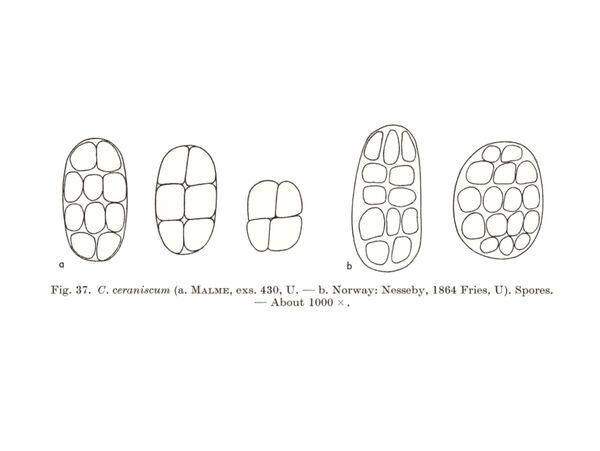
Rostania ceranisca (Nyl.) Otálora, P.M. Jørg. & Wedin
Fungal Divers. (online version), 64: 289, 2013. Basionym: Collema ceraniscum Nyl. - Flora, 48: 353, 1865.
Synonyms: Collema arcticum Lynge; Collema subhumosum Nyl.; Collema tetragonoides Anzi; Leptogium tetragonoides (Anzi) Lettau
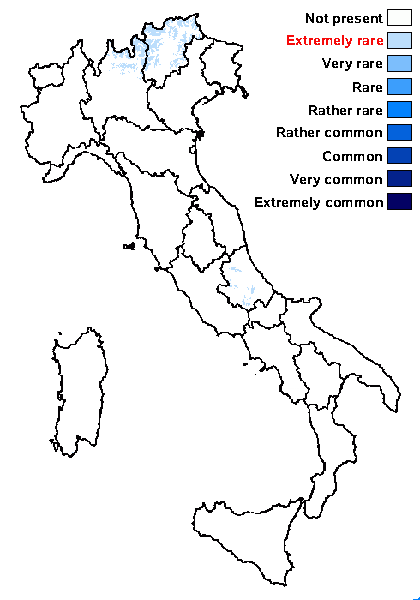
Distribution: N - TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2021), Lomb. C - Abr (Gheza & al. 2021, Di Nuzzo & al. 2021, Vallese & al. 2022)
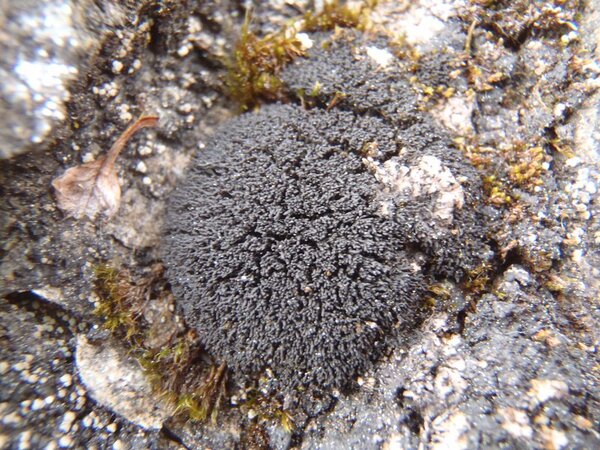
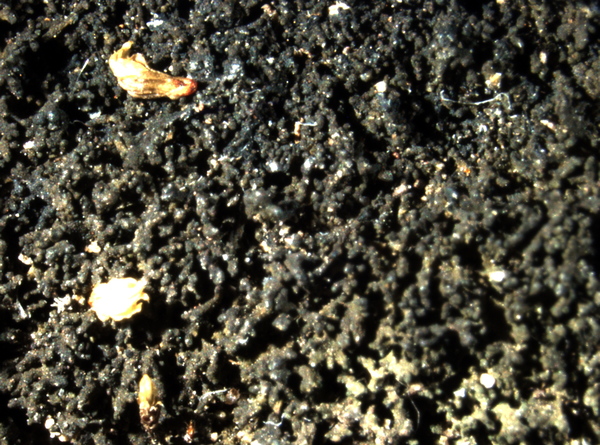
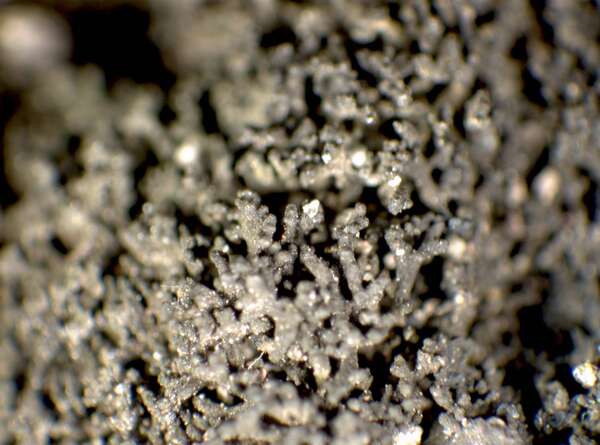
Description: Thallus subfoliose to subfruticose, homoiomerous, gelatinous when wet, dark blackish brown to black, deeply lobed, forming up to 4 cm wide and up to 1 cm thick cushions, the lobes 0.5-2 mm wide, ascending to erect, the lower ones more or less flattened and broader, smooth to knotty, the upper ones subcylindrical-terete and isidia-like, 0.1-0.2 mm thick, densely packed into a sort of cushion. Upper and lower cortex absent. Apothecia common at the tip of lobes, lecanorine, usually numerous, sessile and constricted at base, 0.4-0.8(-1) mm across, with a red-brown to black, usually strongly concave disc and a smooth to papillose-lobulate thalline margin. Thalline exciple sometimes pseudocorticate in basal parts; proper exciple sub- to euparaplectenchymatous, to 70 µm wide; epithecium brownish; hymenium colourless, 150-190 µm high, K/I+ blue; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched, 1.5-2(-3) µm thick at mid-level, the apical cells clavate to subglobose; hypothecium yellowish, K/I+ blue. Asci (2-)4-spored, cylindrical-clavate, the apex strongly thickened, the apical dome K/I+ pale blue, with a downwardly projecting K/I+ deep blue tubular structure. Ascospores muriform, with 3-4 transverse septa and 1-3 longitudinal septa, hyaline to very pale yellow when overmature, broadly ovoid to cuboid, 20-35(-40) x 13-20(-22) µm, the cuboid ones c. 20 x 17 µm. Photobiont cyanobacterial (Nostoc, the cells in long chains). Spot tests: all negative. Chemistry: without lichen substances.Note: an arctic-alpine, perhaps circumpolar lichen found over frost-disturbed, weakly calcareous soil above treeline; to be looked for further in the Alps, where it is perhaps more widespread.
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: extremely rare
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: extremely rare
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS