Thalloidima massatum (Tuck.) Kistenich, Timdal, Bendiksby & S.Ekman
Taxon, 67: 697, 2018.. Basionym: Lecidea massata Tuck. - Lich. Calif.: 25, 1866.
Synonyms: Biatorina glaucomela (Nyl.) Jatta; Lecidea glaucomela Nyl.; Thalloidima glaucomelum (Nyl.) Jatta; Thalloidima kelleri Elenkin; Toninia glaucomela (Nyl.) Boistel; Toninia kelleri (Elenkin) H. Olivier; Toninia massata (Tuck.) Herre
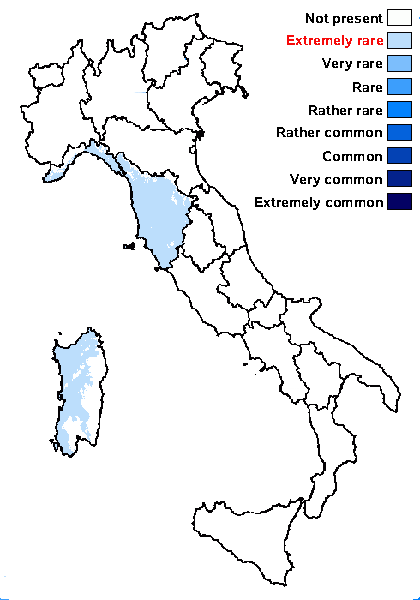
Distribution: N - Lig. C - Tosc (Putortì & al. 1999c), Sar.
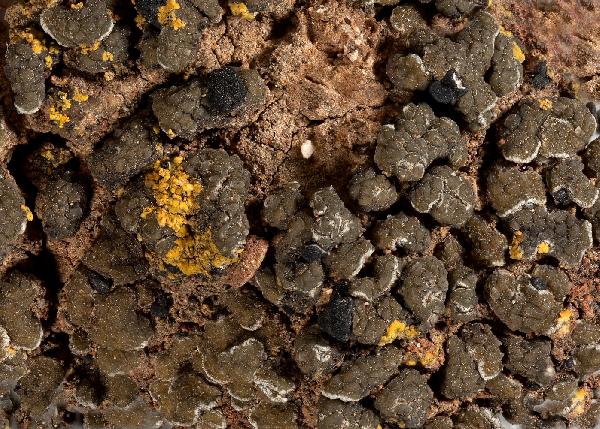
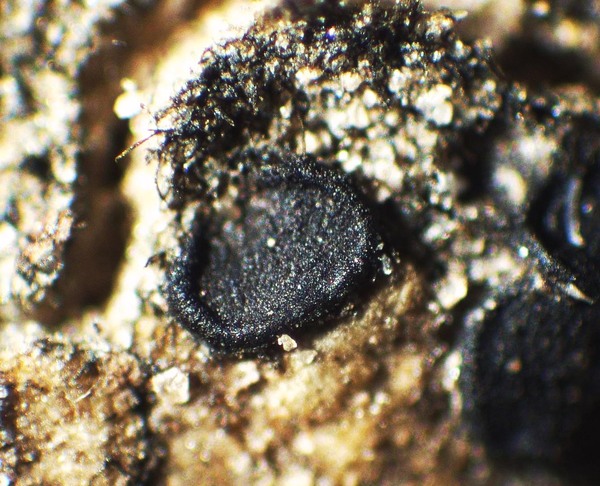
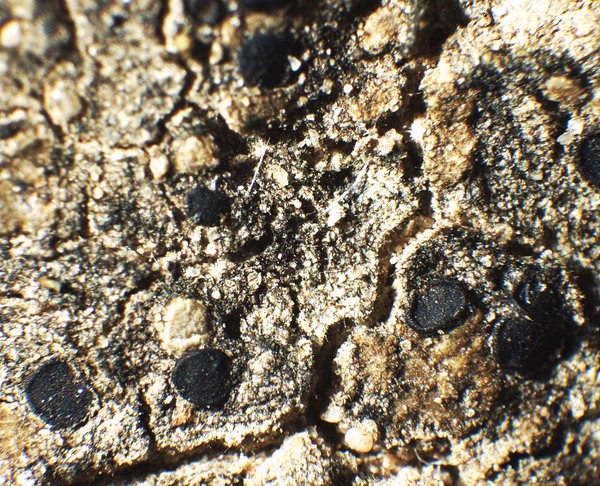
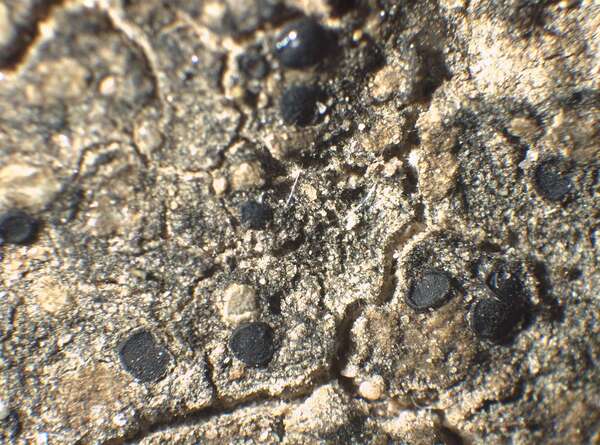
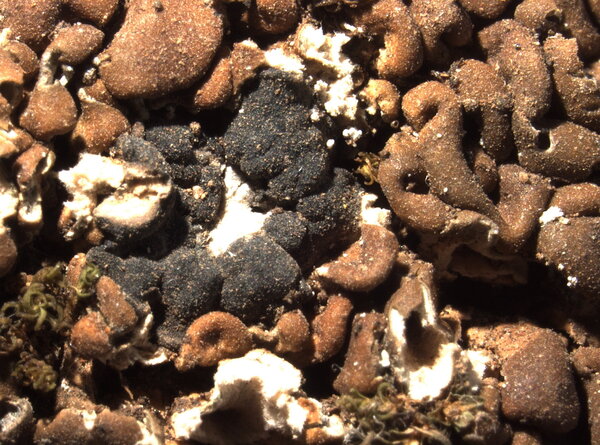
Description: Thallus squamulose, dark grey-green to olivaceous brown, usually epruinose, rarely faintly pruinose, often glossy and with regular fissures in the cortex, the squamules up to 2 mm wide, scattered to contiguous, orbicular or irregularly lobed, slightly convex; lower surface pale. Upper cortex 20-80 µm thick, including an up to 50 µm thick epinecral layer, often with crystals dissolving in K; algal layer continuous; medulla white, often with crystals; lower cortex poorly developed. Apothecia lecideine, sessile, strongly constricted at base, up to 1.5(-2) mm across, with a black, usually epruinose, more or less flat, smooth disc and a thin, smooth, soon excluded proper margin. Proper exciple dark grey in outer part, brownish within, the rim K+ and N+ violet; epithecium grey, K+ and N+ violet; hymenium colourless, 60-70 μm high; paraphyses coherent, simple or sparingly branched and anastomosing in upper part, thin-walled, the apical cell distinctly swollen, with a gelatinous pigment cap; hypothecium brownish. Asci 8-spored, clavate, surrounded by a gelatinous I+ blue coat, with a well-developed I+ blue tholus, a I+ darker blue tube and a well-developed ocular chamber, Bacidia-type. Ascospores 1-septate, hyaline, fusiform, 10-16.5 x 3.5-4.5 μm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-. Chemistry: thallus with terpenoids, rarely without lichen substances; apothecia with the Sedifolia-grey pigment.Note: an incompletely holarctic, mainly southern species of continental areas found on soil and in fissures of basic siliceous rocks with some seepage of water after rain, often in association with cyanobacteria and cyanobacterial lichens, mostly at relatively low elevations.
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF







