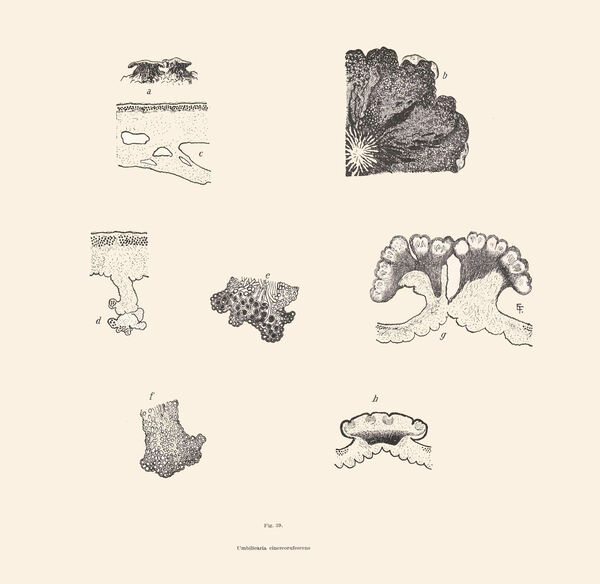
Umbilicaria cinereorufescens (Schaer.) Frey
Hedwigia, 71: 109, 1931. Basionym: Umbilicaria vellea var. spodochroa f. cinereorufescens Schaer. - Enum. Crit. Lich. Eur.: 25, 1850.
Synonyms: Gyrophora cinereorufescens (Schaer.) Schol.; Gyrophora mammulata Ach.
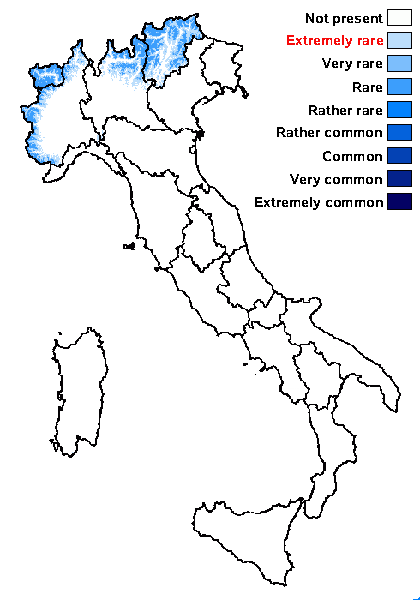
Distribution: N - TAA (Nascimbene 2005), Lomb, Piem, VA (HAL-18699).
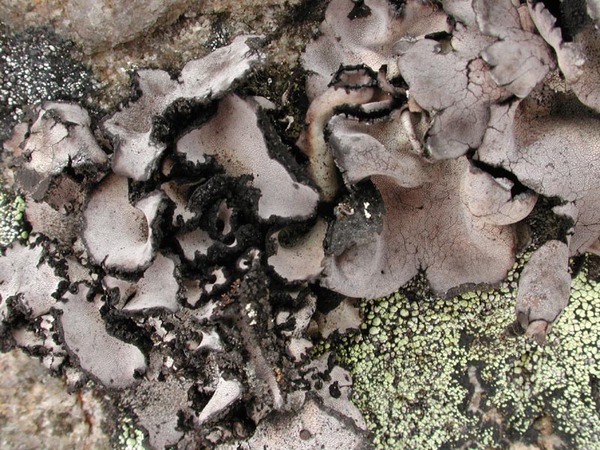
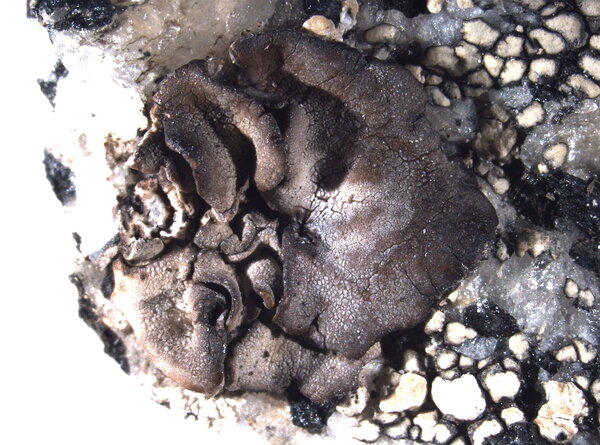
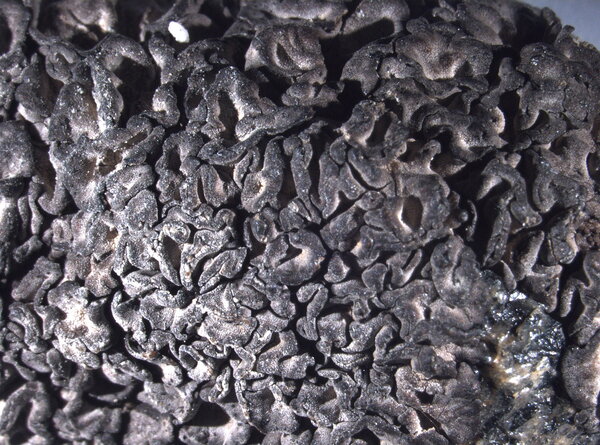
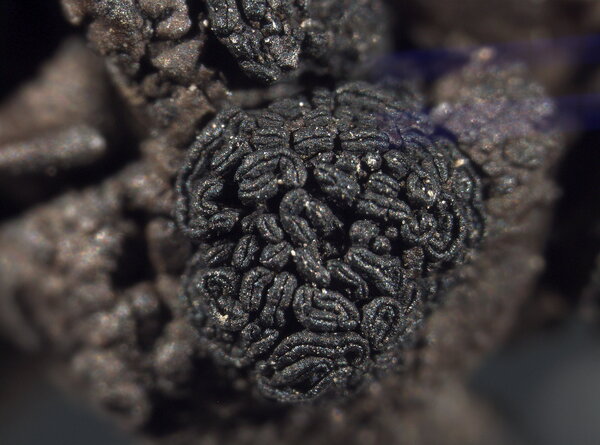
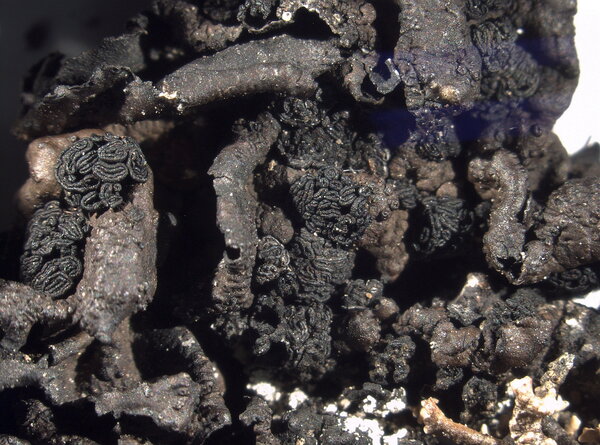
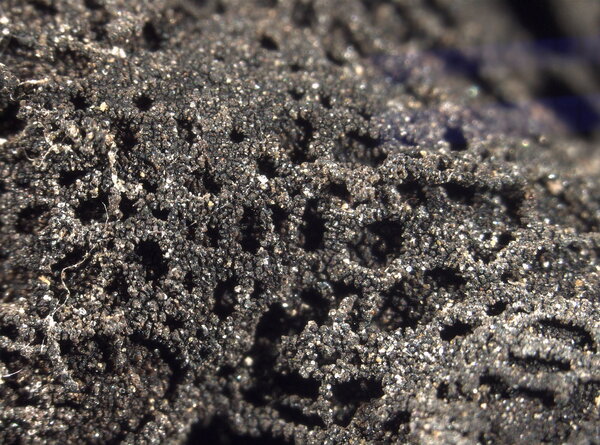
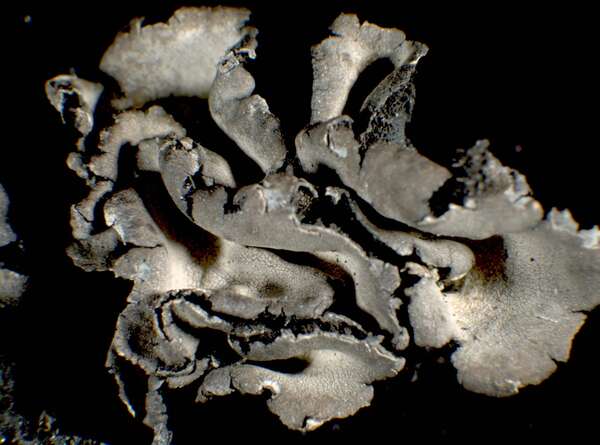
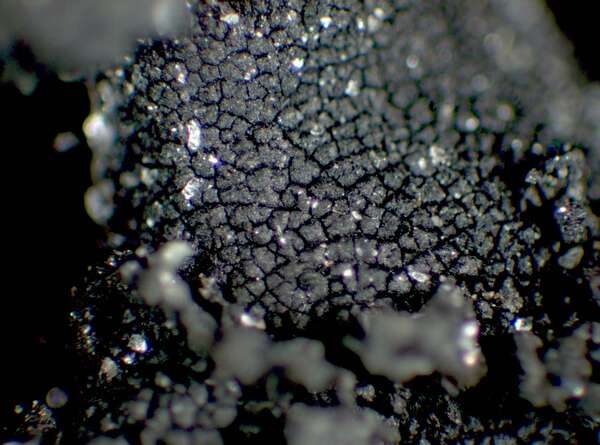
Description: Thallus foliose-umbilicate, heteromerous, dorsiventral, mono-or polyphyllous, 3-4(-7) cm wide, 0.1-0.3 mm thick, coriaceous, rather irregular in shape, attached by a central holdfast. Lobes often deeply incised, the central ones shorter, with wavy, lacerated and perforated, often down-turned margins. Upper surface pale to medium grey with cinnamon brown patches, usually thinly pruinose, smooth, sometimes undulating and irregularly cracked around the umbo; lower surface jet black, trabeculate around the umbilicus, covered with numerous papillae and c 0.4 mm long and 0.2 mm thick, peg-like or irregular-coralloid, black rhizinomorphs bearing clusters of thalloconidia. Thalloconidia usually restricted to the rhizinomorphs, rarely present on the lower surface, 6-20(-40)-celled, subspherical to elongate, dark brown to black, with a roughened surface, c. 20 x 27 µm. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous 20-30 µm; medulla white; lower cortex 40-100 µm thick. Apothecia very rare, adnate, black, gyrodisc. Epithecium brown; hymenium colourless; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched, septate, the apical cells more or less swollen; hypothecium thick, dark. Asci 8-spored, clavate, thick-walled, with an amyloid apical dome, Umbilicaria-type. Ascospores at first simple and hyaline, then muriform and brown, 8-15 x 4-9 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: cortex K-, C-, KC-, P-; medulla K-, C+ red, KC+ red, P-. Chemistry: small amounts of gyrophoric, lecanoric and crustinic acids, especially in the medulla. Note: a holarctic species also known from the mountains of Africa, found on wind-exposed, vertical or slightly rain-sheltered surfaces of hard siliceous rocks in humid upland areas (frequent fog and high rainfall), but in apparently dry situations, reaching the nival belt in the Alps.
Growth form: Foliose, umbilicate
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by conidia and thalloconidia
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rare
Subalpine belt: very rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples

P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14781)
2001/12/05


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14781)
2001/12/05
detail of lower surface
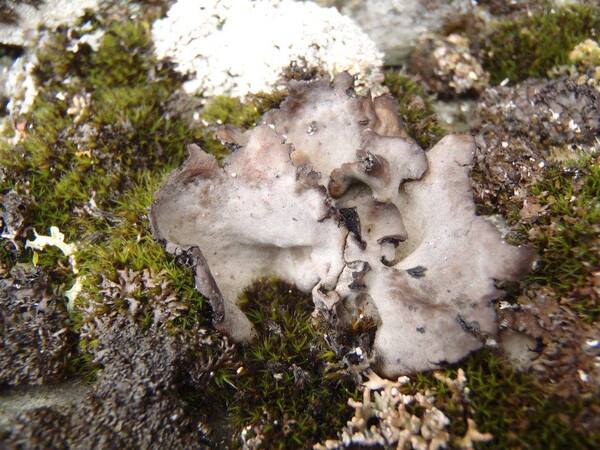


Curtis Randall Björk, - CC BY-SA 4.0
Near Hope Bay, Nunavut, Northwest Territories, Canadaries, CanadaIsland, British Columbia, Canada
19.07.2014


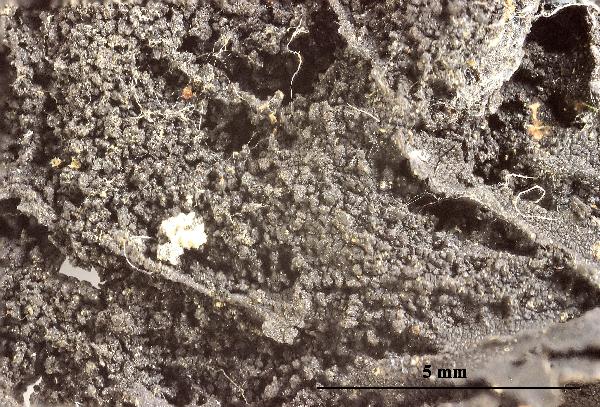
Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1524], Schweiz, Engadin, Rosegtal, am Weg zum Gletscher, Gneis
frontal, 1820 m. Leg, Ed. Frey, 1931, det. Ed. Frey. DUBL. EX HERBARIO
FREY NR. 3332.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1524], Schweiz, Engadin, Rosegtal, am Weg zum Gletscher, Gneis
frontal, 1820 m. Leg, Ed. Frey, 1931, det. Ed. Frey. DUBL. EX HERBARIO
FREY NR. 3332.


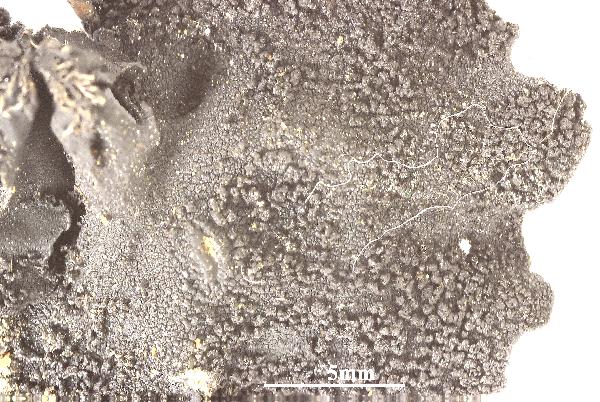
Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1525], Schweiz, Wallis, Val d'Hérens, Arolla Bergsturzblöcke beim
Hotel Viktoria, 1900 m, Granit, stark bemoost. Leg. et det. Ed. Frey,
07.08.1929. EX HERBARIO E. FREY NR. 4491.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1525], Schweiz, Wallis, Val d'Hérens, Arolla Bergsturzblöcke beim
Hotel Viktoria, 1900 m, Granit, stark bemoost. Leg. et det. Ed. Frey,
07.08.1929. EX HERBARIO E. FREY NR. 4491.
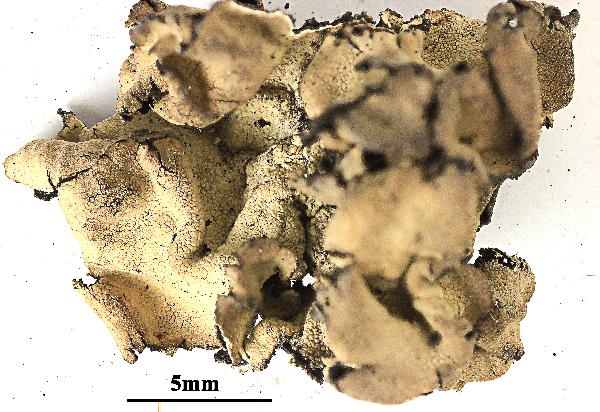

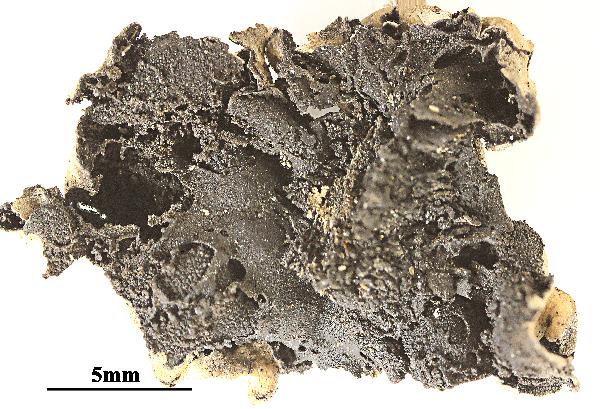
Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[VZ2438], Austria.Carinthia montes Hohe Tauern: Ankogelgruppe,
Mallnitz, in valle Tauerntal, secus viam inter Jamnigalm und Hagener
Hütte, 2100-2000 m. Ad saxa schistosa. Leg. R. Türk, J. Hafellner,
28.07.1989, conf. J. Poelt. EX A. V ZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI
NR. 2438.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[VZ2438], Austria.Carinthia montes Hohe Tauern: Ankogelgruppe,
Mallnitz, in valle Tauerntal, secus viam inter Jamnigalm und Hagener
Hütte, 2100-2000 m. Ad saxa schistosa. Leg. R. Türk, J. Hafellner,
28.07.1989, conf. J. Poelt. EX A. V ZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI
NR. 2438.
Growth form: Foliose, umbilicate
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by conidia and thalloconidia
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rare
Subalpine belt: very rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14781)
2001/12/05


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14781)
2001/12/05
detail of lower surface


Curtis Randall Björk, - CC BY-SA 4.0
Near Hope Bay, Nunavut, Northwest Territories, Canadaries, CanadaIsland, British Columbia, Canada
19.07.2014


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1524], Schweiz, Engadin, Rosegtal, am Weg zum Gletscher, Gneis frontal, 1820 m. Leg, Ed. Frey, 1931, det. Ed. Frey. DUBL. EX HERBARIO FREY NR. 3332.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1524], Schweiz, Engadin, Rosegtal, am Weg zum Gletscher, Gneis frontal, 1820 m. Leg, Ed. Frey, 1931, det. Ed. Frey. DUBL. EX HERBARIO FREY NR. 3332.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1525], Schweiz, Wallis, Val d'Hérens, Arolla Bergsturzblöcke beim Hotel Viktoria, 1900 m, Granit, stark bemoost. Leg. et det. Ed. Frey, 07.08.1929. EX HERBARIO E. FREY NR. 4491.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[1525], Schweiz, Wallis, Val d'Hérens, Arolla Bergsturzblöcke beim Hotel Viktoria, 1900 m, Granit, stark bemoost. Leg. et det. Ed. Frey, 07.08.1929. EX HERBARIO E. FREY NR. 4491.


Felix Schumm - CC BY 4.0
[VZ2438], Austria.Carinthia montes Hohe Tauern: Ankogelgruppe, Mallnitz, in valle Tauerntal, secus viam inter Jamnigalm und Hagener Hütte, 2100-2000 m. Ad saxa schistosa. Leg. R. Türk, J. Hafellner, 28.07.1989, conf. J. Poelt. EX A. V ZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 2438.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS