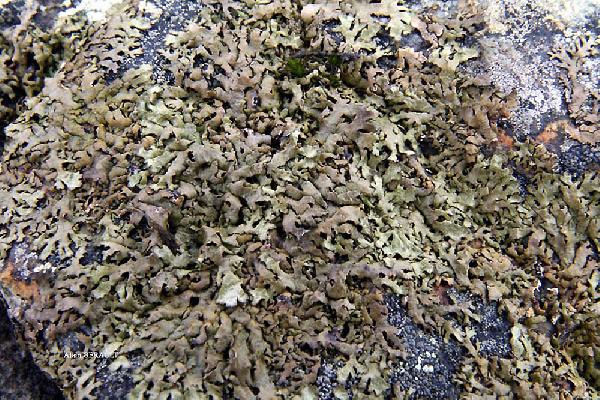
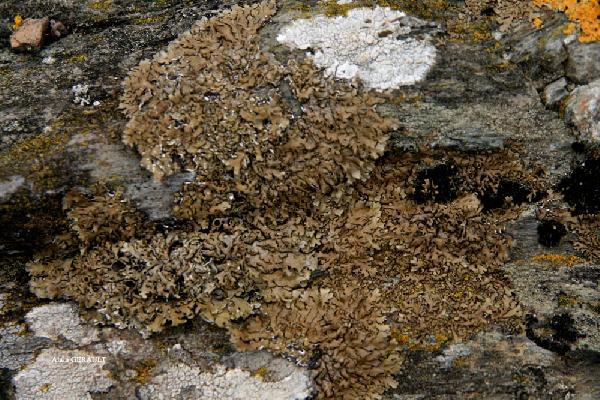
Xanthoparmelia delisei (Duby) O. Blanco, A. Crespo, Elix, D. Hawksw. & Lumbsch
Taxon, 53: 967, 2004. Basionym: Parmelia olivacea var. delisei Duby in DC. - Bot. Gall., 2 éd., 2: 602, 1830.
Synonyms: Neofuscelia delisei (Duby) Essl.; Parmelia delisei (Duby) Nyl.; Parmelia prolixa var. perlata Sambo; Parmelia pulla var. delisei (Duby) H. Magn.; Parmelia samboana Gyeln.
Distribution: N - VG (Giordani & al. 2003), TAA (Giordani & al. 2003), Lomb (Giordani & al. 2003), Piem (Giordani & al. 2003), VA (Piervittori & al. 2001), Emil (Giordani & al. 2003, Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig (Giordani & al. 2003, Rizzi & al. 2006). C - Tosc (Giordani & al. 2003), Marc (Giordani & al. 2003), Laz (Giordani & al. 2003), Sar (Giordani & al. 2003, Rizzi & al. 2011). S - Camp (Garofalo & al. 1999, Ricciardi & al. 2000, Giordani & al. 2003), Si (Giordani & al. 2003).
Description: Thallus foliose, heteromerous, dorsiventral, adpressed to adnate, forming 4-15 cm wide rosettes. Lobes elongated, 1-4 mm wide, radiating toward margins, occasionally pruinose, strongly maculate at tips, yellowish-brown, unevenly rumpled and transversely wrinkled. Lower surface dark brown to black, with simple rhizines. Upper cortex brown, paraplectenchymatous, with a pored epicortex, the cell walls with Xanthoparmelia-type lichenan; medulla white. Apothecia usually numerous, lecanorine, sessile to stipitate, to 12 mm across, with a red-brown disc and a smooth thalline margin. Epithecium brown; hymenium and hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, thick-walled, the apex I+ blue with a wide, divergent axial body, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, 7-11 x 4-6 µm. Pycnidia common, immersed. Conidia weakly bell-shaped, 4.5-7 x c. 1 µm. Photobiont: chlorococcoid. Spot tests: cortex K-, C-, KC+ yellow, P-, UV-, N+ blue-green; medulla K-, C- or C+ faintly red, KC+ orange-red, P-, UV-. Chemistry: medulla with glomellic, glomelliferic and perlatolic acids, often with gyrophoric acid as well, and numerous other accessory compounds. Note: on base-rich siliceous rocks. Perhaps this may be the primary, sexually reproducing species of X. loxodes, chemically different from X. pulla, and probably often confused with it in the earlier Italian literature.
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: rather rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: rather rare
Humid mediterranean belt: rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare
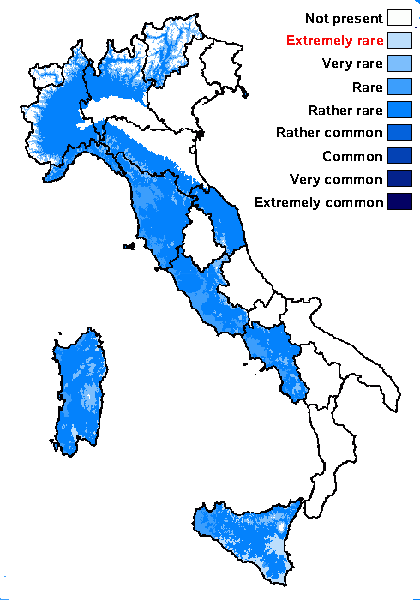
Predictive model

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis


Felix Schumm – CC BY-SA 4.0
Image from: F. Schumm (2008) - Flechten Madeiras, der Kanaren und Azoren. Beck, OHG - ISBN: 978-3-00-023700-3

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis
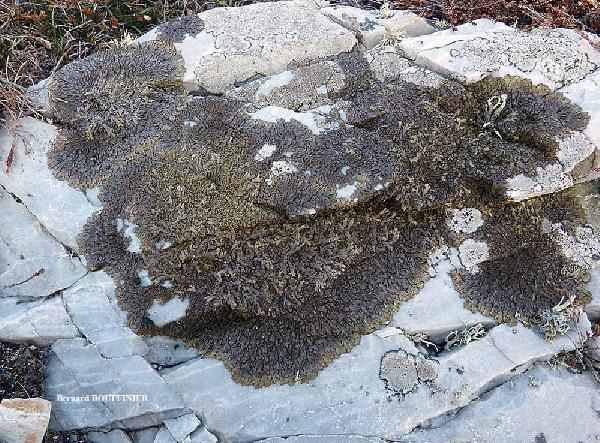

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=89&lang=en
France, Pointe de Pen-Hir
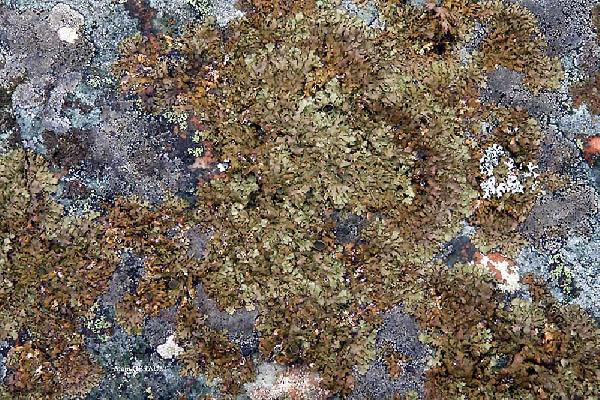

Alain Gerault - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=89&lang=en
France, Pointe de Pen-Hir
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: rather rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: rather rare
Humid mediterranean belt: rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare

Predictive model

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis


Felix Schumm – CC BY-SA 4.0
Image from: F. Schumm (2008) - Flechten Madeiras, der Kanaren und Azoren. Beck, OHG - ISBN: 978-3-00-023700-3

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=89&lang=en
France, Pointe de Pen-Hir

 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF



