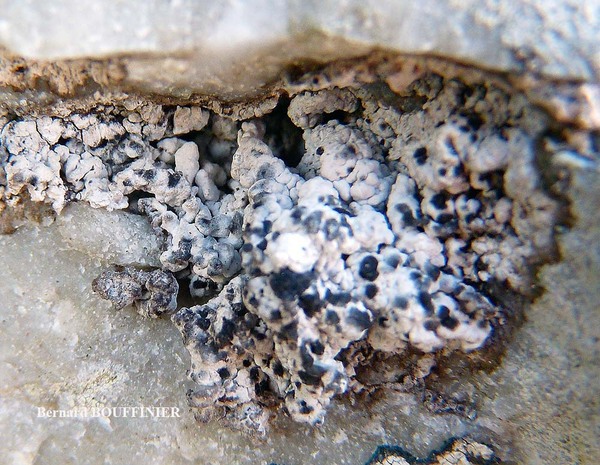
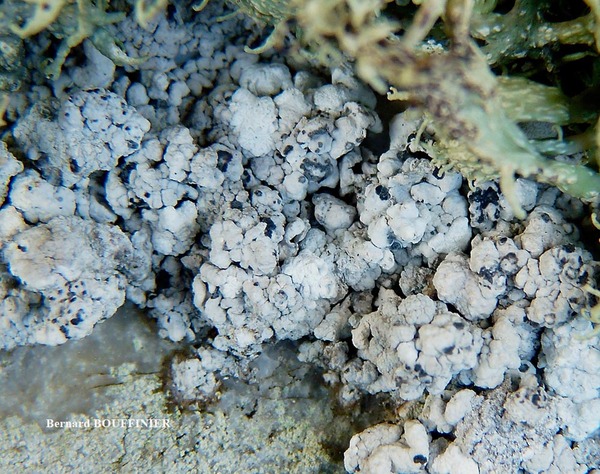
Lecanographa atlantica Ertz & van den Boom
Phytotaxa, 472, 2: 152, 2020.
Synonyms: Lecanactis farinosa auct. non (Hepp) Egea, Torrente & Manrique; Lecanographa farinosa auct. non (Hepp) Egea & Torrente
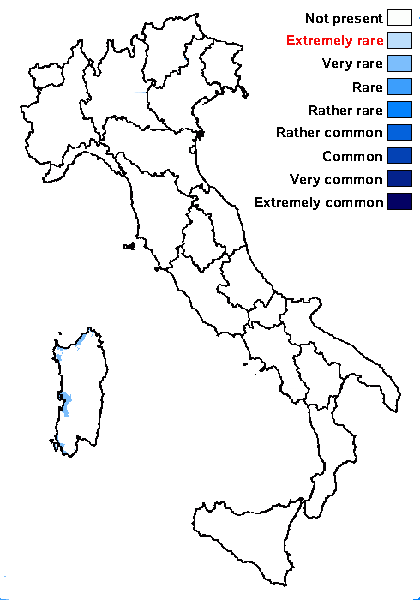
Distribution: C - Sar (Egea & al. 1993, Egea & Torrente 1994).
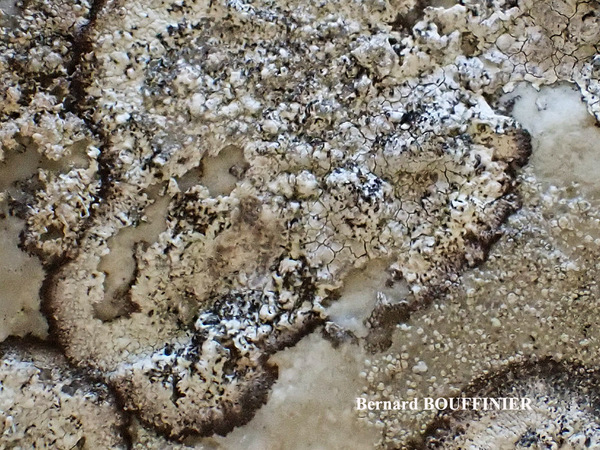
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, white to cream-coloured, rimose-areolate, 0.15.0.3 mm thick but sometimes poorly developed, farinose-granulose, ecorticate, with a cretaceous medulla, delimited by a dark prothallus. Apothecia round, irregular or lirelliform, when round c. 0.4-0.8 mm across, when oblong-lirelliform simple or sparingly branched, 0.5-2(-2.5) x 0.3-0.8 mm, immersed to adnate, black but usually white-pruinose (the pruina dissolving in K), with an expanded, flat to slightly convex disc and a thin, entire to wavy proper margin. Proper exciple black, carbonized, 45-50 μm thick, extending below the hymenium; epithecium brownish, covered in colourless crystals soluble in K; hymenium colourless or pale yellow, (55-)65-75(-80) μm high, I+ pale orange, K/I+ pale blue; paraphysoids richly branched and anastomosing, c. 1(-1.5) μm thick at mid-level, the apical cells hardly swollen, to 2 μm wide; subhymenium pale brown, 12-15 μm high; hypothecium carbonized, black to brown-black, 200-380 µm high. Asci 8-spored, narrowly clavate to cylindrical, fissitunicate, the apex with a narrow, K/I± pale blue apical dome penetrated by a small ocular chamber (Grumulosa-type of Egea & Torrente 1994). Ascospores (3-)5-7-septate, hyaline, spindle-shaped, straight or slightly curved, (18-)20-26 x 3.5-5 μm, the wall slightly thickened at septa, with a 1(1.5) µm thick gelatinous sheath. Photobiont trentepohlioid. Spot tests: thallus K- or K+ pale yellow, C-, KC-, P+ yellow-orange or P-, UV- or UV+ whitish-blue or pale cream to pale orange. Chemistry: 2’-O-methylperlatolic acid, sometimes also psoromic acid, plus an unidentified substance.Note: an Atlantic-Mediterranean species, previously confused with L. farinosa, found beneath overhangs of coastal siliceous rocks protected against salt-spray. For further details see Ertz & van den Boom (2020).
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Taxon bound to maritime-coastal situations
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: h: ttp://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=336&lang=en
France, Kernaveno
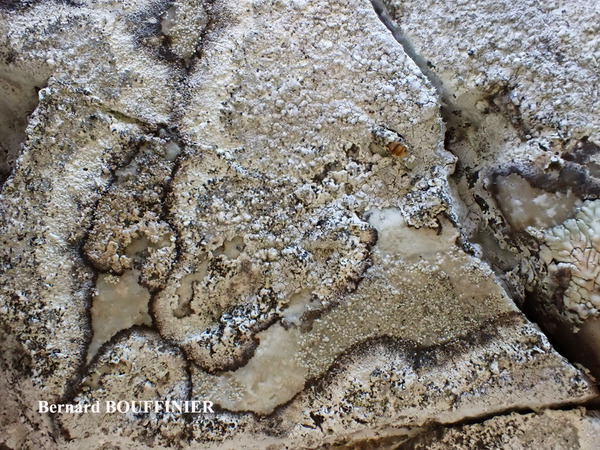

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: h: ttp://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=336&lang=en
France, Kernaveno
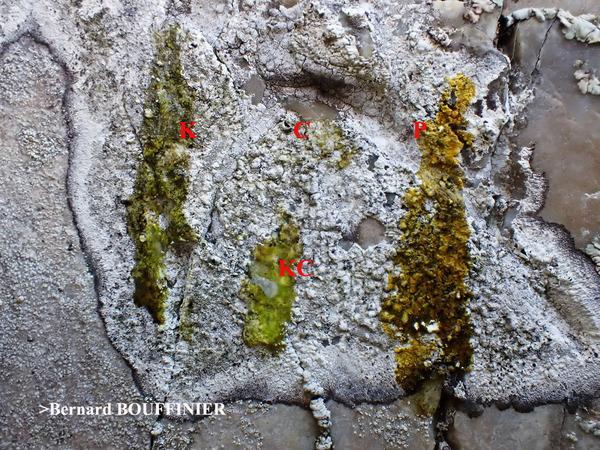

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: h: ttp://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=336&lang=en
France, Kernaveno
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Taxon bound to maritime-coastal situations
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: h: ttp://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=336&lang=en
France, Kernaveno

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: h: ttp://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=336&lang=en
France, Kernaveno




