Lepraria vouauxii (Hue) R.C. Harris
in Egan, Bryologist, 90: 163, 1987. Basionym: Crocynia vouauxii Hue - Bull. Soc. Bot. France, 71: 392, 1924.
Synonyms: Crocynia arctica Lynge; Lepraria arctica (Lynge) Wetmore; Leproloma vouauxii (Hue) J.R. Laundon
Distribution: N - VG (Baruffo & al. 2006), Frl (Baruffo & al. 2006), Ven (Baruffo & al. 2006), TAA (Baruffo & al. 2006, Nascimbene & al. 2007b), Lomb (Baruffo & al. 2006), Piem (Baruffo & al. 2006), Emil (Baruffo & al. 2006, Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig (Baruffo & al. 2006). C - Tosc (Baruffo & al. 2006), Umb (Baruffo & al. 2006, Ravera & al. 2006, Panfili 2007), Abr (Baruffo & al. 2006, Gheza & al. 2021), Sar (Zedda 2000a, 2002, 2002b, Cossu 2013, Neuwirth 2018). S - Pugl (Baruffo & al. 2006), Bas (Baruffo & al. 2006)
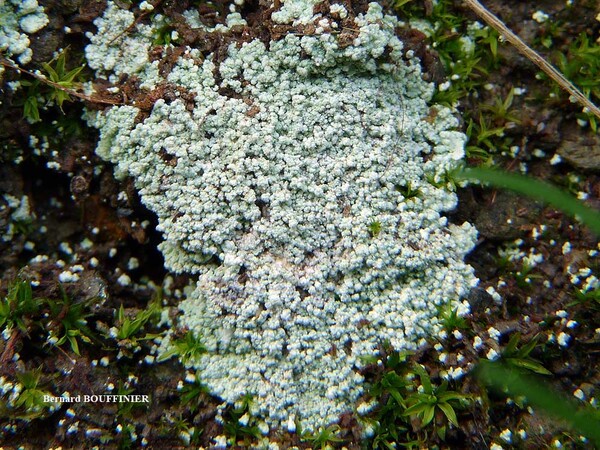
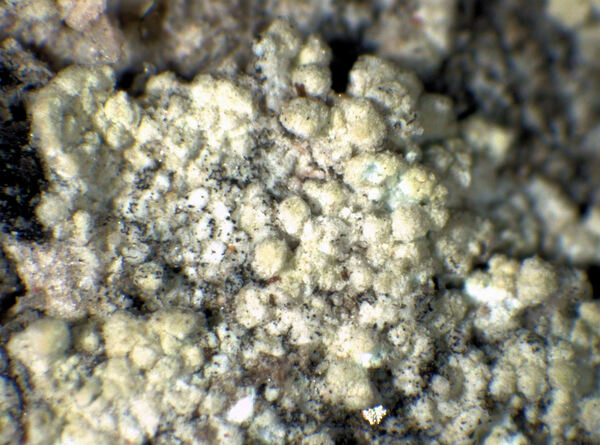
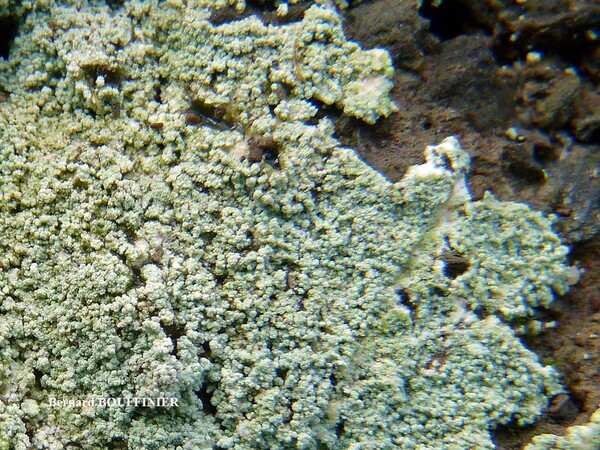
Description: Thallus leprose, cottony, 0.2-0.4 mm thick, forming obscurely lobed rosettes to irregularly delimited or diffuse, composed of a mass of powdery granules, pale yellowish-grey or pale cream-coloured, usually with a yellowish tinge. Granules ecorticate, soredia-like, 30-80(-180) µm wide, rarely gathered in up to 300 µm wide aggregates, without or with short projecting hyphae. Medulla white, weakly developed, the hyphae 2-4 µm thick, anastomosing, most often covered in numerous colourless crystals; lower side of thallus sometimes with orange-brown hyphae forming a weakly developed hypothallus reacting K+ purple-red. Photobiont chlorococcoid, the cells globose, up to 20 µm in diam. Spot tests: K- or K+ dirty yellow to orange, C- or C+ dirty orange, KC-, P- to P+ orange or yellow-orange, UV-. Chemistry: pannaric acid-6 methylester, rarely atranorin and roccellic acid, with or without pannaric acid. Note: on isolated deciduous trees with subneutral to subacid bark, usually in positions which are seldom wetted by rain, sometimes on brick walls, with a wide ecological and altitudinal range; certainly common throughout Italy.
Growth form: Leprose
Substrata: bark and rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by soredia, or soredia-like structures (e.g. blastidia)
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rare
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: rare
Montane belt: rather common
Submediterranean belt: common
Padanian area: rather common
Humid submediterranean belt: rather common
Humid mediterranean belt: rather rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare
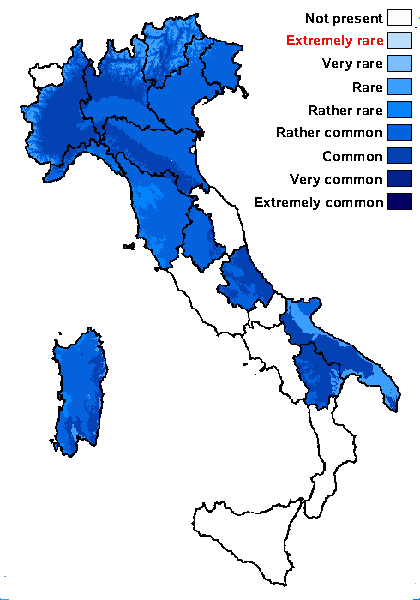
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
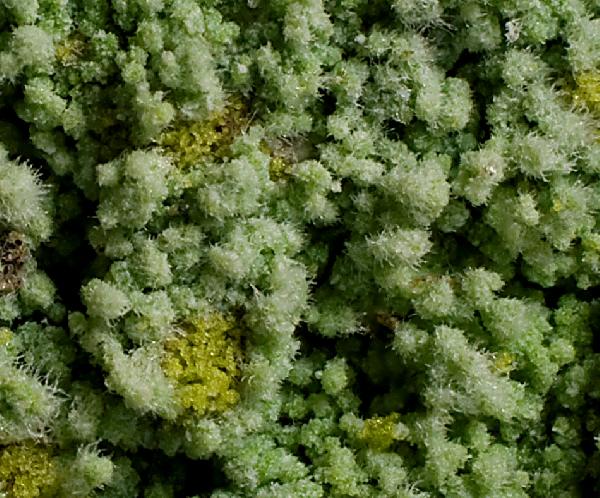

Ulrich Kirschbaum CC BY-SA 4.0 - Source: https://www.thm.de/lse/ulrich-kirschbaum/flechtenbilder
Central Europe; Germany: Hesse.
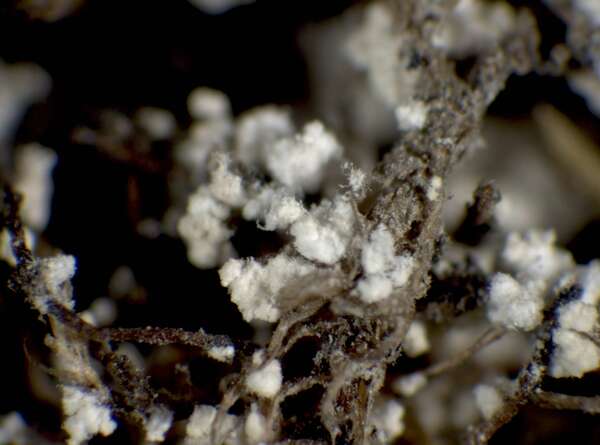


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (32774)
2001/12/13

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis
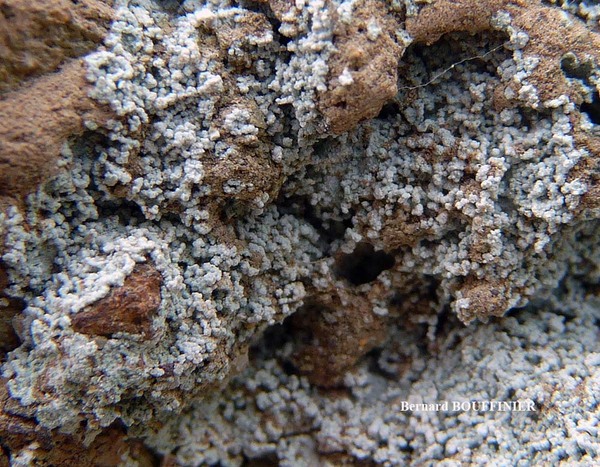

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=695&lang=en
France, Cap de la Chèvre
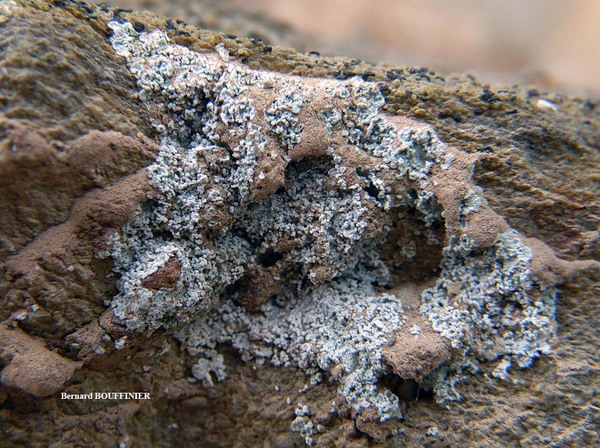

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=695&lang=en
France, Cap de la Chèvre
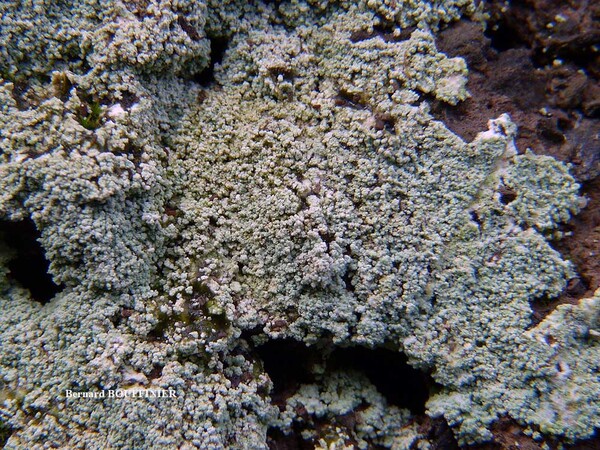

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=695&lang=en
France, Pointe de Dinan
Growth form: Leprose
Substrata: bark and rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by soredia, or soredia-like structures (e.g. blastidia)
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rare
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: rare
Montane belt: rather common
Submediterranean belt: common
Padanian area: rather common
Humid submediterranean belt: rather common
Humid mediterranean belt: rather rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |

Ulrich Kirschbaum CC BY-SA 4.0 - Source: https://www.thm.de/lse/ulrich-kirschbaum/flechtenbilder
Central Europe; Germany: Hesse.


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (32774)
2001/12/13

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=695&lang=en
France, Cap de la Chèvre

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=695&lang=en
France, Cap de la Chèvre

 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS




