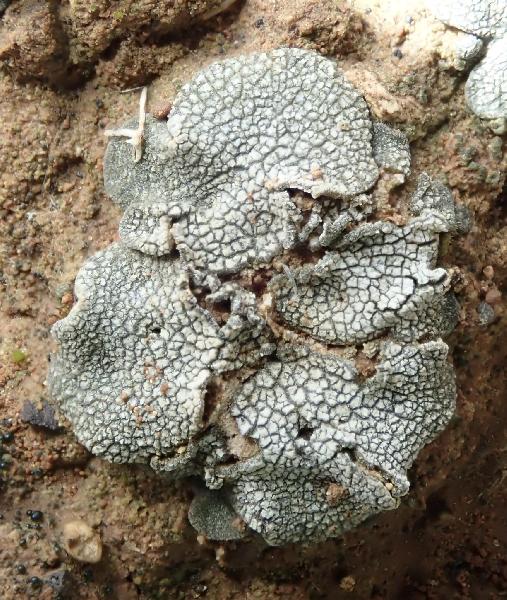
Heppia solorinoides (Nyl.) Nyl.
Syn. Meth. Lich., 2: 46, 1863. Basionym: Lecanora solorinoides Nyl. - Mém. Soc. Sc. Nat. Cherbourg, 2: 323, 1854.
Synonyms: Endocarpon reticulatum Dufour nom. illegit.; Heppia reticulata (Nyl.) Nyl.
Distribution: C - Tosc (TSB 35171). S - Pugl (Nimis & Tretiach 1999), Cal (Puntillo 1996), Si (Caniglia & Grillo 2001, 2005, 2006, Grillo & Caniglia 2004, 2005, Cataldo & Minissale 2013, 2015).
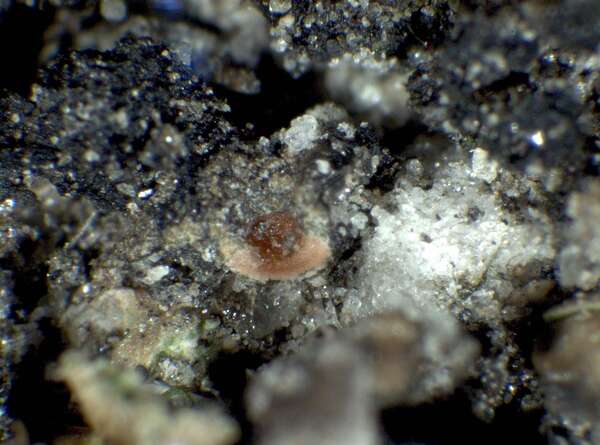
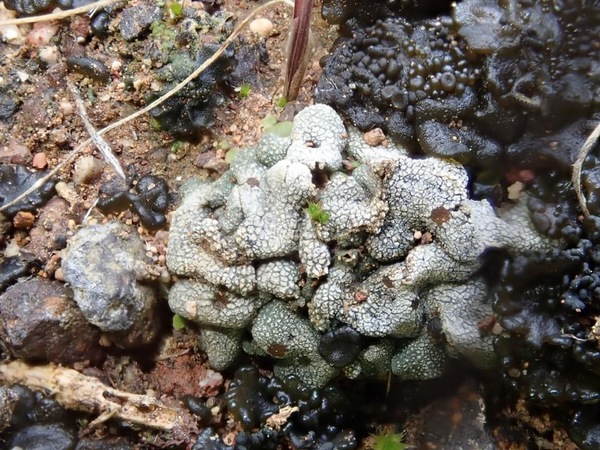
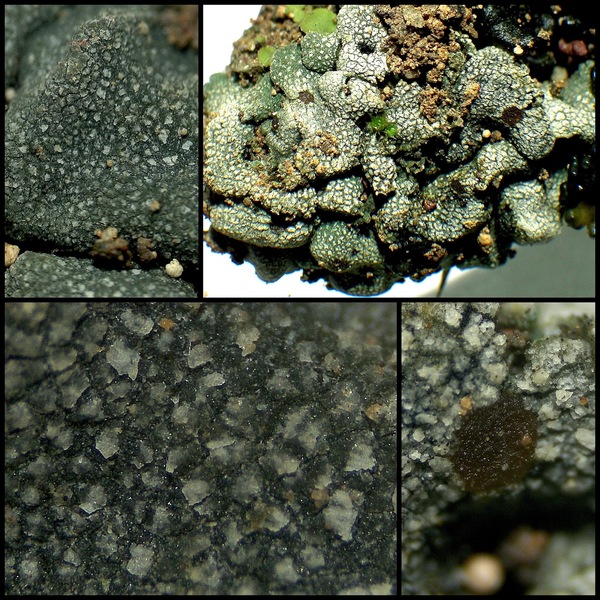
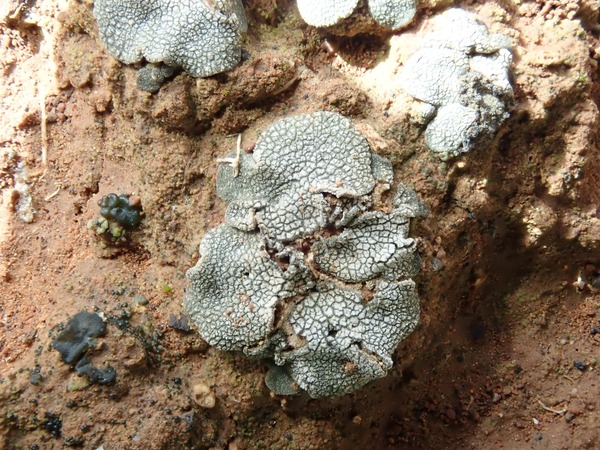
Description: Thallus squamulose, brownish under a thick white layer of clustered crystals (pruina) which tends to accumulate in areolate patches, giving the surface a reticulate appearance. Squamules (2-)3-7 mm broad, 300-400 µm thick, elongate, at first flat, then concave, contiguous, with rounded ends and up-turned, undulate edges, attached by a mat of rhizohyphae. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, 35-75 µm thick, overlain by a 15-25 µm thick epinecral layer; medulla 60-100 µm thick, paraplectenchymatous; lower cortex 25-30 µm thick, paraplectenchymatous, hardly differentiated from the medulla. Apothecia frequent, without a thalline margin, semi-immersed in the squamules, 0.5-1.5(-2.5) mm across, with a reddish brown, at first concave, then flat disc. Proper exciple poorly developed: epithecium orange-brown, K-; hymenium colourless, 150-200 µm high; paraphyses mostly simple, lax, distinctly thickened above; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, cylindrical to obovoid, with a very thin wall disintegrating or opening by apical ruptures, Lichina-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, thin-walled, 16-26(-29) x (6-)8-12(-13) µm. Pycnidia dark, immersed. Conidia bacilliform. Photobiont cyanobacterial, Scytonema-like. Spot tests: K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-. Chemistry: without lichen substances.Note: on clay or sandy-clay soil, restricted to very dry grasslands in Mediterranean Italy.
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
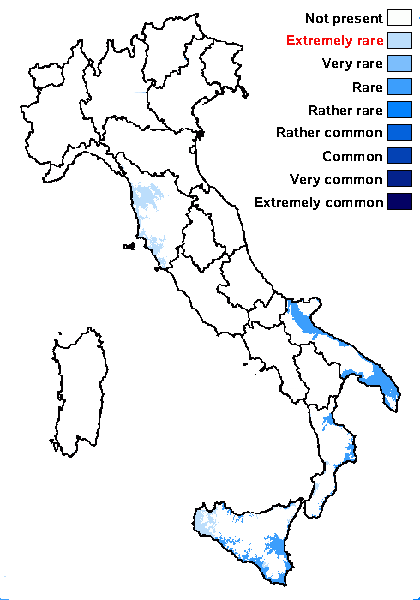
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
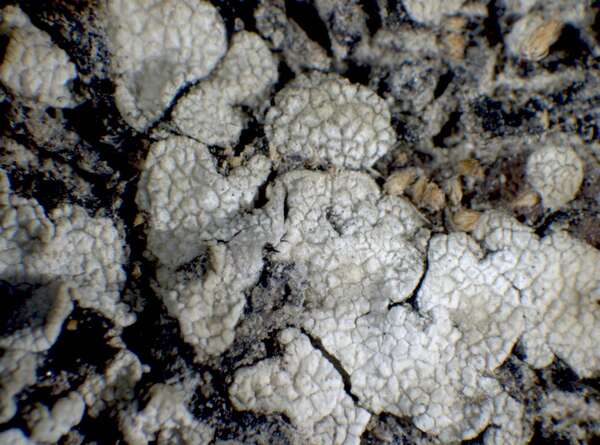


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (9454)
2001/11/24
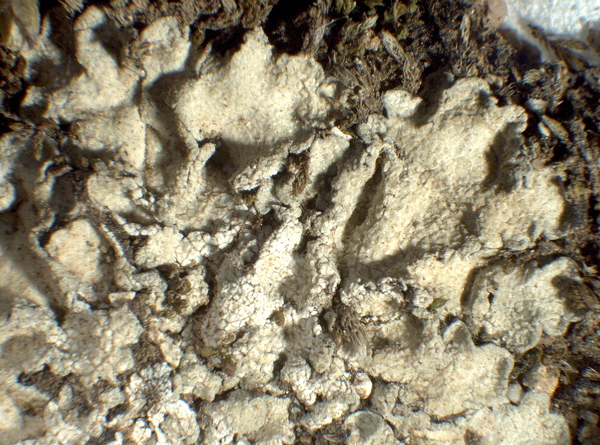


P.L.Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (38434)
2008.02.25
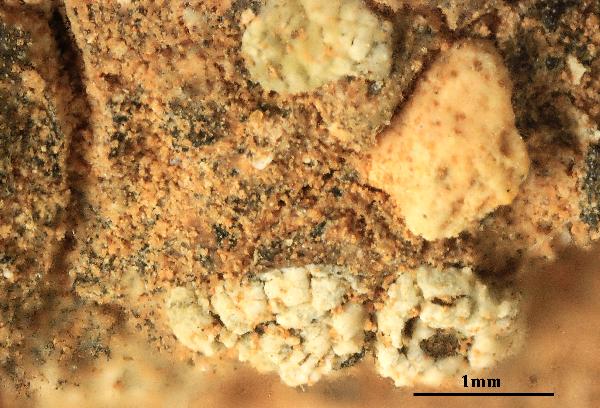


Felix Schumm - CC BY-4.0
[VZR36], Italia. Pelagiae insulae: insula Lampedusa, in parte centrali
insulae, 20 m. Ad terram calcaream. Leg. G. Lazzarin, P. L. Nimis & A.
Vezda. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES RARIORES EXSICCATI NR. 36.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-4.0
[VZR36], Italia. Pelagiae insulae: insula Lampedusa, in parte centrali
insulae, 20 m. Ad terram calcaream. Leg. G. Lazzarin, P. L. Nimis & A.
Vezda. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES RARIORES EXSICCATI NR. 36.
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (9454)
2001/11/24


P.L.Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (38434)
2008.02.25


Felix Schumm - CC BY-4.0
[VZR36], Italia. Pelagiae insulae: insula Lampedusa, in parte centrali insulae, 20 m. Ad terram calcaream. Leg. G. Lazzarin, P. L. Nimis & A. Vezda. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES RARIORES EXSICCATI NR. 36.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF







