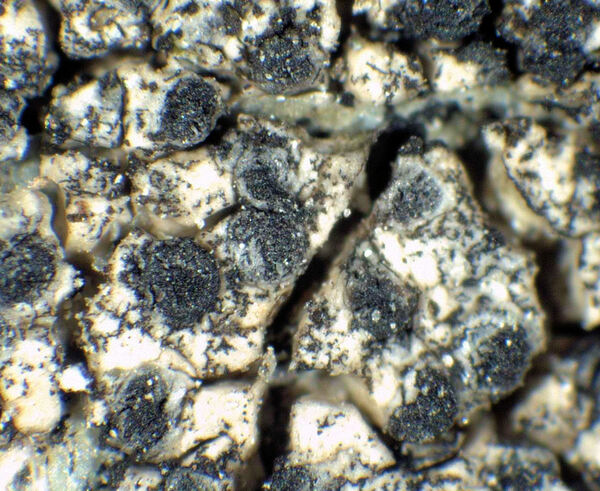
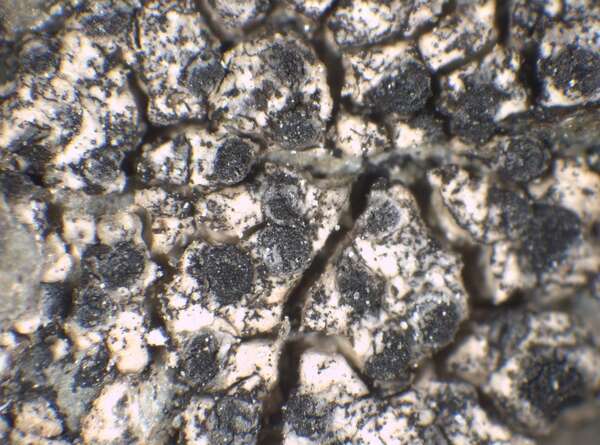
Buellia leptocline (Flot.) A. Massal.
Geneac. Lich.: 20, 1854. Basionym: Lecidea leptocline Flot. - Bot. Zeit., 8: 555, 1850.
Synonyms: Buellia gevrensis Th. Fr.; Buellia hypopodioides (Nyl.) Arnold; Buellia leptocline f. mougeotii (Hepp ex Arnold) Th. Fr.; Buellia leptocline var. inarimensis Jatta?; Lecidea hypopodioides f. ferruginascens Nyl.; Lecidea hypopodioides Nyl.; Lecidea mougeotii Hepp
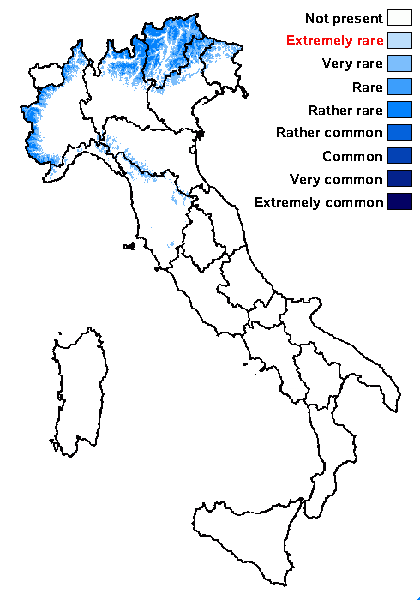
Distribution: N - Frl (Tretiach & Hafellner 2000), Ven, TAA (Caniglia & al. 2002, Nascimbene & al. 2022), Lomb, Piem (Favero-Longo & al. 2015), Emil (Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig. C - Tosc (Ravera & al. 2016).
Description: Thallus crustose, of variable thickness, endo- to episubstratic, continuous to rimose-areolate, whitish to grey; cortex overlain by a thin epinecral layer inspersed with crystals; medulla strongly amyloid, I+ violet. Apothecia lecideine, black, 0.5-1.2 mm across, sessile and constricted at base, with a flat to convex disc, and a thick, prominent, persistent proper margin. Proper exciple c. 100 µm wide, Leptocline-type, homogeneously dark brown, with an additional orange pigment reacting K+ reddish (solution), the inner part of long-celled, interwoven hyphae, the outer part of long-celled, parallel, strongly agglutinated and thick-walled hyphae; epithecium brown; hymenium colourless, not inspersed with oil droplets, c. 75 µm high; hypothecium dark brown. Asci 8-spored, clavate to cylindrical-clavate, the apical dome K/I+ dark blue with a pale, conical-pointed apical cushion (axial mass), the wall I-, but the thin outer gel I+ blue, Bacidia-type. Ascospores 1-septate, brown, oblong, not constricted at septum, 12-16(-18) x (6-)7.5-8.5(-11) µm, Physconia-type, with a rugulate wall (but smooth-walled when young). Pycnidia black, immersed in thallus. Conidia bacilliform, 4-5 x c. 1 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus K+ yellow, C-, KC-, P- or P+ very faintly yellow. Chemistry: atranorin. Note: a mainly boreal-montane species found on steeply inclined to rain-sheltered surfaces of hard siliceous rocks in upland areas. Earlier records (Nimis 1993: 140) from Central and Southern Italy, plus that from Sicily by Grillo (1998) could refer to other related species (B. halonia, B. sardiniensis, B. saxorum, B. sejuncta and B. subdisciformis), and are not considered here.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF




