Porocyphus rehmicus (A. Massal.) Zahlbr.
Cat. Lich. Univ., 2: 765, 1924. Basionym: Psorotichia rehmica A. Massal. - Miscell. Lichenol.: 23, 1856.
Synonyms: Collemopsis rehmii (Körb.) H. Olivier; Porocyphus byssoides Hepp; Porocyphus globulosus (A. Massal.) Couderc; Porocyphus rehmii (Körb.) Harm.; Porocyphus riparius (Arnold) Körb.; Psorotichia riparia Arnold
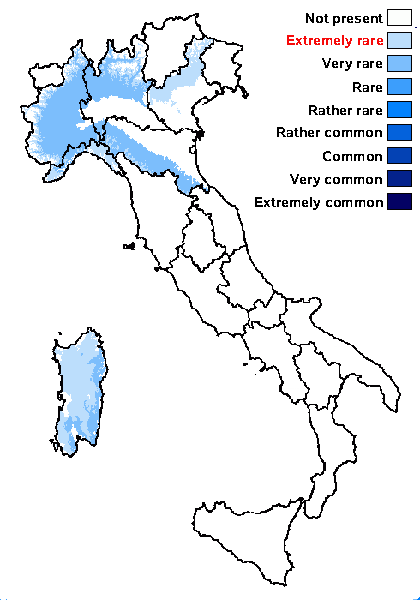
Distribution: N - Ven, Lomb, Piem, Emil (Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig. C - Sar.
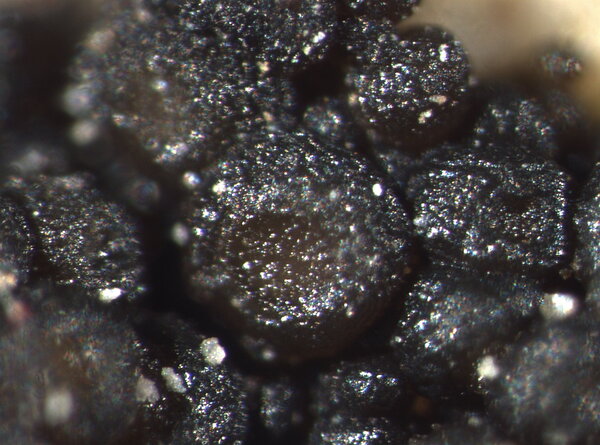
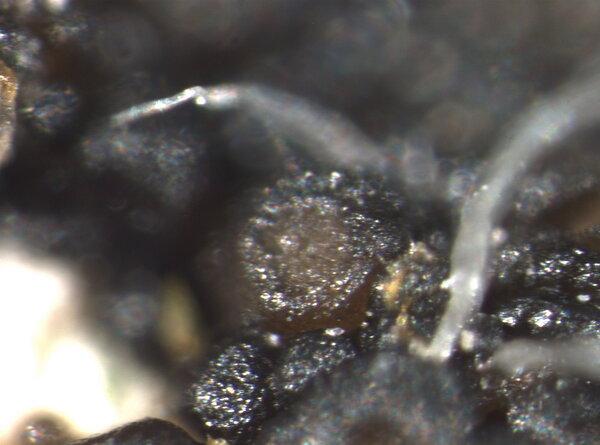
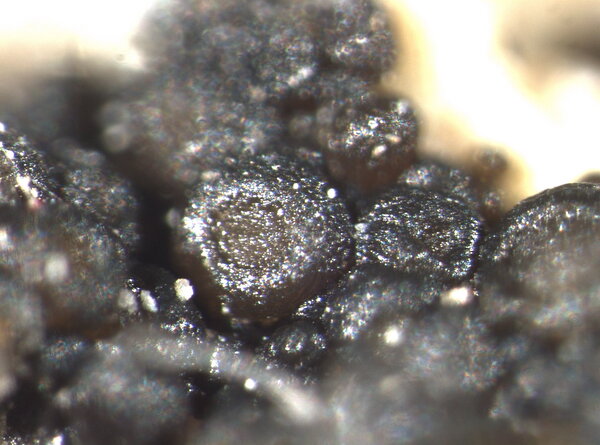
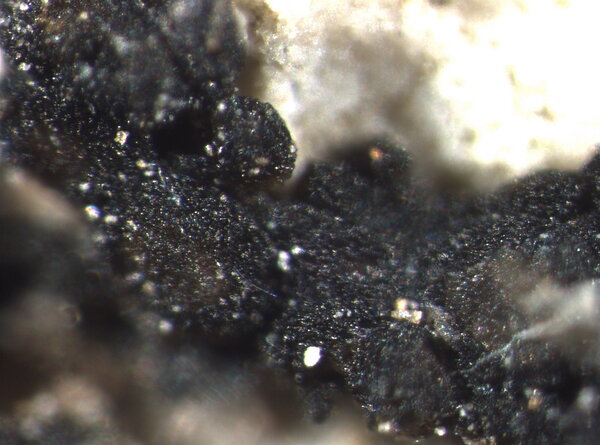
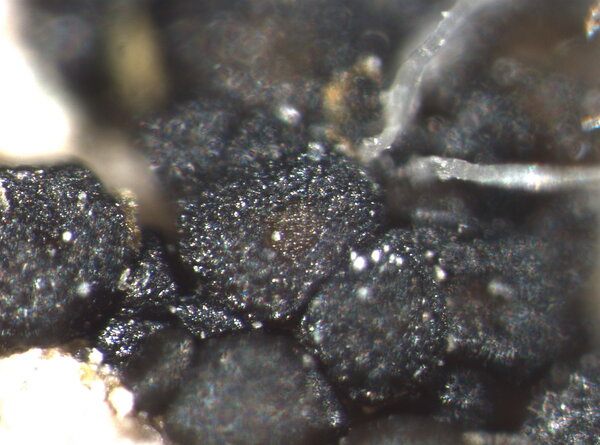
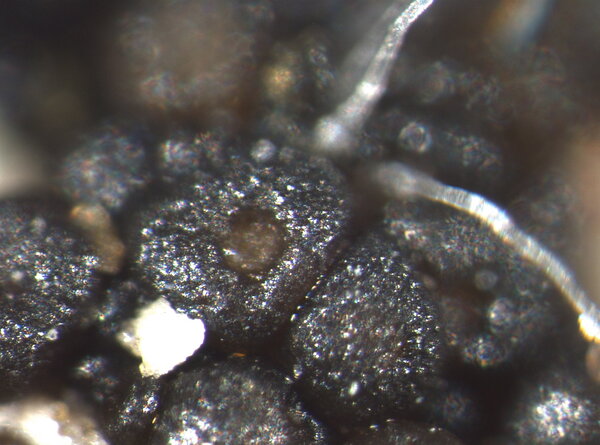
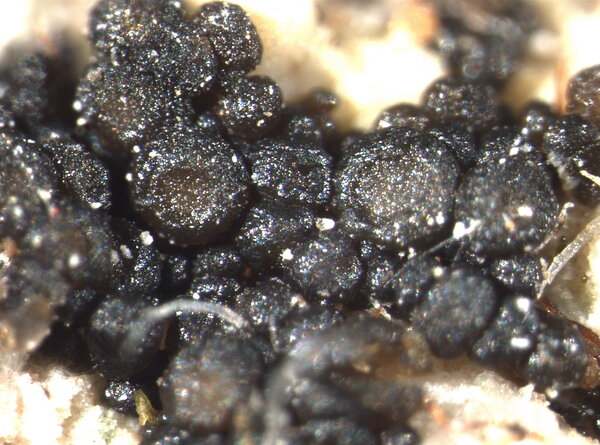
Description: Thallus crustose, irregularly rimose-areolate to subsquamulose, greenish black to black, subgelatinous when wet, ecorticate, homoiomerous. Areoles 0.3-1(-1.5) mm wide, 0.2-0.5(-1) mm thick, usually uneven, warty to granulose (never smooth), often dissolved into more or less erect, 50-200 µm long, 20-50 µm thick, coralloid granules, attached by rhizohyphae; thallus anatomy paraplectenchymatous, with irregularly arranged, 2-4(-5) µm thick hyphae. Apothecia pycnoascocarps (developing from pycnidia), semi-immersed to sessile, 1-3(-8) per areole, 0.15-0.3(-0.5) mm across, with a reddish brown, at first poriform, finally expanded, convex, reddish brown disc, a paler parathecial ring most evident in wet apothecia, and a soon excluded, usually shiny thalline margin. Thalline exciple 20-40 µm wide; proper exciple cupuliform, colourless and 10-20 µm wide at base, brownish and 35-55(-65) µm wide in upper part; epithecium orange-brown, 5-10 µm high; hymenium colourless, 90-130 µm high, I+ blue; paraphyses very thin, indistinctly septate, sparingly branched and anastomosing, c. 2 µm thick, the apical cells to 3 µm wide; subhymenium colourless, 20-30 µm high. Asci 8-spored, cylindrical, prototunicate, thin-walled, K/I-, without thickened apex or amyloid structures. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid or broadly ellipsoid, sometimes subglobose, 11-17(-22) x 5-9(-13) µm. Pycnidia immersed or slightly projecting, globose to broadly pyriform, with a colourless wall, 0.01-0.125 mm across. Conidia simple, hyaline, short-cylindrical, c. 2.5 x 1 µm. Photobiont cyanobacterial (Calothrix), the cells measuring 4-7 x 4-5 µm, isolated or arranged in small clusters. Spot tests: all negative. Chemistry: without lichen substances.Note: on seepage tracks of base-rich or slightly calciferous rocks, more rarely along creeks and rivers, often on sandstone walls.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, coccaceous (e.g. Gloeocapsa)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Periodically submerged (e.g. in creeks)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: very rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, coccaceous (e.g. Gloeocapsa)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Periodically submerged (e.g. in creeks)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: very rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF









