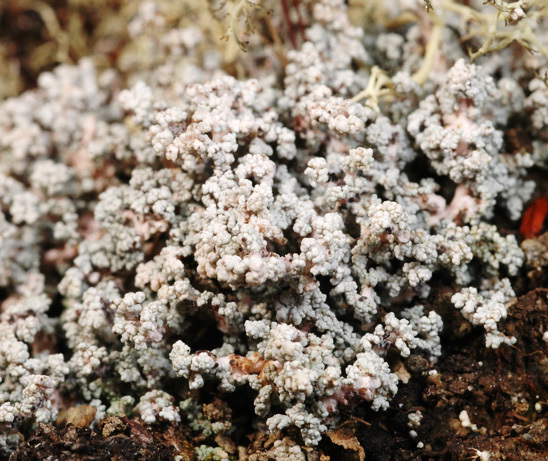
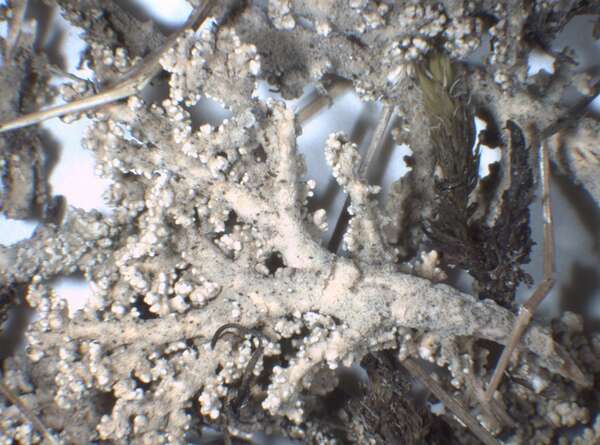
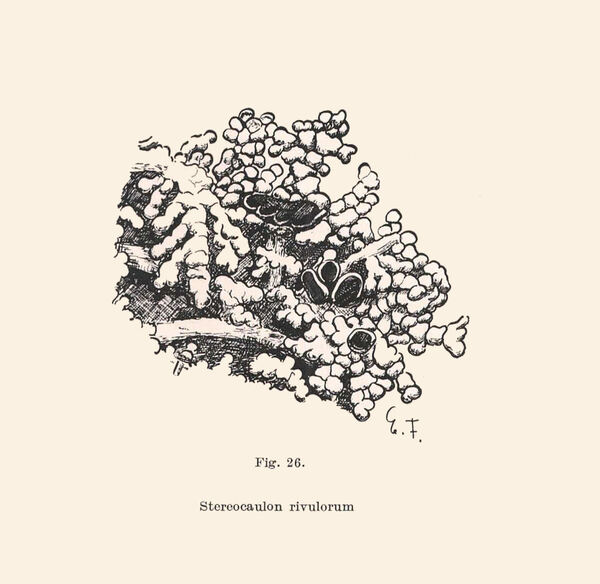
Stereocaulon rivulorum H. Magn.
Göteb. K. Vetensk. Samh. Handl., 30: 63, 1926.
Synonyms:
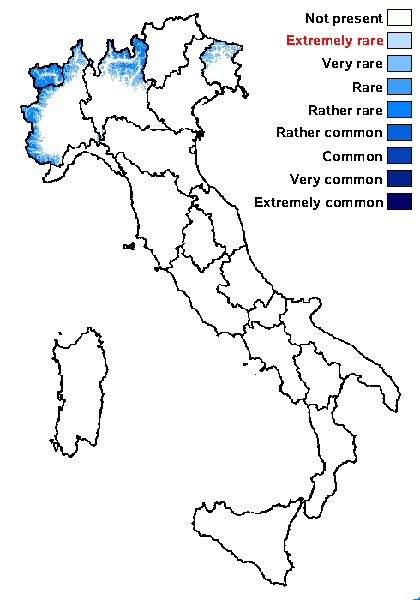
Distribution: N - Frl (TSB 14044), Lomb (Rivellini 1994, Rivellini & Valcuvia 1996), Piem, VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999).
Description: Primary thallus crustose, ephemeral, usually absent in mature individuals, secondary thallus fruticose, forming low, lax tufts. Pseudopodetia ascending, terete, sparingly branched, sometimes without a distinct main axis, 1-2 cm tall, 0.5-1.2 mm thick, glabrous or with a pinkish white tomentum, very brittle when dry, with a solid cartilaginous axis of parallel hyphae surrounded by a lax medulla. Phyllocladia 0.2-1 mm, glaucous white with a bluish tinge, granular to slightly elongate, broader at apices, dispersed in groups along the pseudopodetia which are partly naked. Cephalodia infrequent, inconspicuous, violet brown, tubercular to slightly elongate, with a rough surface, containing Nostoc, mostly located on the lower side of pseudopodetia. Apothecia frequent, terminal, 1-4 mm across, with a dark brown, convex disc and a thin, paler, finally excluded proper margin. Proper exciple brown in outer part, colourless within; epithecium brown, K-; hymenium colourless, 60-70 µm high; paraphyses mostly simple, c. 1.5 µm thick at mid-level, the apical cells up to 4.5 µm wide, with a dark cap; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, cylindrical-clavate, with a K/I+ blue outer layer and apical dome, and a central, K/I+ darker blue tube, Porpidia-type. Ascospores 3-septate, hyaline, fusiform but narrower at one end, (20-)25-30(-37) x 3-4(-5) µm. Pycnidia dark, immersed. Conidia 1-celled, hyaline, cylindrical, straight or slightly curved, 5-6(-8) x 1-1.2 µm. Main photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: K+ yellow, C-, KC- or KC+ violet (reaction often difficult to observe macroscopically, best evident on acetone extract on filter paper!), P- or P+ yellowish, UV- or UV+ blue-white. Chemistry: atranorin and variable amounts of lobaric acid, sometimes also with perlatolic and anziaic acids.Note: an arctic-alpine to boreal-montane lichen found on gravel and sand in snow-beds or on banks of streams near glaciers, sometimes on weakly calciferous schists; restricted to the Alps in Italy.
Growth form: Fruticose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia (primary); cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema) (secundary, e.g. in cephalodia)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Pioneer species
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: very rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[KU691], Svalbard. Spitsbergen. Bohemanflya. On rock, 100-200 m.
Leg. H. Kashiwadani (no.23262), 30.07.1985, det. H. Kashiwadani. -
Ex S. KUROKAWA & H. KASHIWADANI: LICHENES RARIORES ET CRITICI
EXSICCATI NR. 691.
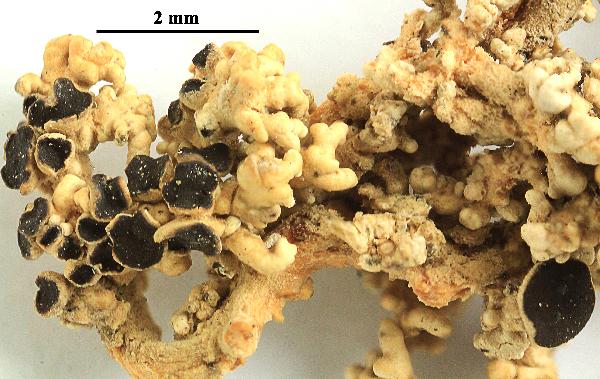

Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[KU691], Svalbard. Spitsbergen. Bohemanflya. On rock, 100-200 m.
Leg. H. Kashiwadani (no.23262), 30.07.1985, det. H. Kashiwadani. -
Ex S. KUROKAWA & H. KASHIWADANI: LICHENES RARIORES ET CRITICI
EXSICCATI NR. 691.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[KU691], Svalbard. Spitsbergen. Bohemanflya. On rock, 100-200 m.
Leg. H. Kashiwadani (no.23262), 30.07.1985, det. H. Kashiwadani. -
Ex S. KUROKAWA & H. KASHIWADANI: LICHENES RARIORES ET CRITICI
EXSICCATI NR. 691.
Growth form: Fruticose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia (primary); cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema) (secundary, e.g. in cephalodia)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Pioneer species
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: very rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[KU691], Svalbard. Spitsbergen. Bohemanflya. On rock, 100-200 m. Leg. H. Kashiwadani (no.23262), 30.07.1985, det. H. Kashiwadani. - Ex S. KUROKAWA & H. KASHIWADANI: LICHENES RARIORES ET CRITICI EXSICCATI NR. 691.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[KU691], Svalbard. Spitsbergen. Bohemanflya. On rock, 100-200 m. Leg. H. Kashiwadani (no.23262), 30.07.1985, det. H. Kashiwadani. - Ex S. KUROKAWA & H. KASHIWADANI: LICHENES RARIORES ET CRITICI EXSICCATI NR. 691.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS