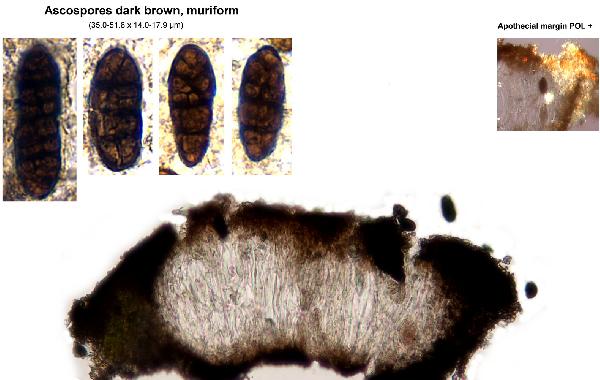
Rhizocarpon macrosporum Räsänen
Feddes Rep., 52: 139, 1943.
Synonyms: Rhizocarpon riparium var. helveticum Räsänen; Rhizocarpon sphaerosporum Räsänen
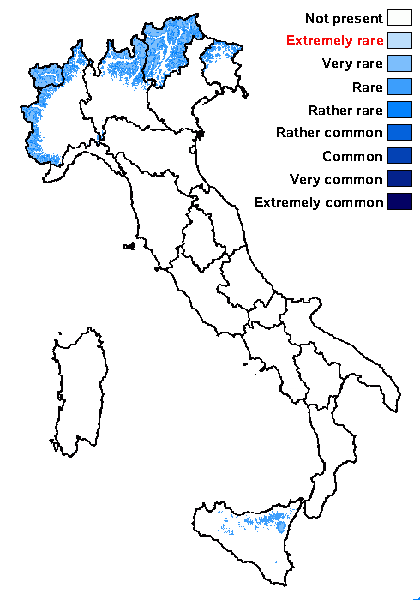
Distribution: N - Frl (TSB 13638), TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2022), Lomb, Piem (Morisi & Sereno 1995, Isocrono & al. 2004, Isocrono & Piervittori 2008, Giordani & al. 2014), VA (Revel & al. 2001, Matteucci & al. 2008c). S - Si (Grillo & Caniglia 2004).
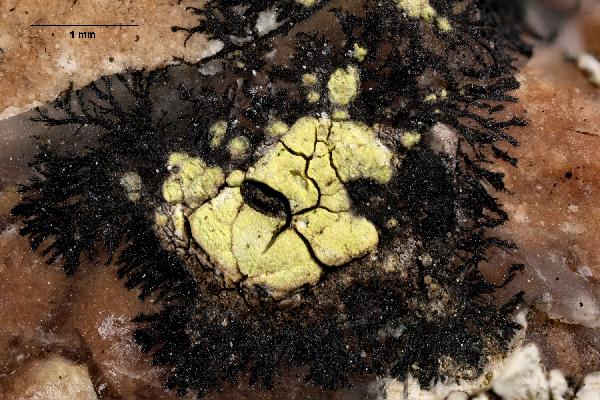
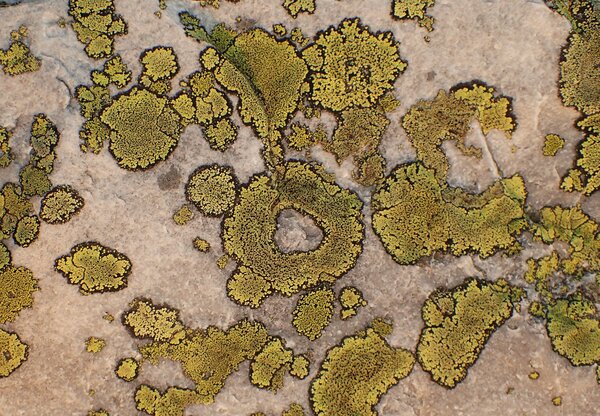
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, areolate, bright yellow-green, forming 1-6 cm wide patches, sometimes delimited by a thin black prothallus, the areoles round to angular, contiguous, flat to weakly convex, 0.5-1.2 mm wide, smooth, dull or glossy, epruinose, sometimes forming a crescent-shaped collar around the apothecia. Cortex 40-80 µm thick, without a distinct structure; medulla white, I+ blue. Apothecia lecideine, black, more or less angular, 0.3-0.7 mm across, with a concave to flat, epruinose disc and a soon excluded proper margin. Proper exciple brown in outer part, paler within, K+ reddish; epithecium brown, K+ purple-red or K-; hymenium colourless or greenish, 150-220 µm high; paraphysoids coherent, branched and anastomosing, the apical cells clavate; hypothecium brown, K-. Asci 8-spored, clavate, fissitunicate, with a well-developed tholus that is K/I- in lower part and K/I+ blue near the apex, lacking an ocular chamber, Rhizocarpon-type. Ascospores densely muriform, with 28-34 cells visible in optical view, at first hyaline or pale green-brown, soon turning dark green-brown, ellipsoid, 30-60 x 15-22 µm, halonate at least when young. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: medulla K-, C-, KC-, P- or P+ orange. Chemistry: cortex with rhizocarpic acid; medulla without lichen substances or with stictic acid. Note: a chemically heterogeneous species of dust-impregnated, exposed siliceous rocks, including walls in small settlements, most common in upland areas.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: very rare
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis

Curtis Randall Björk, - CC BY-SA 4.0
Red Mountain, first western range of the Rocky Mountains over the Robson Valley, British Columbia, Canada
13.08.2018

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis
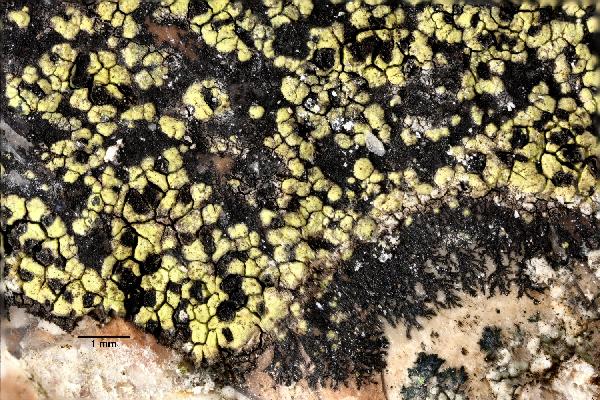

Ulrich Kirschbaum CC BY-SA 4.0 - Source: https://www.thm.de/lse/ulrich-kirschbaum/flechtenbilder
On silicatic (?) rocks, sorrounded by limestone.
SE-Europe; N-Cyprus; SE of Girne; Beşparmak Mountains; between Girne Kayasi and Armenian Monastery (Sourp Margar)
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: very rare
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis


Curtis Randall Björk, - CC BY-SA 4.0
Red Mountain, first western range of the Rocky Mountains over the Robson Valley, British Columbia, Canada
13.08.2018

Harrie Sipman – Source http://www.bgbm.fu-berlin.de/sipman/Zschackia/AegeanLichens/CaloplacaAC.htm - As Caloplaca oasis

 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS