Tetramelas thiopolizus (Nyl.) Giralt & P. Clerc
Lichenologist, 43: 418, 2011. Basionym: Lecidea thiopoliza Nyl. - Flora, 56: 244, 1878.
Synonyms: Buellia hypophana (Nyl.) Zahlbr.; Buellia reagens H. Magn.; Buellia thiopoliza (Nyl.) Boistel; Lecidea hypophana Nyl.
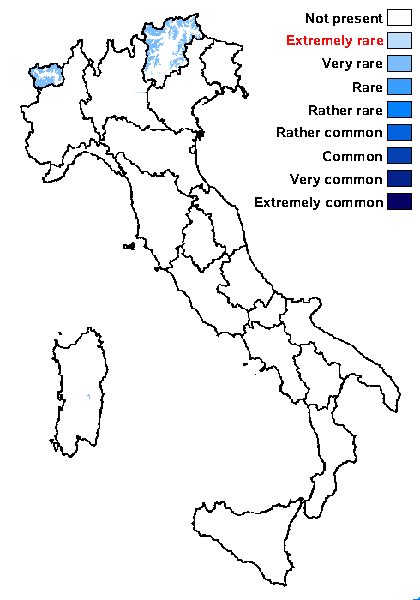
Distribution: N - TAA (Nimis & al. 1996), VA (Piervittori & al. 2004). C - Sar (Nöske 2000).
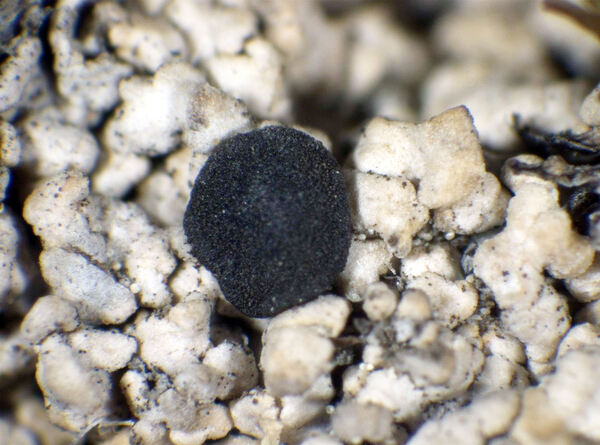
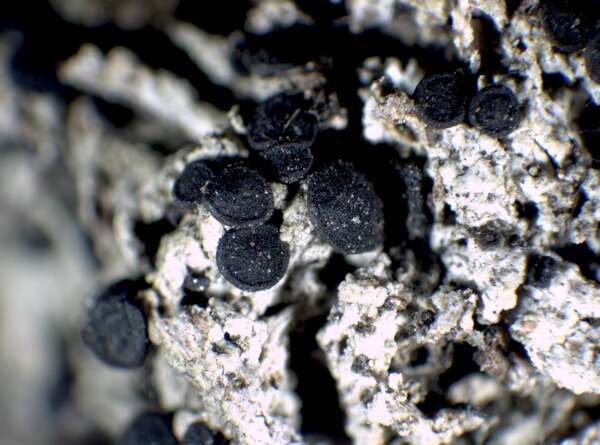
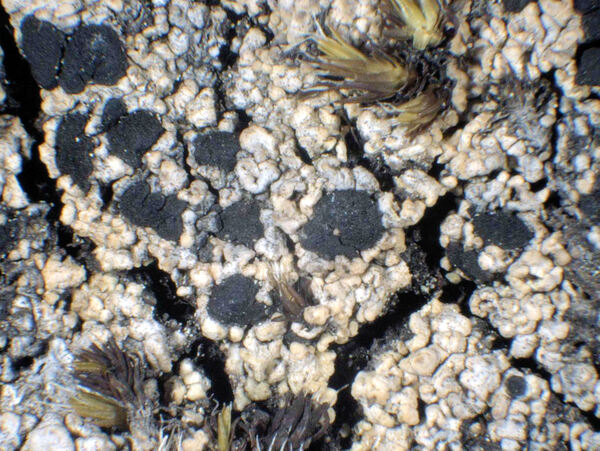
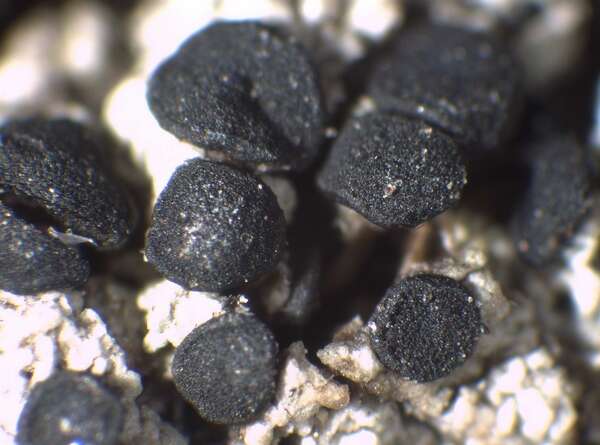
Description: Thallus crustose to subsquamulose, episubstratic, areolate, yellowish grey, ochraceous, yellowish or dull brown, the areoles usually contiguous, sublobate, some of them almost lobate-effigurate, flat to strongly convex and wart-like, the basal parts sometimes with a yellow pigment reacting K+ purple-red, attached by black, rhizoid bundles of hyphae. Medulla white, usually I+ weakly blue (microscope!), rarely I-. Apothecia lecideine, adnate to sessile, black, up to 1.5(-1.8) mm across, often confluent, with a flat to convex, epruinose disc and an initially prominent, finally excluded proper margin. Proper exciple up to 100 μm thick, with a few C+ orange crystals, prosoplectenchymatous, brown and N- in outer part, paler within; epithecium brown, N-, with a C+ orange epipsamma; hymenium colourless, 60-100 μm high, without oil droplets; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched in upper part, the apical cells strongly swollen, up to 7 μm wide, with a brown cap; hypothecium dark brown, the basal part with a yellow pigment reacting K+ purple-red. Asci 8-spored, clavate to cylindrical-clavate, the apical dome K/I+ dark blue with a pale, conical-pointed apical cushion (axial mass), the wall I-, but the thin outer gel I+ blue, Bacidia-type. Ascospores 1-septate, brown, straight or slightly curved, with pointed apices, (14-)17-23(-27) x 6.5-9(-11) μm, when young with subapical inner wall thickenings (Callispora-type), at maturity thin-walled throughout and Buellia-type; overmature spores sometimes with a pseudo-septum in each cell (better seen in K); ontogeny of type C (subapical inner wall thickenings produced before septum formation). Pycnidia black, unilocular. Conidia bacilliform 4-6 x c. 1 μm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: Thallus K+ yellow-orange to orange, C+ pale to deep orange, KC+ orange, P-, UV+ orange; basal part of medulla often K+ red. Chemistry; 6-O-methylarthothelin, arthothelin and an unknown yellow pigment, plus sometimes low concentrations of several additional unknowns.Note: on Grimmia spp. and other mosses overgrowing siliceous rocks with optimum above treeline; probably more widespread in the Alps.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: very rare
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: very rare
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS






