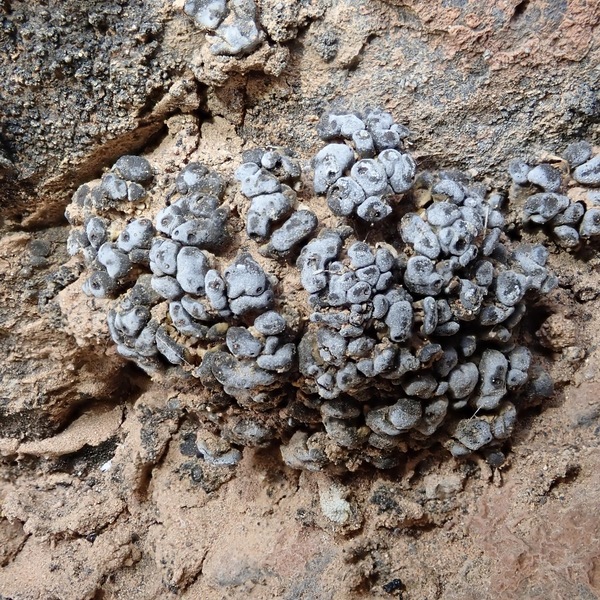
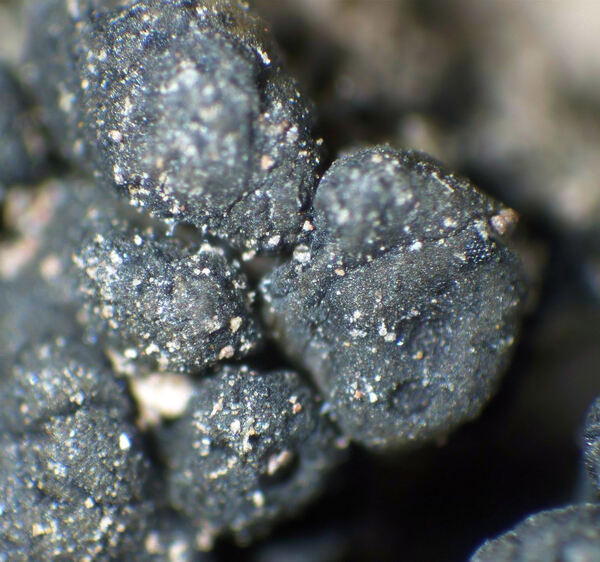
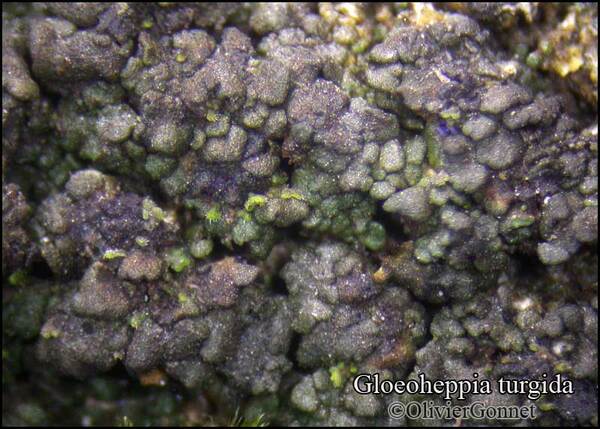
Gloeoheppia turgida (Ach.) Gyeln.
Feddes Rep., 38: 528, 1935. Basionym: Endocarpon turgidum Ach. - Lichenogr. Univ.: 305, 1810.
Synonyms: Heppia endocarpea (Fr.) Hue; Heppia turgida (Ach.) Nyl.; Lecanora endocarpea (Fr.) Nyl.
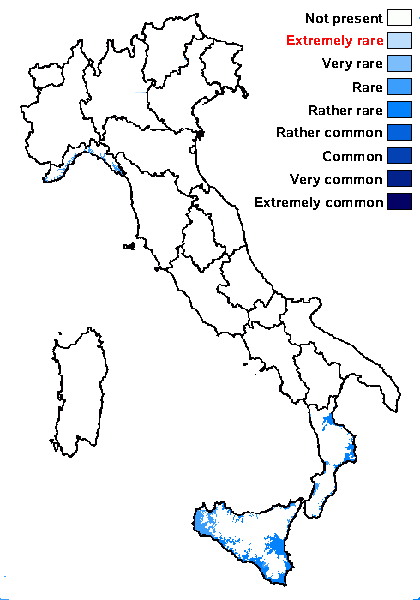
Distribution: N - Lig. S - Cal (Puntillo 1996), Si (Nimis & al. 1994, Ottonello & al. 1994, Caniglia & Grillo 2001, 2006, Grillo & Caniglia 2004).
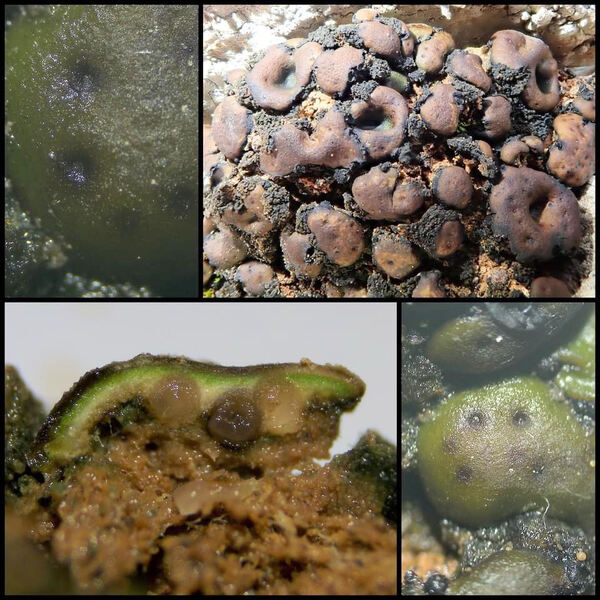
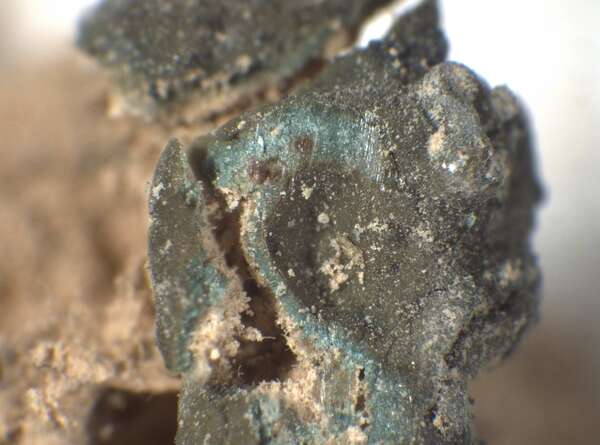
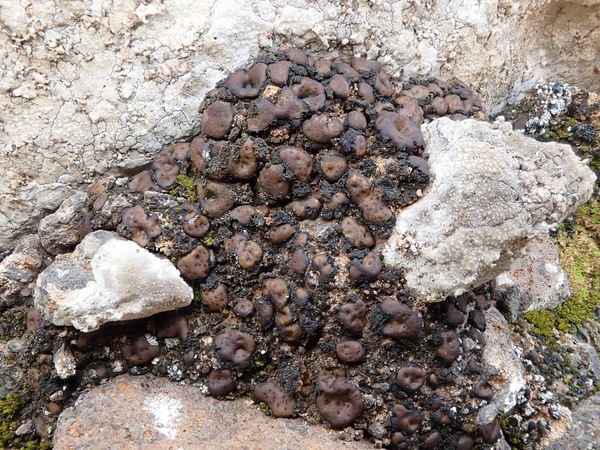
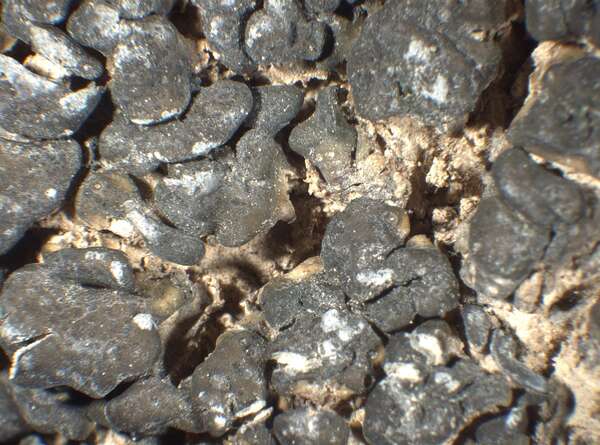
Description: Thallus squamulose, dark olive brown to brown-black, sometimes faintly whitish-pruinose, turning green when wet, 250-300(-400) μm thick, forming up to 1 cm wide patches. Squamules (2-)3-7 mm wide, rounded, often lobulate, strongly convex, smooth to weakly fissured, contiguous, with a down-turned edge, attached by a dense net of rhizinomorphs; lower surface usually much paler than upper surface. Upper cortex thin, weakly differentiated, covered with a 8-16 μm thick epinecral layer; photobiont layer of reticulately branched hyphae with cylindrical or roundish cells surrounding the colonies of the small-celled cyanobiont; lower cortex absent. Apothecia one to many per squamule, immersed, at first urceolate-perithecioid, then slightly expanded, 0.2-0.4 mm across when young, up to 1 mm across when old (several apothecia tending to coalesce), with a concave to flat, dark reddish brown to blackish disc and a thin thalline margin. Epithecium orange-brown, K-; hymenium colourless, 70-130 μm high, I+ blue; paraphyses simple, free, the apical cells distinctly thickened; hypothecium colourless, I+ blue. Asci 8-spored, prototunicate, cylindrical to obclavate, thin-walled, the wall I-. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, thin-walled, 9-15(-18) x 4-8 μm. Pycnidia black, immersed in the squamules. Conidia formed terminally, c. 1.5-2.5 x c. 1 μm. Photobiont cyanobacterial (probably a member of Chroococcales), unicellular. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-. Chemistry: without lichen substances.
Note: a mainly Mediterranean lichen found on calciferous soil in dry grasslands, occasionally on weathered basic siliceous rocks.
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rather rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rather rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF









