Lecanora valesiaca (Müll. Arg.) Stizenb.
Ber. Thät. St. Gall. Naturw. Ges.: 342, 1882. Basionym: Placodium valesiacum Müll. Arg. - Bull. Trav. Soc. Murithienne Valais, 10: 56, 1881.
Synonyms: Squamaria valesiaca (Müll. Arg.) H. Olivier
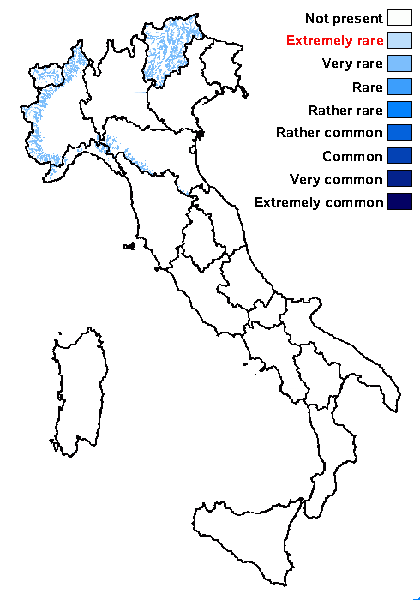
Distribution: N - TAA, Piem (Clerc & al. 1999), VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999), Emil (Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig (Petrak 1960).
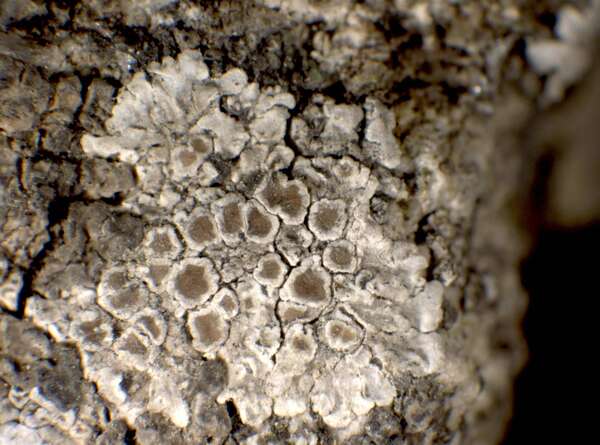
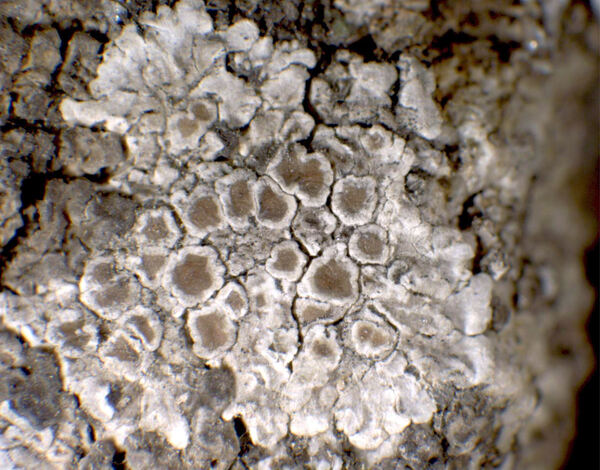
Description: Thallus crustose-placodioid, episubstratic, pale greenish yellow but densely pruinose throughout and appearing whitish to yellowish white, 0.1-0.5(-1) mm thick, rimose-areolate in central parts, forming regular, 1-2(-4) cm wide rosettes, the central areoles contiguous, 0.5-0.7 mm wide, flat, the marginal lobes flat to slightly convex, 1-2(-5 mm) long, 0.3-0.7(-1) mm wide, clearly radiating, moderately crenate-incised, with undulating margins. Cortex 20-30 µm thick, inspersed with greyish crystals insoluble in K, not overlain by an epinecral layer; medulla white, thickly inspersed with granules. Apothecia common, lecanorine, at first semi-immersed, then sessile, 0.5-1.5(-2) mm across, with a yellowish brown to brown, flat to convex, sometimes pruinose disc and an entire to crenate, persistent, incurved margin which is usually level with disc, sometimes with an indistinct parathecial ring which is paler than disc. Thalline exciple corticate, with an algal layer extending below the hypothecium, the medullary part with coarse crystals insoluble in K; proper exciple pale grey in outer part, colourless or pale yellow in inner part; epithecium yellow-brown to partially greenish (the green parts N+ violet-red). inspersed with fine yellow-brown granules soluble in K; hymenium colourless, 55-75 µm high; paraphyses mostly simple, scarcely thickened at tips; subhymenium pale grey, 30-60 µm high; hypothecium 30-130 µm high in central part. Asci 8-spored, clavate, very thin-walled, with a K/I+ blue, tall tholus penetrated by a faintly amyloid apical cushion, the wall K/I-, surrounded by a blue outer layer, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid to broadly ellipsoid, (8-)9-11(-12) x 4-7 µm. Pycnidia immersed, often inconspicuous. Conidia thread-like, mostly curved, 15-20 µm long. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC- or KC+ pale yellow, P-. Chemistry: cortex with usnic acid; medulla with roccellic acid.Note: on base-rich rocks (gneiss, porphyry, schists, etc.) containing some calcium, in warm-dry situations. For the non-accepted records from Southern Italy see Nimis (1993: 373).
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS