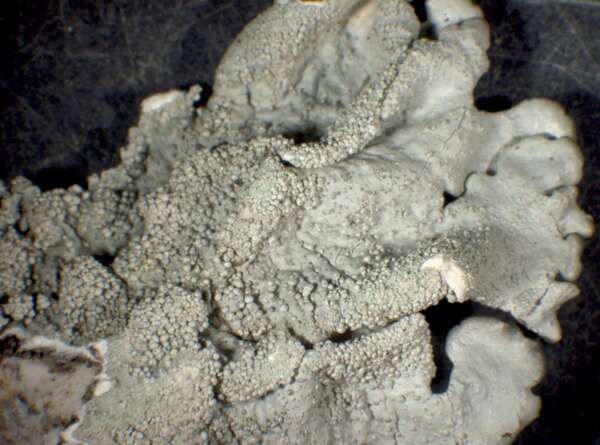
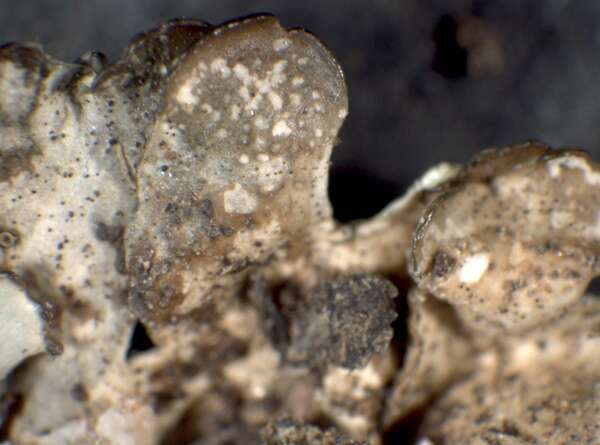
Xanthoparmelia mexicana (Gyeln.) Hale
Phytologia, 28: 488, 1974. Basionym: Parmelia mexicana Gyeln. - Feddes Rep., 29: 488, 1931.
Synonyms:
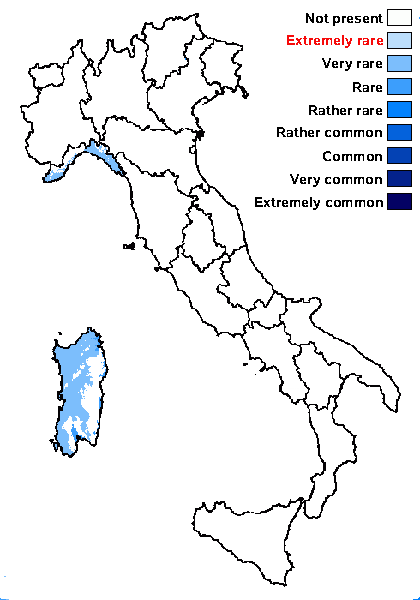
Distribution: N - Lomb (Favero-Longo & al. 2023), Lig (Giordani & al. 2009). C - Sar (Nöske 2000, Giordani & al. 2002b, Rizzi & al. 2011).
Description: Thallus foliose, heteromerous, dorsiventral, rather tightly adnate, forming orbicular to irregular, 4-10 cm wide rosettes. Lobes elongate, flat to slightly convex, separate to somewhat imbricate, (0.5-)1.5-4 mm wide, the upper surface greenish yellow, shiny, smooth, emaculate, with at first subglobose, but soon cylindrical-coralloid, 0.1-0.2 mm thick, 0.1-0.5 mm tall isidia with dark tips. Lower surface pale brown, with simple, concolorous, 0.2-0.5 mm long rhizines. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, with a pored epicortex, the cell walls with Xanthoparmelia-type lichenan; medulla white; lower cortex paraplectenchymatous. Apothecia rare, lecanorine, substipitate, 2-7 mm across, with a brown disc and an often isidiate thalline margin. Epithecium brown; hymenium and hypothecium colourless; paraphyses simple; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, clavate, the K/I+ blue tholus penetrated by a faintly amyloid apical cushion with parallel or diverging flanks, the wall K/I-, surrounded by a K/I+ blue outer layer, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, 9-10 x 4-5 µm. Pycnidia rare, black, immersed. Conidia bifusiform, 6-7 x 1 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: upper cortex K-, C-, KC- or KC+ yellow, P-; medulla K+ yellow turning dark red, C-, KC-, P+ orange. Chemistry: upper cortex with usnic acid; medulla with salazinic acid (major) consalazinic acid (minor), and usually norstictic and protocetraric acids (trace).Note: on siliceous rocks wetted by rain, perhaps more widespread in Mediterranean Italy and in the dry Alpine valleys. Molecular data indicate that American and European samples, although morphologically and chemically similar, are only distantly related (Barcenas-Peña & al. 2018).
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by isidia, or isidia-like structures (e.g. schizidia)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: very rare
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL77778], Brazil, Mato Grosso do Sul, along road W of Morraria do
Sul, in Atlantic rain forest on siliceous rock. 21°07’44'' S, 56°30’41'' W,
800 m. Leg. A. Aptroot (no 77778), 6.11.2018, det. A. Aptroot, 2019.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL77778], Brazil, Mato Grosso do Sul, along road W of Morraria do
Sul, in Atlantic rain forest on siliceous rock. 21°07’44'' S, 56°30’41'' W,
800 m. Leg. A. Aptroot (no 77778), 6.11.2018, det. A. Aptroot, 2019.
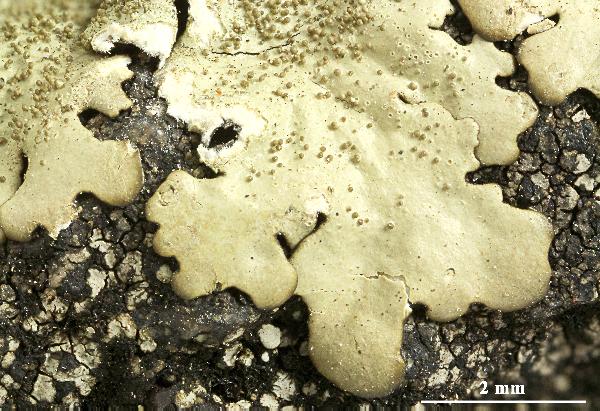


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL77778], Brazil, Mato Grosso do Sul, along road W of Morraria do
Sul, in Atlantic rain forest on siliceous rock. 21°07’44'' S, 56°30’41'' W,
800 m. Leg. A. Aptroot (no 77778), 6.11.2018, det. A. Aptroot, 2019.
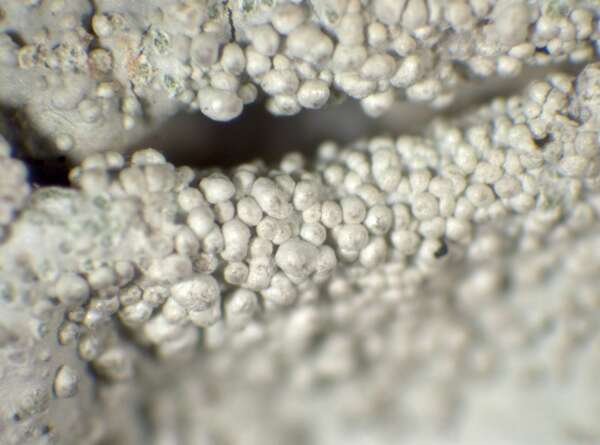


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: GE
2002/02/13
isidia, specimen from Sardinia
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by isidia, or isidia-like structures (e.g. schizidia)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: very rare
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL77778], Brazil, Mato Grosso do Sul, along road W of Morraria do Sul, in Atlantic rain forest on siliceous rock. 21°07’44'' S, 56°30’41'' W, 800 m. Leg. A. Aptroot (no 77778), 6.11.2018, det. A. Aptroot, 2019.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL77778], Brazil, Mato Grosso do Sul, along road W of Morraria do Sul, in Atlantic rain forest on siliceous rock. 21°07’44'' S, 56°30’41'' W, 800 m. Leg. A. Aptroot (no 77778), 6.11.2018, det. A. Aptroot, 2019.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL77778], Brazil, Mato Grosso do Sul, along road W of Morraria do Sul, in Atlantic rain forest on siliceous rock. 21°07’44'' S, 56°30’41'' W, 800 m. Leg. A. Aptroot (no 77778), 6.11.2018, det. A. Aptroot, 2019.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF



