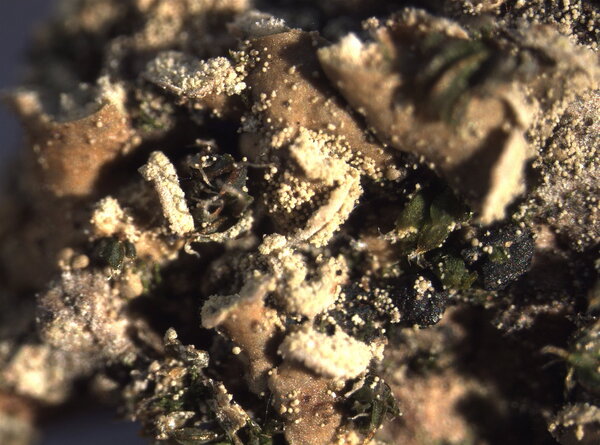
Waynea stoechadiana (Abbassi Maaf & Cl. Roux) Cl. Roux & P. Clerc
Bull. Soc. linn. Provence, 42: 130, 1991. Basionym: Hypocenomyce stoechadiana Abbassi Maaf & Cl. Roux - Bull. Soc. linn. Provence, 36: 191, 1985.
Synonyms:
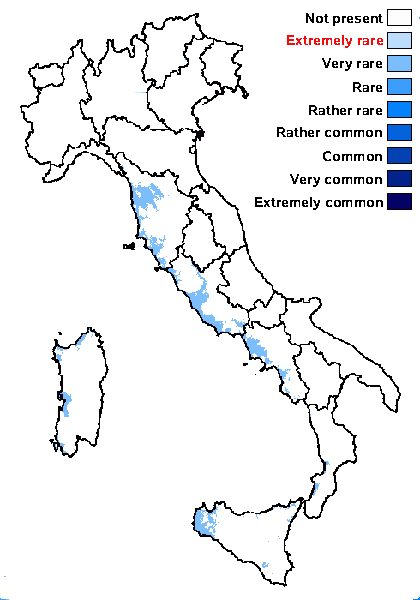
Distribution: C - Tosc (Stofer 2006), Laz (Roux & al. 1995, Ravera & al. 1999, 2000, 2003, Munzi & al. 2007, 2012, Lich. Ital. Exs. 4: Puntillo & al. 2017), Sar (Zedda 2002, Rizzi & al. 2011, Di Nuzzo & al. 2022). S - Camp (Ravera & al. 2020), Cal (Puntillo 1996, Puntillo & Puntillo 2004, Llop 2006, Potenza & al. 2023), Si (Ottonello & Puntillo 2009, Ottonello & al. 2011, Ravera & al. 2023b).
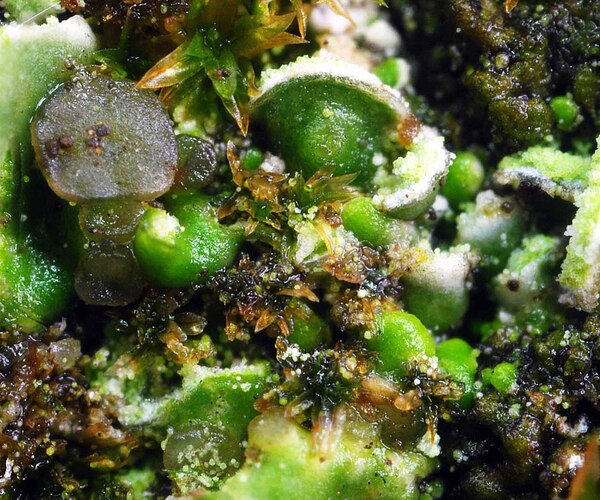
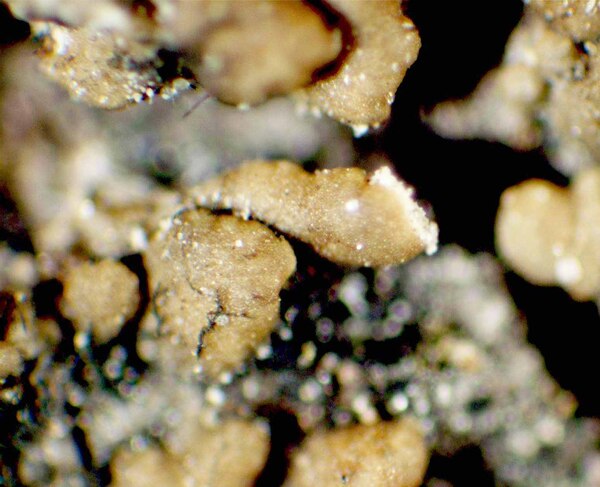
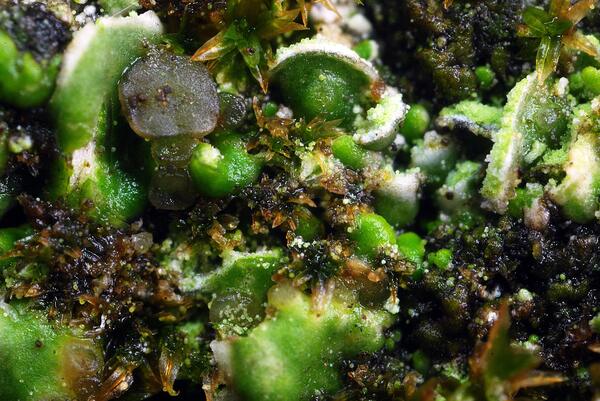
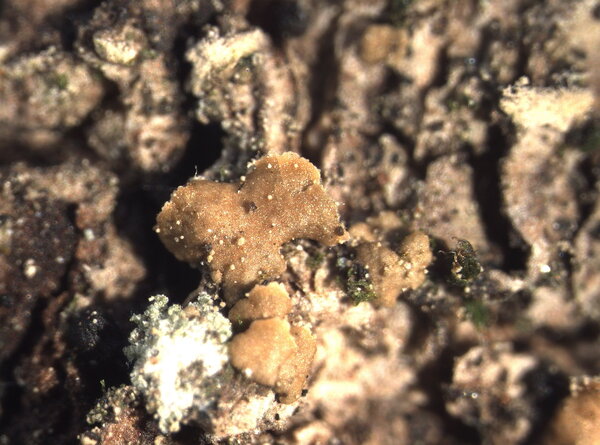
Description: Thallus squamulose, sorediate. Squamules numerous, flat to slightly convex, spathulate, 0.3-1.5(2.5) mm wide, ascending, contiguous or densely imbricate, attached by the base, the upper surface smooth, green to greenish brown (turning brown in the herbarium), slightly glossy, the lower surface whitish, with whitish to pale green, marginal, labriform soralia, the soredia 14-38 μm wide, sometimes extending to the lower surface. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, (12-)40-60 µm thick; medulla white, 50-100 µm thick, the individual hyphae 3-4.5(-6.5) µm wide; lower cortex absent. Apothecia rare, laminal, sessile, biatorine or cryptolecanorine, 0.3-1.5 mm across, with a flat to convex, grey to black, epruinose disc, a concolorous or paler, persistent to finally excluded proper margin and a poorly developed thalline rim which is sometimes visible at the very base of young apothecia. Proper exciple K+ yellow; epithecium pale green to greenish grey, K+ violet, N+ purple, without granules and crystals; hymenium colourless, 30-50 µm high, I+ blue; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched in upper part, 1.5-2.5 µm thick at base, the apical cells 3-4 µm wide, surrounded by a thin, pigmented, gelatinous layer; hypothecium colourless or pale yellow, prosoplectenchymatous, subtended by an algal layer, the pigmented parts K+ yellow. Asci 8-spored, clavate, distinctly thickened at apex, with a I+ blue tholus, the outer gelatinous coat I+ pale blue, Bacidia to Biatora-type. Ascospores (0-)1(-2)-septate, hyaline, narrowly ellipsoid to subfusiform, straight or slightly curved, 9-13(-17) x 2–3(-3.5) µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests; cortex K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-; medulla K+ weakly yellow. Chemistry: thallus with an unidentified depsidone and sometimes traces of lecanoric acid; Arceutina-yellow pigment in subhymenium, Sedifolia-grey pigment in epithecium.
Note: a Mediterranean-Macaronesian species found on ancient specimens of evergreen broadleaved trees, such as Olea and Quercus ilex, in warm-humid areas; exclusively Tyrrhenian in Italy. It is included in the Italian red list of epiphytic lichens as “Vulnerable” (Nascimbene & al. 2013c).
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF







