Xanthoparmelia glabrans (Nyl.) O. Blanco, A. Crespo, Elix, D. Hawksw. & Lumbsch
Taxon, 53: 967, 2004. Basionym: Parmelia glabrans Nyl. - Flora, 58: 15, 1875.
Synonyms: Neofuscelia glabrans (Nyl.) Essl.; Parmelia pulla subsp. glabrans (Nyl.) Clauzade & Cl. Roux
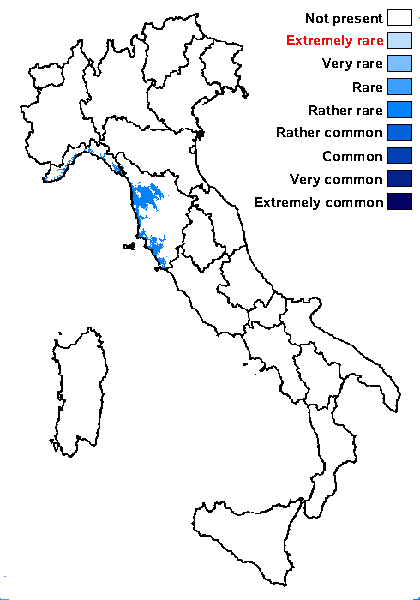
Distribution: N - TAA (Giordani & al. 2003), Lomb (Favero-Longo & al. 2023), VA (Matteucci & al. 2012, 2013, 2015c, 2015d), Lig (S- F185259, Watson 2014). C - Tosc (Ravera & al. 2018b).
Description: Thallus foliose, heteromerous, dorsiventral, adpressed to adnate, forming up to 10 cm wide, sometimes confluent rosettes. Lobes 0.5-3 mm wide, sublinear to linear-elongate, imbricate or loosely entangled. Upper surface brown to dark brown, uneven and rugose. Lower surface brown at margins, black in central parts, dull, slightly rugulose, moderately rhizinate; rhizines black, simple or fasciculate, to 1 mm long. Upper cortex brown, paraplectenchymatous, with a pored epicortex, the cell walls with Xanthoparmelia-type lichenan; medulla white; lower cortex paraplectenchymatous. Apothecia usually numerous, lecanorine, sessile to stipitate, to 4 mm across, with a brown disc and a smooth thalline margin. Epithecium brown; hymenium and hypothecium colourless; paraphyses simple; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, clavate, the K/I+ blue tholus penetrated by a faintly amyloid apical cushion with parallel or diverging flanks, the wall K/I-, surrounded by a K/I+ blue outer layer, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, 8-11 x 4-7 µm. Pycnidia common, immersed. Conidia bifusiform, 5–8 x c. 1 µm. Photobiont: chlorococcoid. Spot tests: upper cortex K-, C-, KC-, P-, N+ blue green; medulla K-, C-, KC- or rarely KC+ pink, P-, UV+ strongly blue-white. Chemistry: medulla with alectoronic acid, α-collatolic acid and more rarely gyrophoric acid. Note: on siliceous rocks. Differing from X. pulla for the presence of collatolic and alectoronic acids. Despite the purported preference for a Mediterranean climate, most Italian records are from continental alpine valleys. Earlier records from Sardinia and Puglia are dubious.
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: rather rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: rather rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF





