Ramalina sinensis Jatta
N. Giorn. Bot. Ital., n. ser., 9: 462, 1902.
Synonyms: Ramalina calicaris f. fibrillosa Th. Fr.; Ramalina calicaris var. nervosa (Nyl.) Räsänen; Ramalina fastigiata var. nervosa Nyl.; Ramalina landroënsis Zopf; Ramalina nervosa (Nyl.) Räsänen
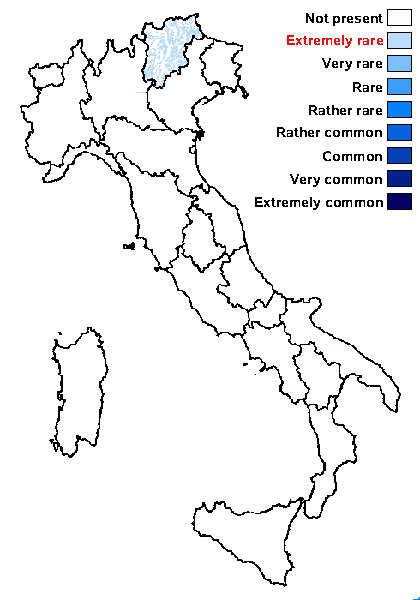
Distribution: N - TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2007b).
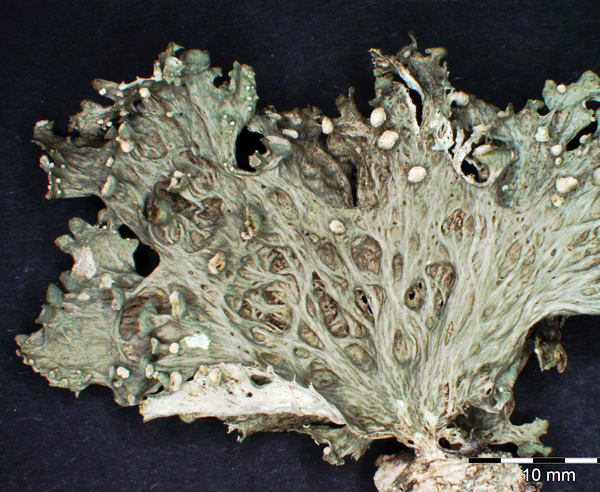
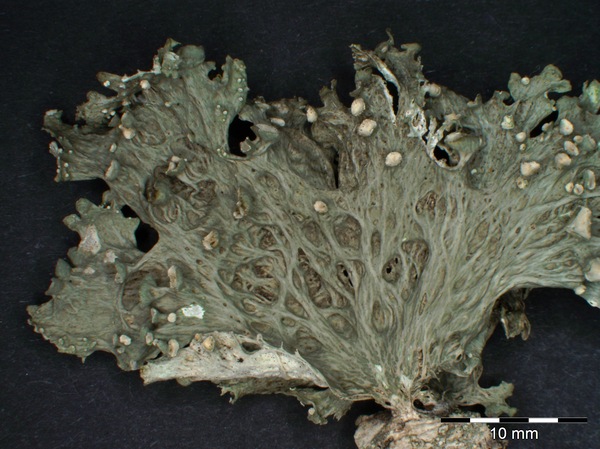
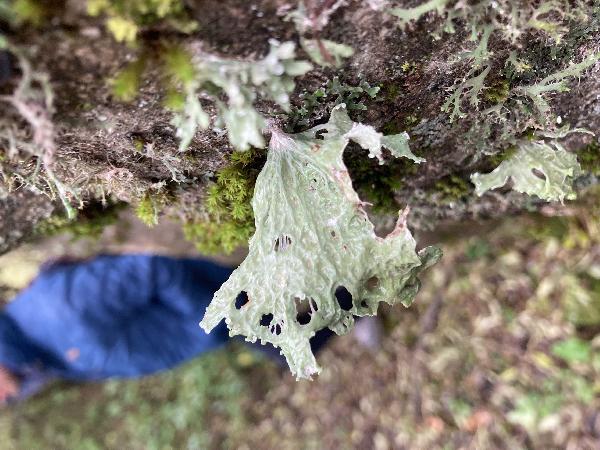
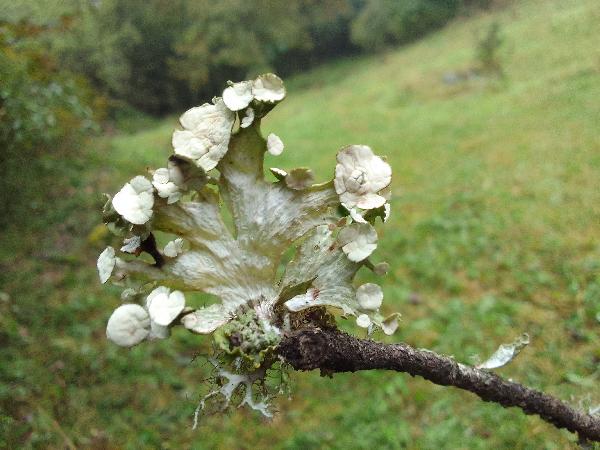
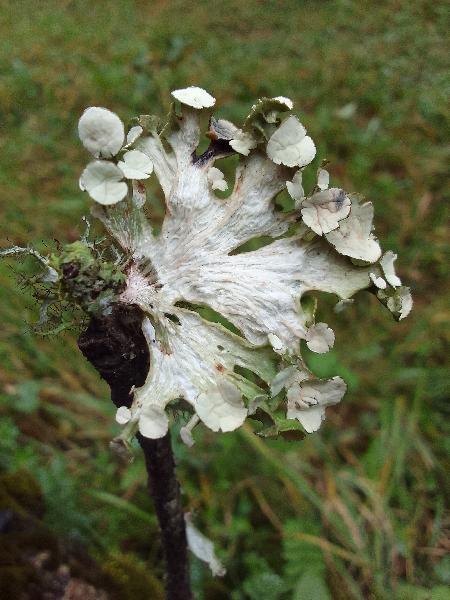
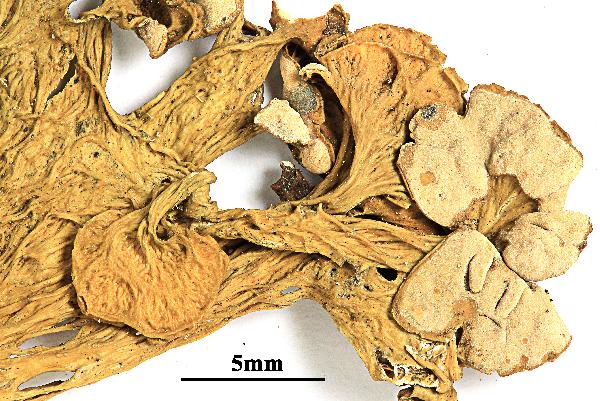
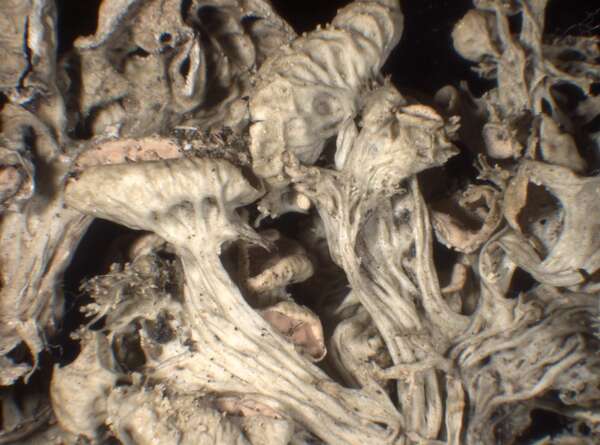
Description: Thallus fruticose, straw-coloured to greenish, flaccid when wet, with more or less scattered, erect or hanging laciniae growing from a basal holdfast. Laciniae often monophyllous, fan-shaped, up to 5 cm long (usually less), to 2(-3) cm wide at apex, simple or palmately divided, flattened, rather thin, slightly dorsiventral. Upper surface longitudinally or reticulately wrinkled, with elevated chondroid strands; lower surface paler than the upper one, with more or less longitudinally oriented, anastomosing low
ridges and white, decorticate intercalary interstices (pseudocyphellae), especially towards the holdfast but sometimes throughout the entire surface. Cortex 2-layered, the outer part paraplectenchymatous, the inner part of cartilaginous chondroid strands; medulla white, compact. Apothecia lecanorine, laminal or subterminal, 3-10 mm across, with a flat to convex, greenish disc and a concolorous, ridged-reticulate thalline margin. Epithecium pale brownish-olive; hymenium and hypothecium colourless; paraphyses thick-walled, richly branched in upper part. Asci 8-spored, the apical dome K/I+ dark blue with a pale, conical-pointed apical cushion (axial mass), the wall I-, but the thin outer gel I+ blue, Bacidia-type. Ascospores 1-septate, hyaline, ellipsoid, straight or curved, 12-17 x 6-7 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: K-, C-, KC- or KC+ pale yellow (cortex only), P-, UV-. Chemistry: cortex with usnic acid; medulla without lichen substances (traces of atranorin reported from N America).Note: on twigs of trees and shrubs in montane forests, this species is abundant in Picea obovata-stands along rivers in Central Asia (e.g. in the Altay Mnts., Burjatja, the Baikal region, TSB). I have never seen a sample from Italy, but the old record from Trentino might be correct, while that from Campania (see Nimis 1993: 604), being dubious, is not accepted here. The species was included as “Regionally Extinct” in the Italian red list of epiphytic lichens (Nascimbene & al. 2013c).
Growth form: Fruticose
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (29011)
2003/03/17
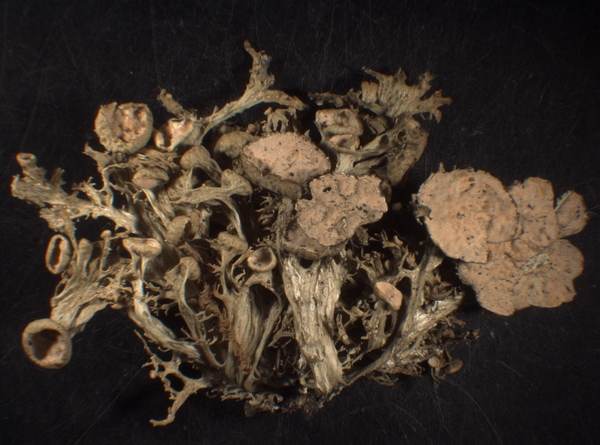


E. Pittao; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (29011)
2008.04.02
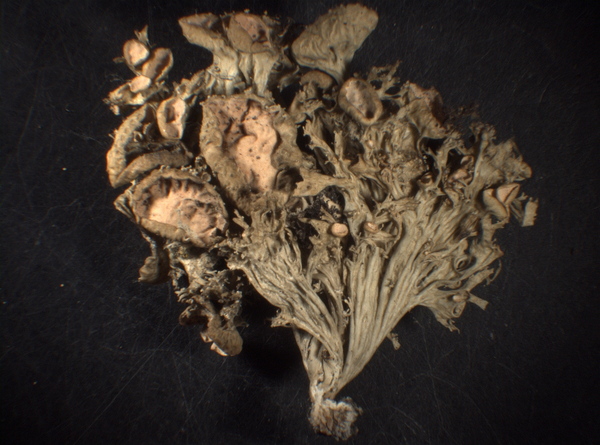


E. Pittao; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (29011)
2008.04.02
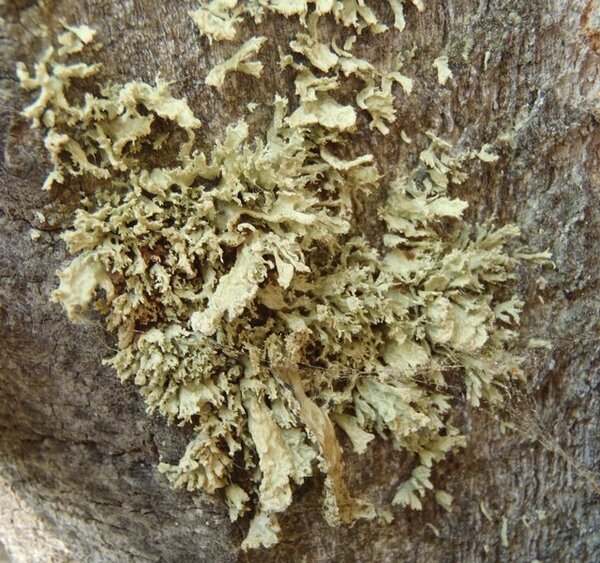


Curtis Randall Björk – CC BY-SA 4.0
ritish Columbia, Fraser Plateau, near Prince George Date: 2012-09-08 Corticolous, riparian forest; thalli uncharacteristic, sickened by poor air quality due to three nearby pulp mills and other urban-source pollution
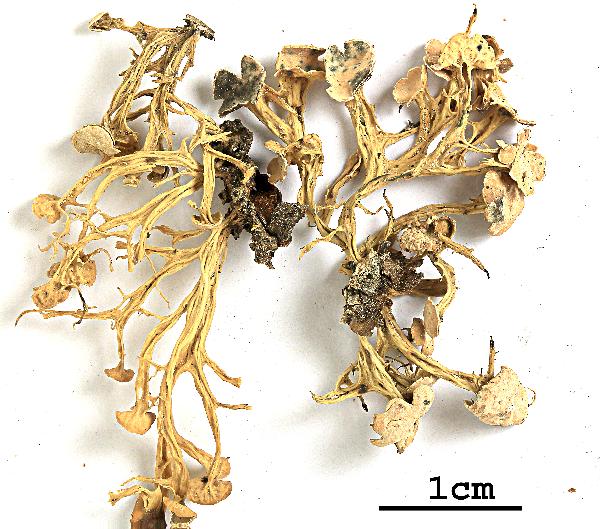


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[KW348], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba Songpan County: ca. 20 km
E of Chuanxi Temple (32°45' N, 103°39' E). On bark of Picea sp., 3300
m. Leg. K. H. Moon (no. 5013), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX
H.KASHIWADANI: LICHENES MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 348. - Note by Nimis: not typical.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[KW348], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba Songpan County: ca. 20 km
E of Chuanxi Temple (32°45' N, 103°39' E). On bark of Picea sp., 3300
m. Leg. K. H. Moon (no. 5013), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX
H.KASHIWADANI: LICHENES MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 348. - Note by Nimis: not typical.
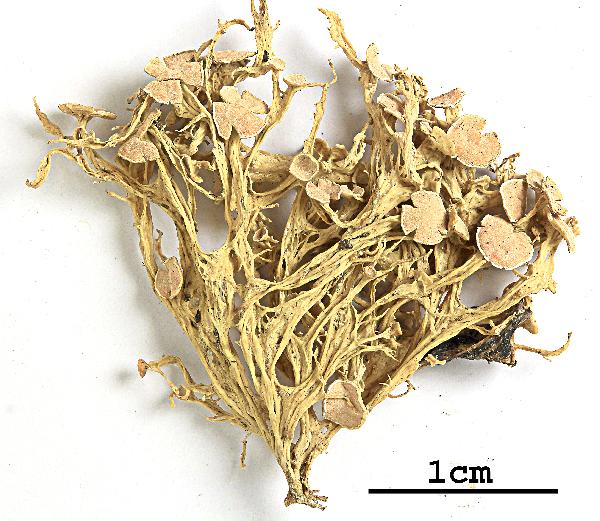


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[OH421], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba. Songpan County: ca. 20 km
E of Chuanxi Temple. On bark of Picea sp., 3300 m. Leg. K. H. Moon
(no. 4981), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX Y. OHMURA: LICHENES
MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 421. - Note by Nimis: not typical.
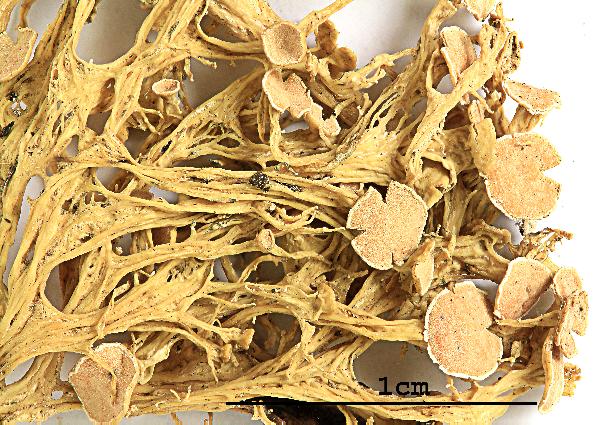


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[OH421], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba. Songpan County: ca. 20 km
E of Chuanxi Temple. On bark of Picea sp., 3300 m. Leg. K. H. Moon
(no. 4981), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX Y. OHMURA: LICHENES
MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 421. - Note by Nimis: not typical.
Growth form: Fruticose
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (29011)
2003/03/17


E. Pittao; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (29011)
2008.04.02


E. Pittao; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (29011)
2008.04.02


Curtis Randall Björk – CC BY-SA 4.0
ritish Columbia, Fraser Plateau, near Prince George Date: 2012-09-08 Corticolous, riparian forest; thalli uncharacteristic, sickened by poor air quality due to three nearby pulp mills and other urban-source pollution


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[KW348], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba Songpan County: ca. 20 km E of Chuanxi Temple (32°45' N, 103°39' E). On bark of Picea sp., 3300 m. Leg. K. H. Moon (no. 5013), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX H.KASHIWADANI: LICHENES MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 348. - Note by Nimis: not typical.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[KW348], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba Songpan County: ca. 20 km E of Chuanxi Temple (32°45' N, 103°39' E). On bark of Picea sp., 3300 m. Leg. K. H. Moon (no. 5013), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX H.KASHIWADANI: LICHENES MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 348. - Note by Nimis: not typical.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[OH421], China. Prov. Sichuan. Pref. Aba. Songpan County: ca. 20 km E of Chuanxi Temple. On bark of Picea sp., 3300 m. Leg. K. H. Moon (no. 4981), 08.10.1999, det. H. Kashiwadani. EX Y. OHMURA: LICHENES MINUS COGNITI EXSICCATI NO. 421. - Note by Nimis: not typical.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS









