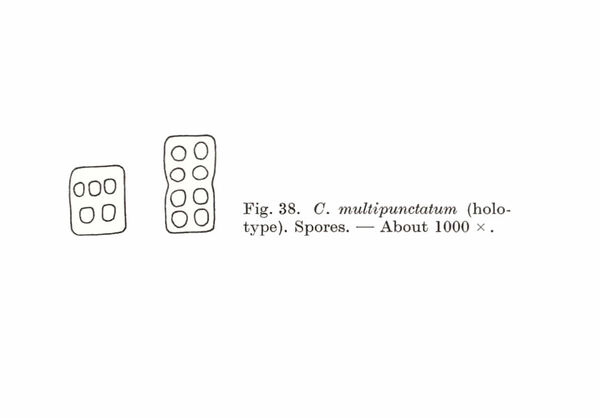
Rostania multipunctata (Degel.) Otálora, P.M. Jørg. & Wedin
Fungal Divers., 64, 1: 289, 2013. Basionym: Collema multipunctatum Degel. - Symb. Bot. Upsal., 13, 2: 260, 1954.
Synonyms: Collema verruciforme (Ach.) Nyl.
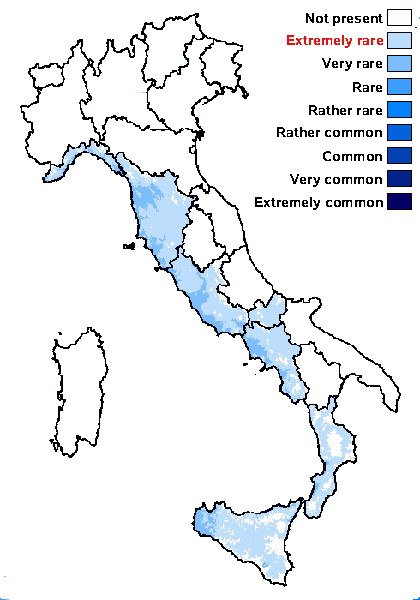
Distribution: N - Lig (Valcuvia & al. 2000, Giordani & Incerti 2008). C - Tosc (Loppi & al. 1997, 1998b), Laz, Mol (Nimis & Tretiach 1999, Caporale & al. 2008). S - Camp (Nimis & Tretiach 2004), Cal (Puntillo 1996), Si (Ottonello & al. 2011).
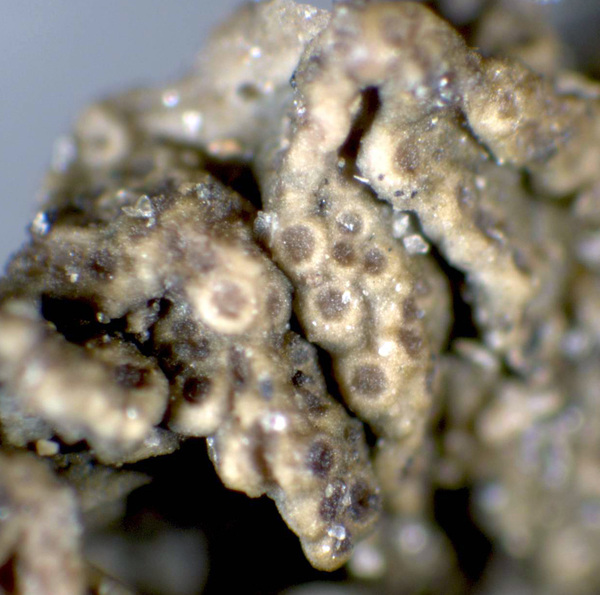
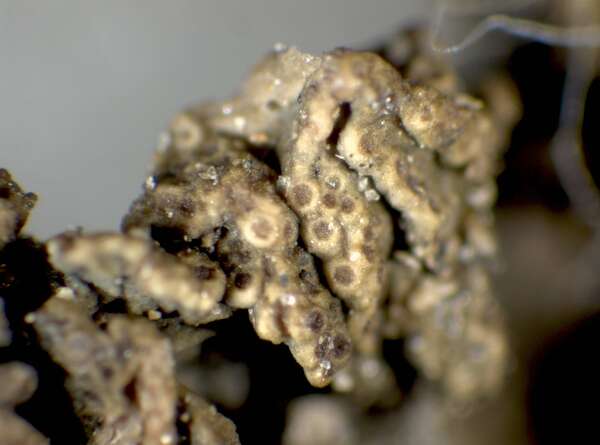
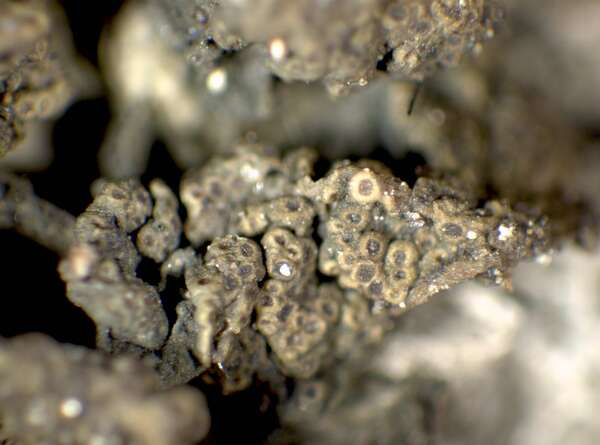
Description: Thallus subcrustose to subfoliose, homoiomerous, gelatinous and 80-350 μm thick when wet, rather loosely attached, olive-green to dark brownish green, strongly wrinkled, forming 10-25 mm wide, more or less orbicular pillows. Lobes scarce, usually poorly evident, <0.7 mm wide. Lower surface paler than upper surface, attached by a few white hapters. Upper and lower cortex absent. Apothecia common, lecanorine, numerous and crowded, at first punctiform and immersed, later sometimes subsessile, 0.1-0.3 mm across, with a concave to flat, brown disc, a thin, often soon excluded thalline margin, substituted by a paler proper margin. Thalline exciple ecorticate: proper exciple thin, euthy-subparaplectenchymatous, up to 25 μm wide laterally; epithecium brownish; hymenium colourless, 75-105 μm high, I+ blue; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched in upper part, 1.5-2 μm thick at mid-level, the apical cells not or only slightly wider; hypothecium pale yellow. Asci 8-spored, cylindrical-clavate, the apex strongly thickened, the apical dome K/I+ pale blue, with a downwardly projecting K/I+ deep blue tubular structure. Ascospores submuriform or muriform, with 1-3 transverse septa and 1-2 longitudinal septa, hyaline, cuboid to rectangular, some of them rarely subglobose, (9-)12-17 x (5-)6.5-13 μm. Pycnidia absent. Conidia formed in fascicles inside the thallus, oblong, 10-12 x 2 μm. Photobiont cyanobacterial (Nostoc, the cells in long chains). Spot tests: all negative. Chemistry: without lichen substances. Note: a mild-temperate, Mediterranean-Atlantic species found on more or less isolated trees in warm-humid areas, especially on Olea; mostly Tyrrhenian in Italy. It is included in the Italian red list of epiphytic lichens under the “Least Concern” category (Nascimbene & al. 2013c).
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF