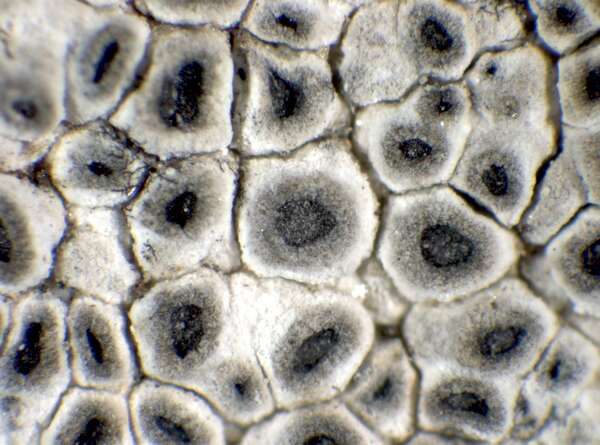
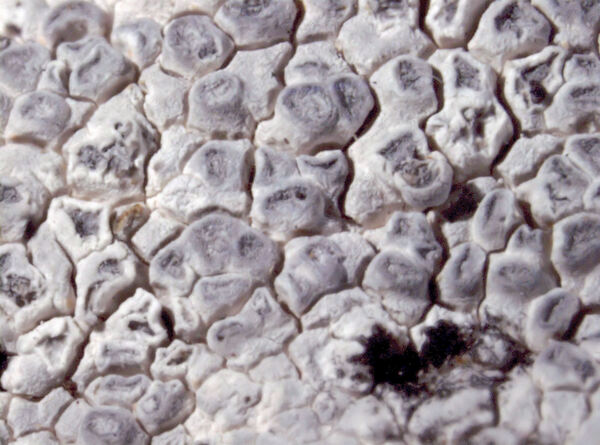
Aspicilia candida (Anzi) Hue
Nouv. Arch. Mus. Hist. Nat., Paris, 5 sér., 2: 64, 1912 (“1910”). Basionym: Aspicilia polychroma var. candida Anzi - Cat. Lich. Sondr.: 59, 1860.
Synonyms: Aspicilia marcii B. de Lesd.; Aspicilia rosacea Hue; Lecanora candida (Anzi) Nyl.
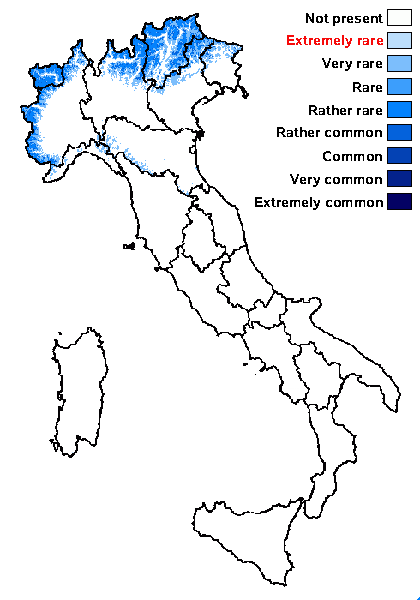
Distribution: N - Frl (TSB 17100), Ven (Nascimbene & al. 2021), TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2022), Lomb, Piem (Isocrono & al. 2004), VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999, Piervittori & al. 2004), Emil (Tretiach & al. 2008, Fariselli & al. 2020, Brackel 2025), Lig (TSB 33383).
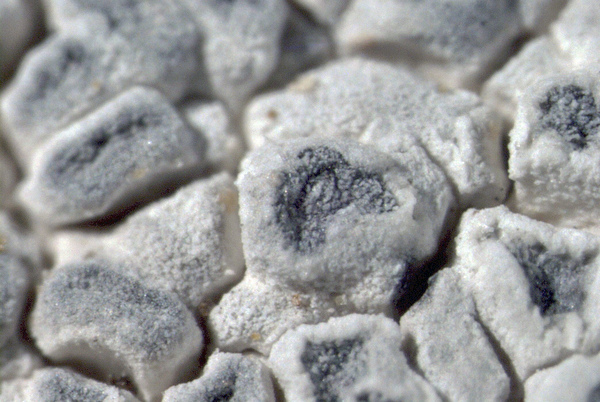
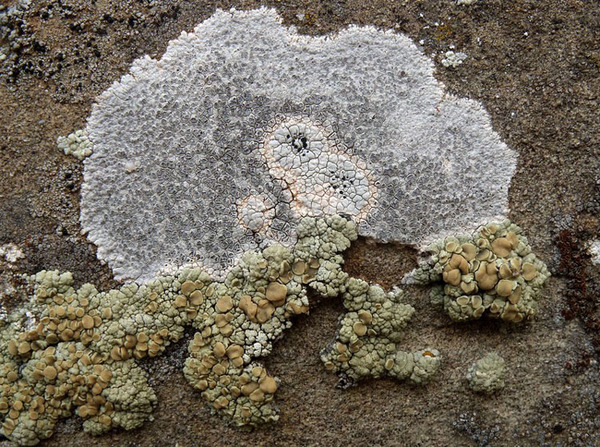
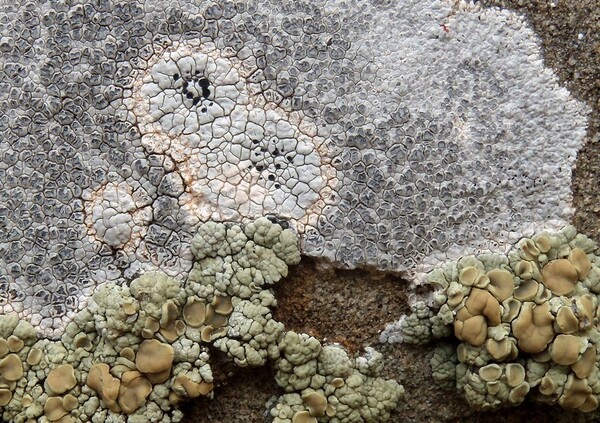
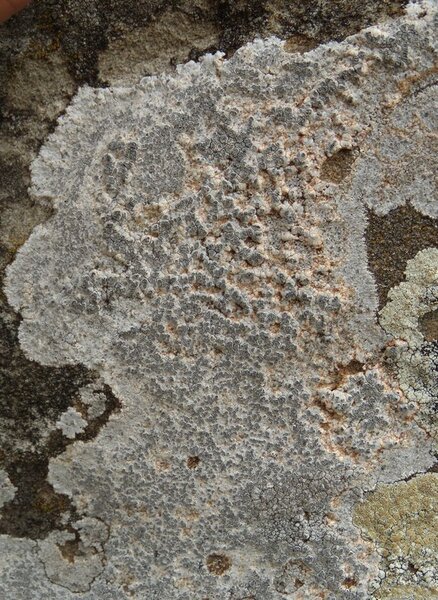
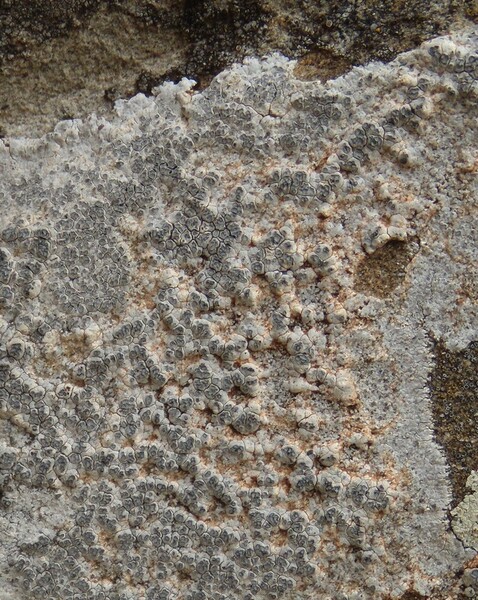
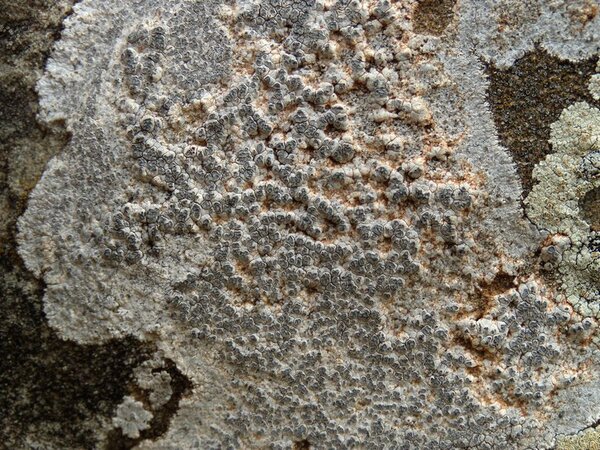
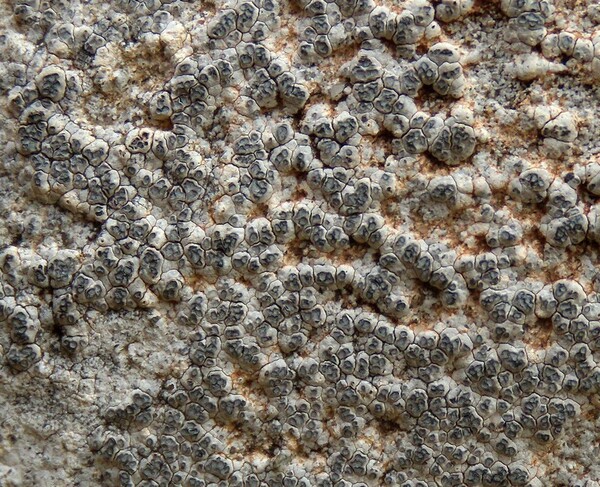
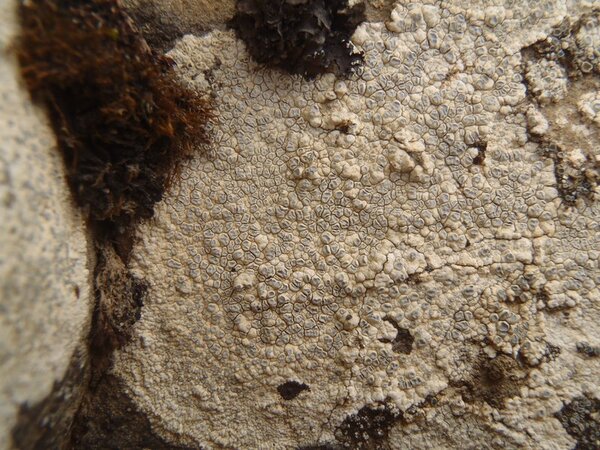
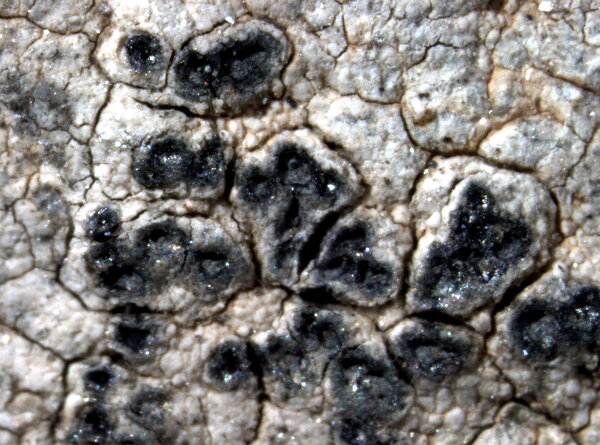
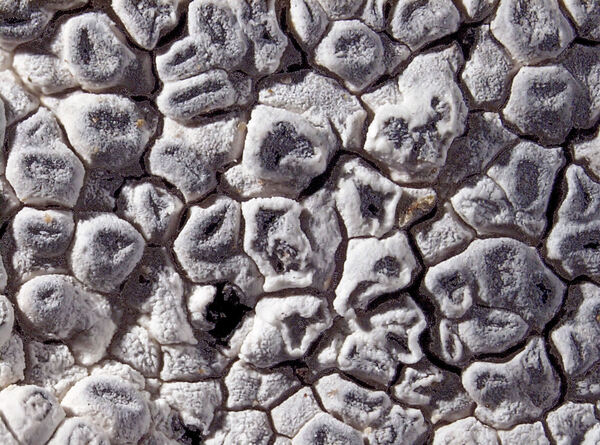
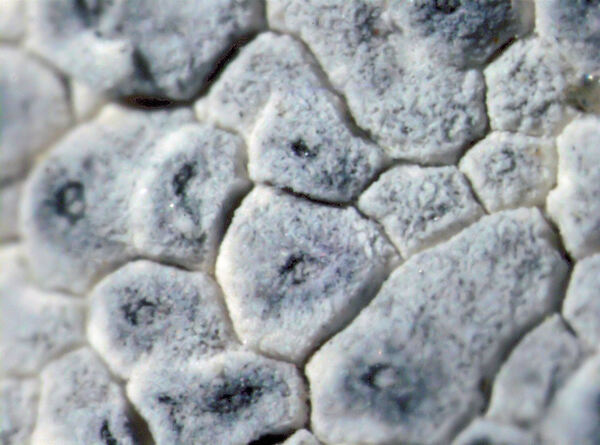
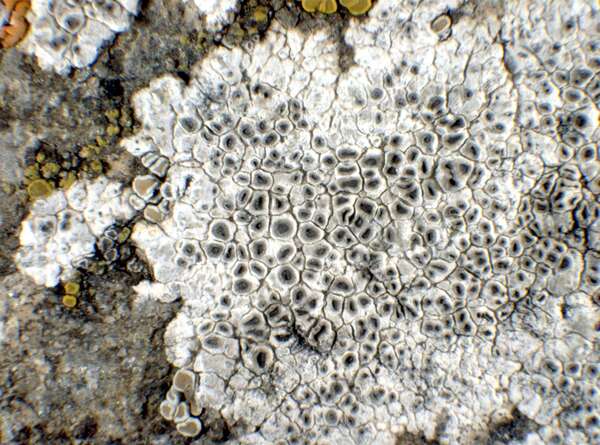
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, up to 0.7 mm thick, continuous to slightly rimose-areolate, more or less pruinose, chalky white, cream-white or pale bluish-grey, forming up to 15(-20) wide orbicular patches, often delimited by a black prothallus. Areoles flat to convex, the marginal ones often elongated and more or less radiating. Cortex 50-60 µm thick, filled with crystals; medulla white, I-; algal layer not extending below the hypothecium. Apothecia lecanorine-aspicilioid, round, 0.2-0.8 mm across, at first immersed in the thallus and more or less crateriform, then slightly protruding, with a concave to flat, black but most often grey-pruinose disc, and a 0.15-0.3 mm thick, prominent, farinose-pruinose thalline margin. Epithecium brownish green, N+ emerald green; hymenium colourless, 70-85 µm high, I+ reddish brown; paraphyses coherent, submoniliform, the apical cells to 3 µm wide; hypothecium colourless to pale yellowish brown, 35-45 µm high, I+ blue. Asci 8-spored, clavate, the thin outer coat K/I+ blue, the wall and apical dome K/I-. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, broadly ellipsoid, 13-25 x 9-18 µm, thin-walled. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Pycnidia black, immersed. Conidia curved, 14-22 x c. 1 µm. Spot tests: thallus K- or very rarely K+ yellow, C-, KC-, P-; apothecial margin K+ pale yellow to yellowish brown. Chemistry: substictic acid as the major compound, mostly limited to the margin of the apothecia. Note: known from Europe and North America, this lichen occurs in the Alps on weakly calciferous rocks, especially calcareous schists, mostly near or above treeline. Earlier records from Southern Italy (see Nimis 1993: 98), being dubious, are not accepted here. The species is chemically variable (see e.g. Roux & coll. 2014).
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rather common
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rather common
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS