Xanthoparmelia angustiphylla (Gyeln.) Hale
Mycotaxon, 33: 401, 1988. Basionym: Parmelia conspersa var. angustiphylla Gyeln. - Feddes Rep., 29: 153, 1931.
Synonyms: Parmelia angustiphylla (Gyeln.) Gyeln.; Parmelia conspersa var. panniculosa Erichsen; Parmelia subconspersa f. marusica Gyeln.
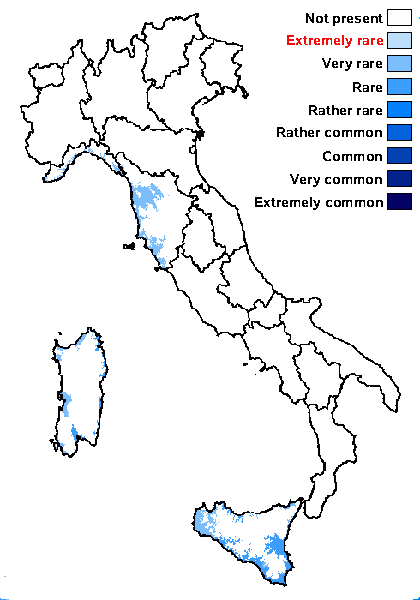
Distribution: N - Lomb (Favero-Longo & al. 2023), VA (Matteucci & al. 2015c), Lig (Giordani & al. 2002b, Rizzi & al. 2006). C - Tosc (Benesperi 2006, 2007b, Pasquinelli 2014), Sar (Nöske 2000, Giordani & al. 2009, Rizzi & al. 2011, Neuwirth 2018 as X. 'angustifolia'). S - Si (Giordani & al. 2002b).
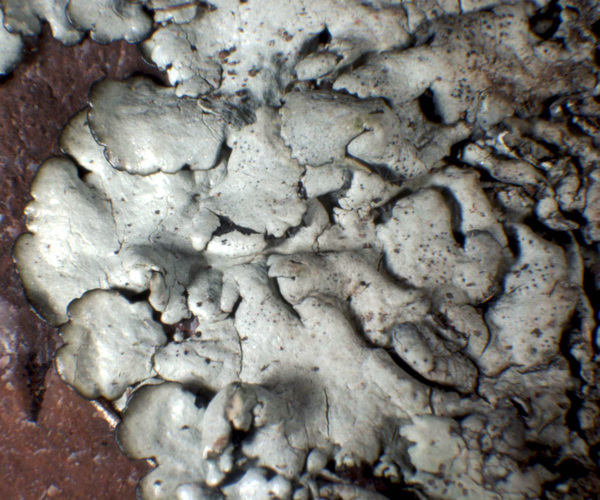
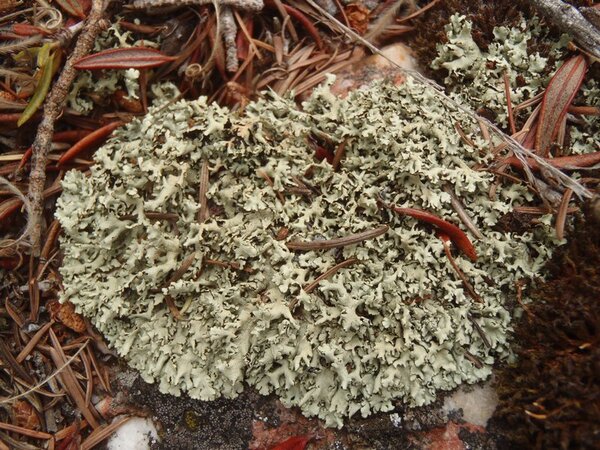
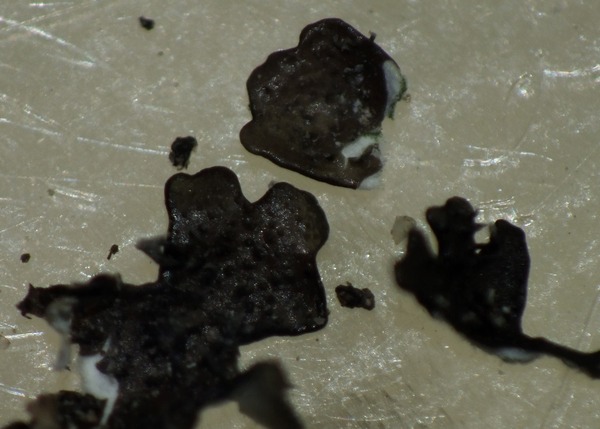
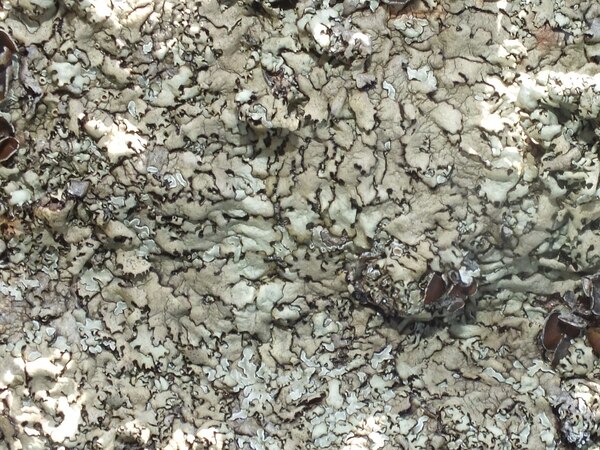
Description: Thallus foliose, heteromerous, dorsiventral, the upper surface yellowish green, loosely adnate, with subirregular to sublinear, dichotomously branched, 0.8-1.5(-2) mm wide lobes which often become densely laciniate, highly imbricate and pulvinate with age, forming regular to irregular, up to 5(-10) cm wide rosettes; lower surface jet black, with 0.2-0.8 mm long, simple, black rhizines. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, of anticlinally arranged hyphae or of isodiametrical cells, with a pored epicortex, the cell walls with Xanthoparmelia-type lichenan; medulla white; lower cortex paraplectenchymatous. Apothecia lecanorine, 3-10 mm across, substipitate, with a concave to flat, brown disc, and a rather thin thalline margin. Epithecium brown; hymenium and hypothecium colourless; paraphyses simple; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, clavate, the K/I+ blue tholus penetrated by a faintly amyloid apical cushion with parallel or diverging flanks, the wall K/I-, surrounded by a K/I+ blue outer layer, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, 9-10 x 5-6 μm. Pycnidia common, black, immersed. Conidia dumbbell-shaped, 5-6 x. c. 0.5 μm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: upper cortex K-, KC-, KC+ yellowish, P-; medulla K+ yellow-orange, C-, KC+ orange-red, P+ orange, UV-. Chemistry: upper cortex with usnic acid; medulla with the stictic acid syndrome (stictic, constictic, hypostictic and norstictic acids, with traces of cryptostictic and peristictic acids).Note: a southern species in Europe, found on siliceous boulders, that might be more widespread in Mediterranean Italy. Perhaps better treated as a subspecies of X. conspersa (see Roux & coll. 2014: 1279).
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
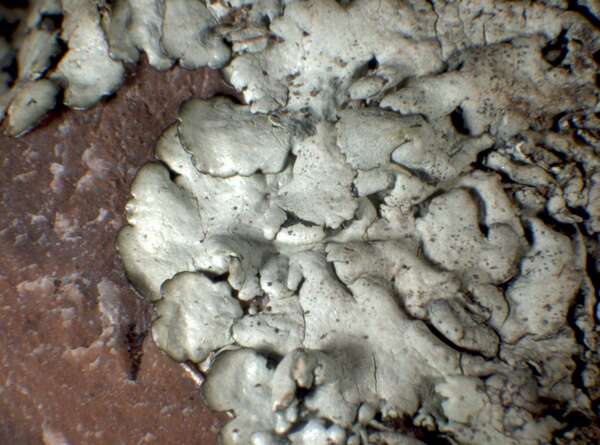


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: GE (I3/01)
2002/02/13
specimen from Liguria, det. J. Elix
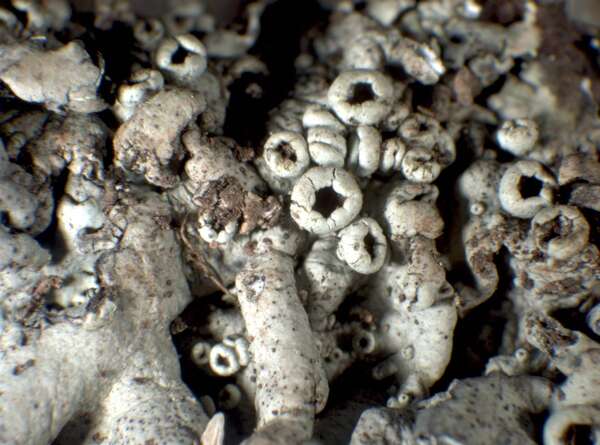


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: GE (I3/01)
2002/02/13
apothecia
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: GE (I3/01)
2002/02/13
specimen from Liguria, det. J. Elix


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF





