Xanthoparmelia tinctina (Maheu & A. Gillet) Hale
Phytologia, 28: 489, 1974. Basionym: Parmelia tinctina Maheu & A. Gillet - Bull. Soc. Bot. France, 72: 860, 1925.
Synonyms: Parmelia algeriensis B. de Lesd.; Parmelia conspersa subsp. tinctina (Maheu & A. Gillet) Clauzade & Cl. Roux; Parmelia conspersa var. isidiosa Nyl.; Parmelia tokajensis Gyeln.
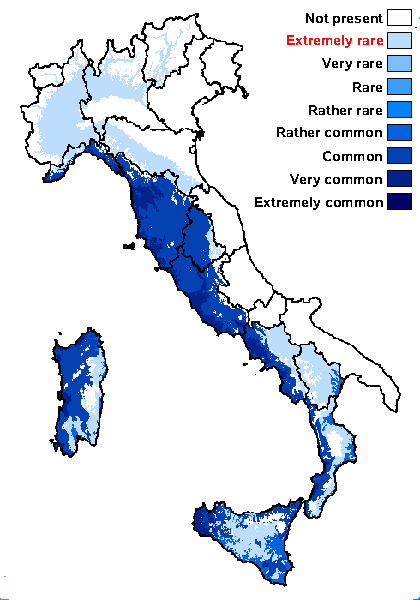
Distribution: N - TAA (Giordani & al. 2002b), Lomb (Valcuvia & Delucchi 2001, Giordani & al. 2002b, Valcuvia & al. 2003, Favero-Longo & al. 2023), Piem (Isocrono & Falletti 1999, Giordani & al. 2002b, Favero-Longo & al. 2004, 2005, 2006b, Favero-Longo & Piervittori 2012, Gheza & Nascimbene 2024), VA (Matteucci & al. 2012, 2015c), Emil (Valcuvia & Delucchi 2001, Giordani & al. 2002b, Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig (Giordani & Brunialti 2000, Giordani & al. 2002b, 2016). C - Tosc (Giordani & al. 2002b, Benesperi 2006, Lastrucci & al. 2009, Brackel 2015), Umb (Panfili 2000b, Giordani & al. 2002b, Ravera & al. 2006), Laz (Giordani & al. 2002b, Giordani & al. 2002b, Zucconi & al. 2013), Sar (Monte 1993, Zedda 1995, 2002, 2002b, Nöske 2000, Giordani & al. 2002b, 2013, Piccotto & al. 2009, Piccotto & Tretiach 2010, Rizzi & al. 2011, Neuwirth 2018). S - Camp (Aprile & al. 2002, Giordani & al. 2002b, Nimis & Tretiach 2004, Catalano & al. 2016), Bas (Nimis & Tretiach 1999, Potenza 2006), Cal (Puntillo 1996, Giordani & al. 2002b, Puntillo & Puntillo 2004, Brackel & Puntillo 2023), Si (Ottonello 1995, Nimis & al. 1996b, Schicchi & al. 1997, Clocchiatti & al. 2000, 2002b, Giordani & al. 2002b, Merlo 2004b, Ottonello & al. 2011, Cataldo & Cannavò 2014, Puglisi & Cataldo 2019, Campisi & al. 2020).
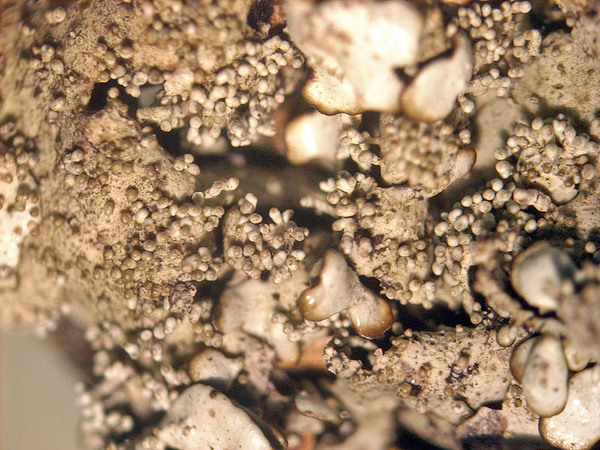
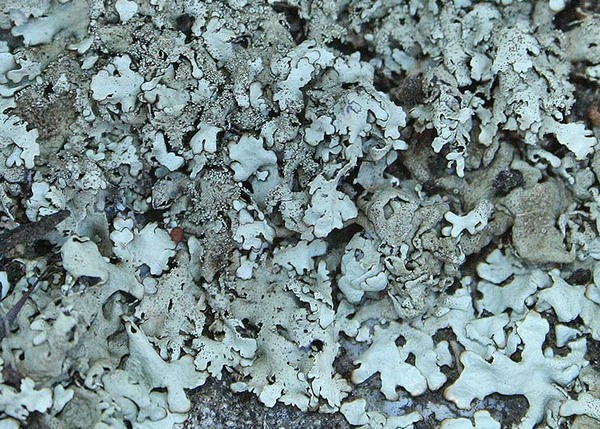
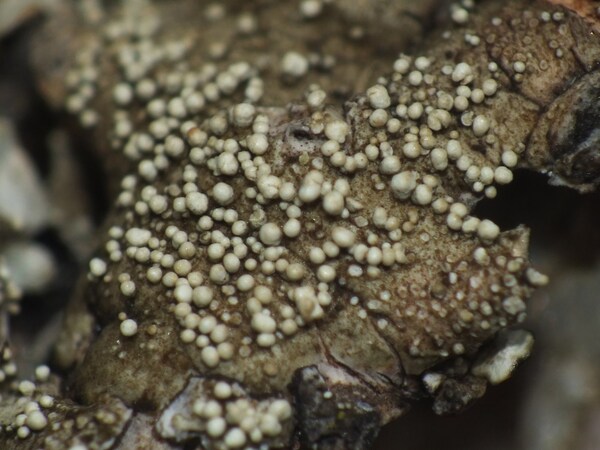
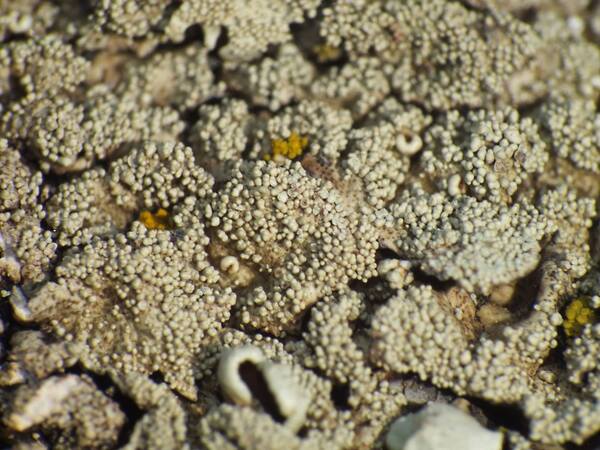
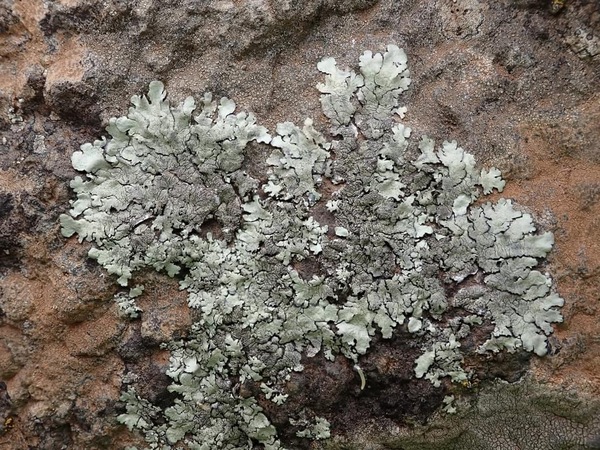
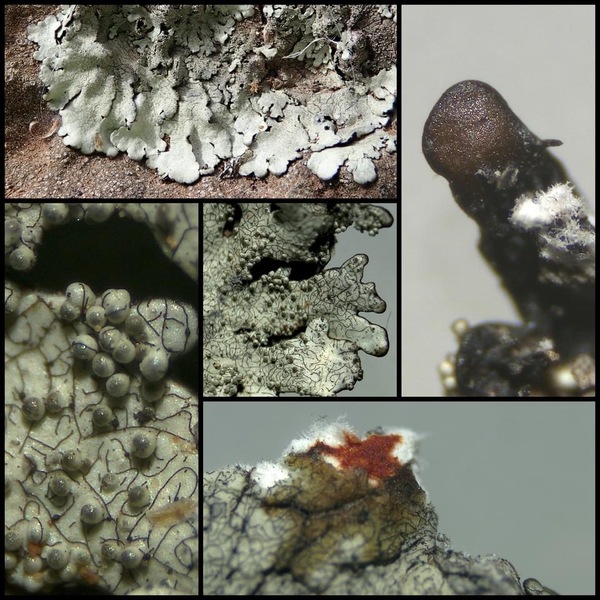
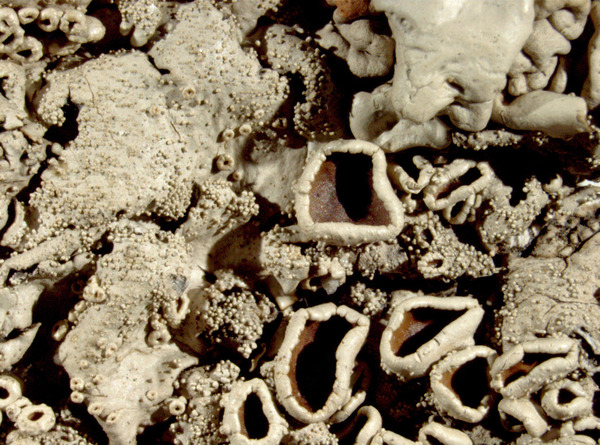
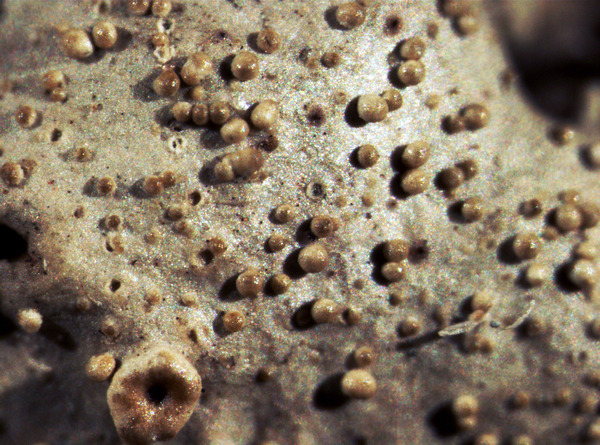
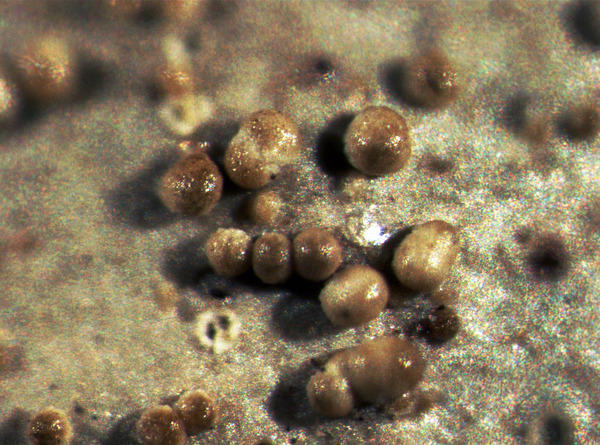
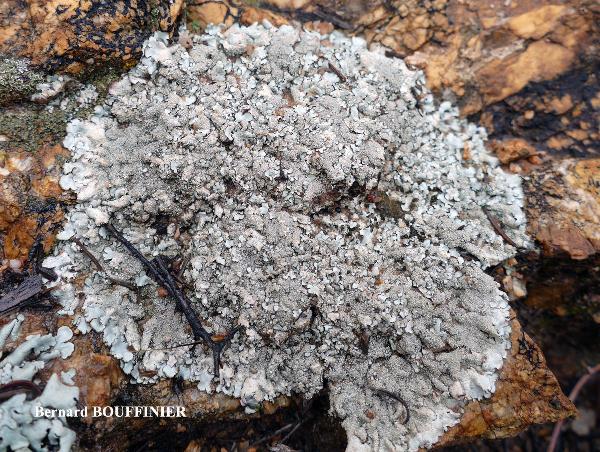
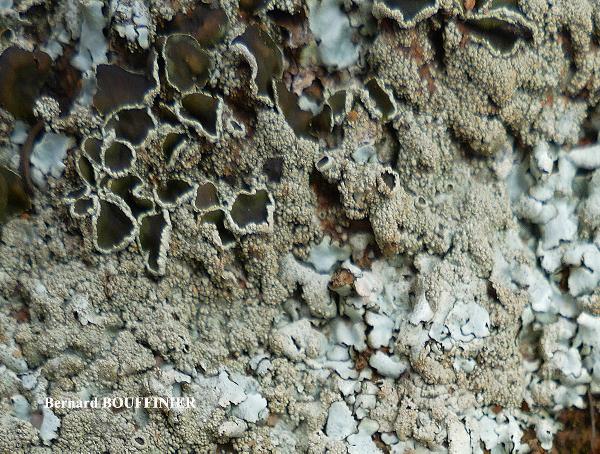
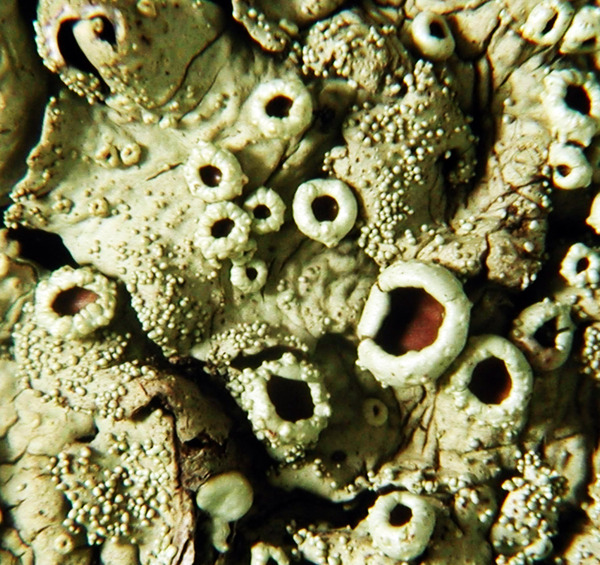
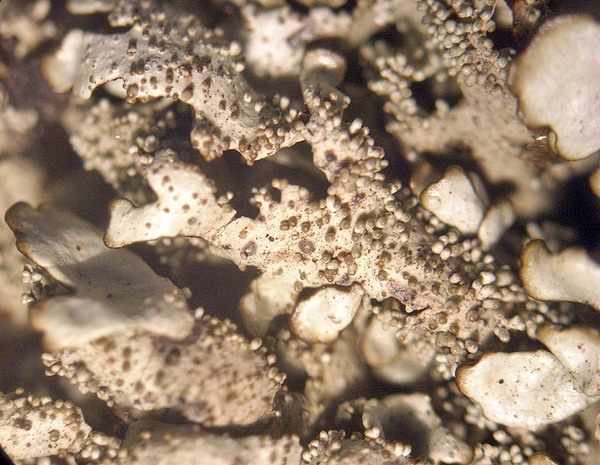
Description: Thallus foliose, heteromerous, dorsiventral, adnate, forming regular to irregular, 3-12 cm wide rosettes. Lobes flat to slightly convex, separate to more or less imbricate, 1.5-4 mm wide, with subrotund apices, the upper surface yellowish-green, smooth, shiny, epruinose and emaculate, with sparse to usually abundant, initially globose, then egg-shaped, 0.1-0.25 mm thick, 0.1-0.3 mm tall isidia with dull brown tips; lower surface black, with black, mostly simple, 0.2-0.6 mm long rhizines. Upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, of anticlinally arranged hyphae or of isodiametrical cells, with a pored epicortex, the cell walls with Xanthoparmelia-type lichenan; medulla white; lower cortex paraplectenchymatous. Apothecia rather rare, lecanorine, substipitate, 2-10 mm across, with a brown disc and a smooth to isidiate thalline margin. Epithecium brown; hymenium and hypothecium colourless; paraphyses simple; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, clavate, the K/I+ blue tholus penetrated by a faintly amyloid apical cushion with parallel or diverging flanks, the wall K/I-, surrounded by a K/I+ blue outer layer, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, 9-10 x 5-6 µm. Pycnidia rare, black, immersed. Conidia bifusiform, 5-6 x c. 1 µm. Spot tests: upper cortex K-, C-, KC- or KC+ pale yellow, P-; medulla K+ yellow turning dark red, C-, KC-, P+ red, UV-. Chemistry: upper cortex with usnic acid; medulla with salazinic acid (major) consalazinic acid (minor) and often with norstictic and protocetraric acids (traces).Note: a mainly southern species found on siliceous rocks (including serpentine) in sunny situations, common in the Mediterranean belt, but also occurring in dry-warm Alpine valleys.
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by isidia, or isidia-like structures (e.g. schizidia)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: common
Humid mediterranean belt: very common
Dry mediterranean belt: rather common
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
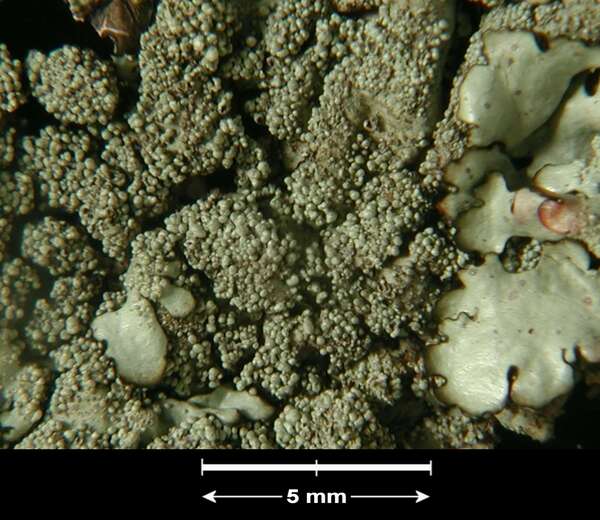


G. Incerti; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (33895)
2001/11/26
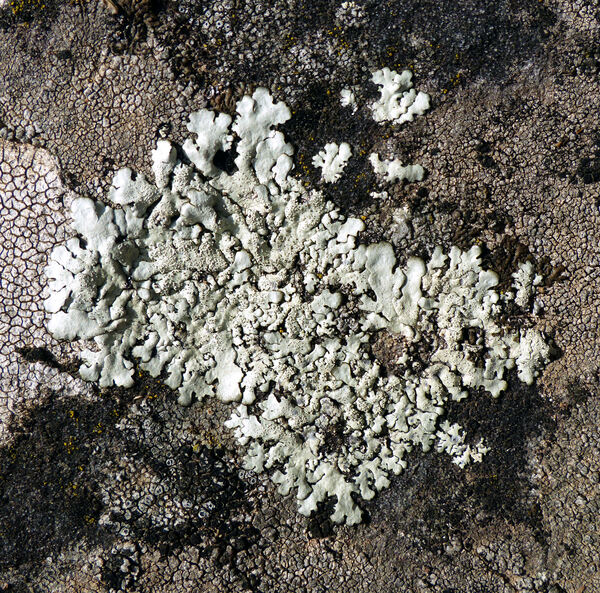


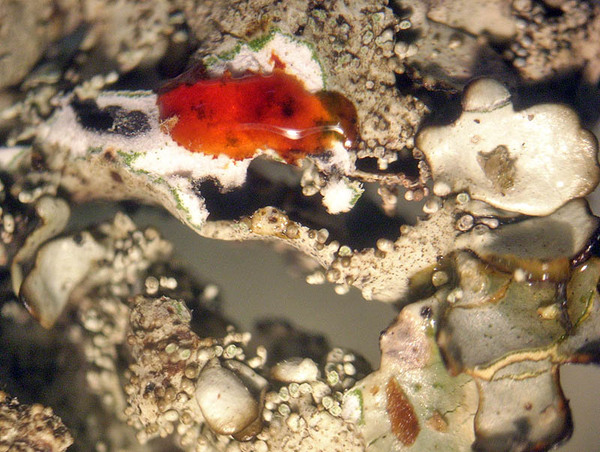
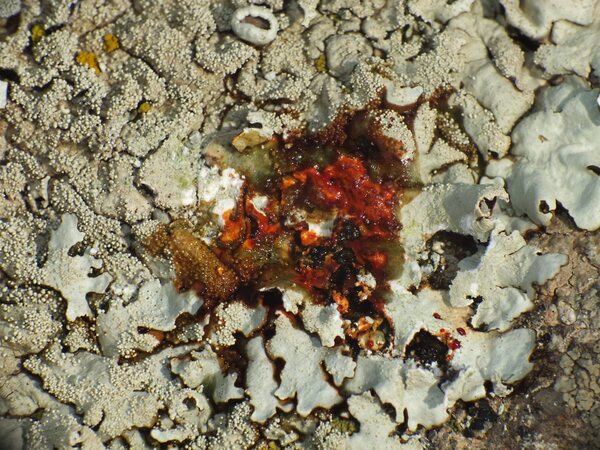
Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017
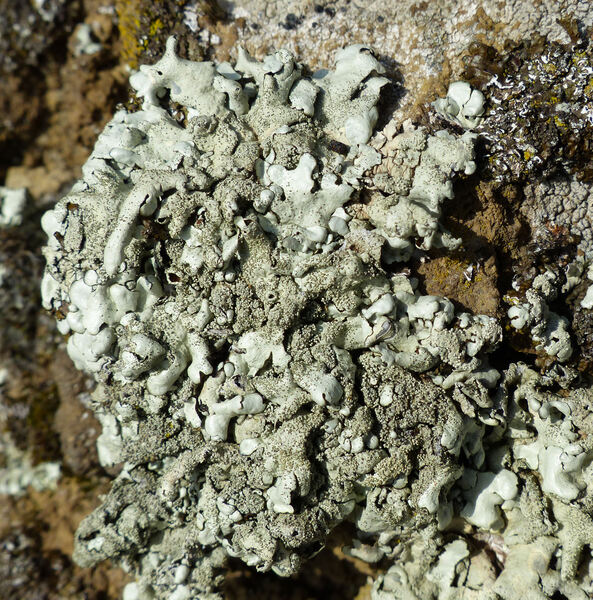


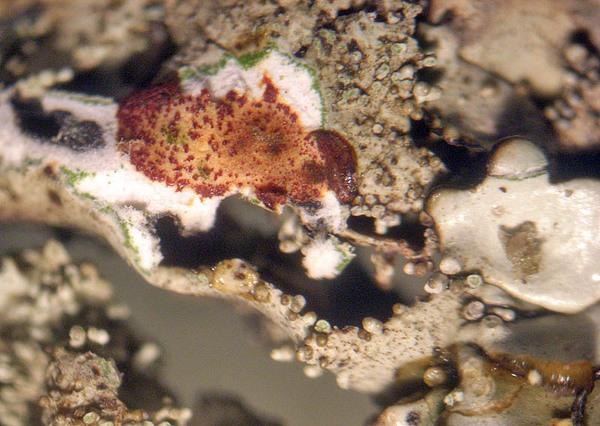
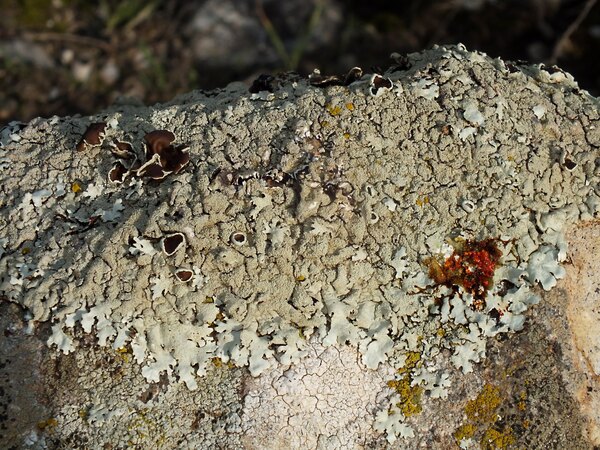
Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017
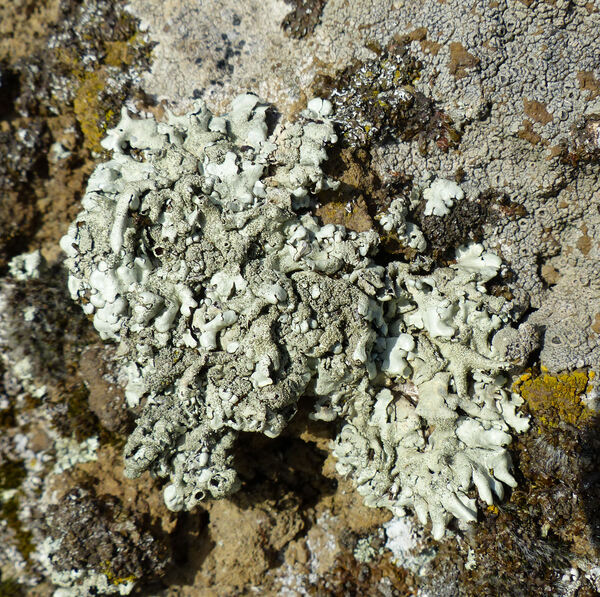


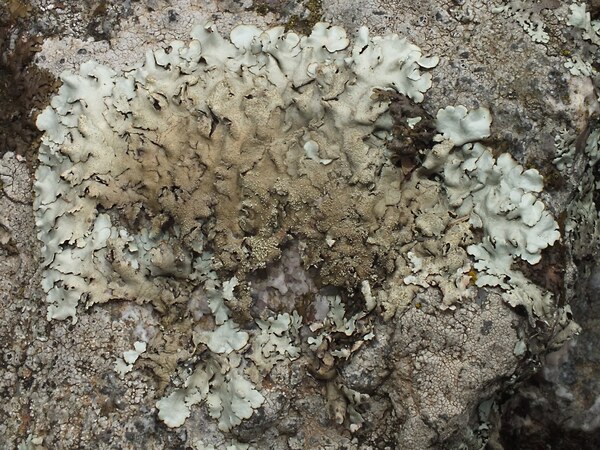
Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017
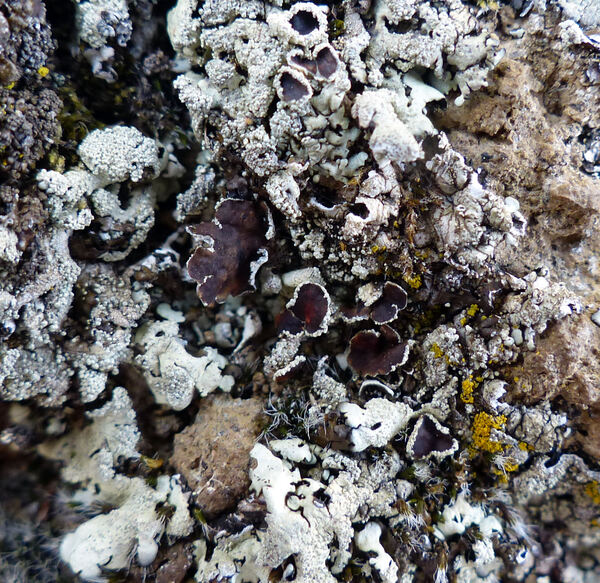


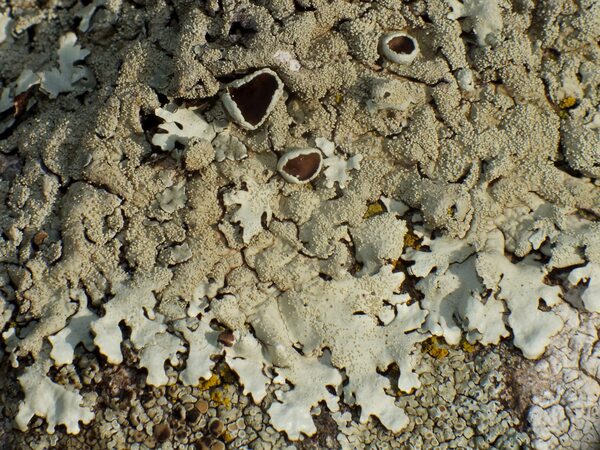
Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017
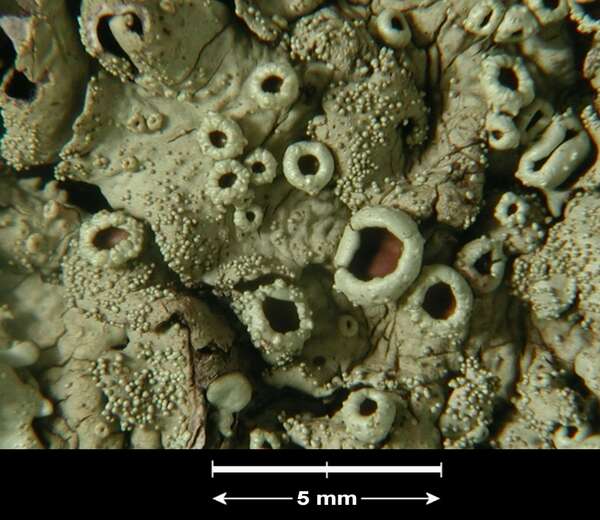


G. Incerti; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (33895)
2001/11/26
apothecia and isidia
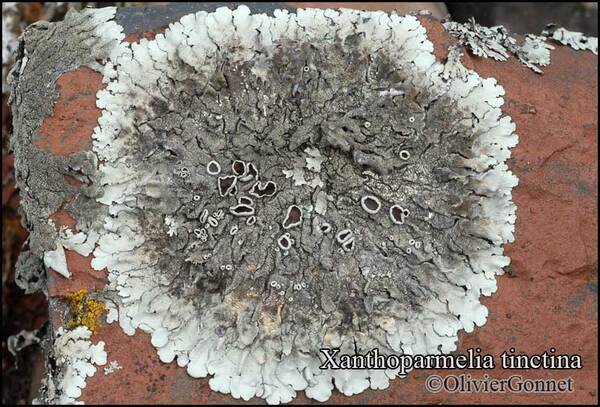

Courtesy Danièle et Olivier Gonnet - Source: https://www.afl-lichenologie.fr/Photos_AFL/Photos_AFL_X/Xanthoparmelia_tinctina.htm
France, session AFL 2010 - Hérault
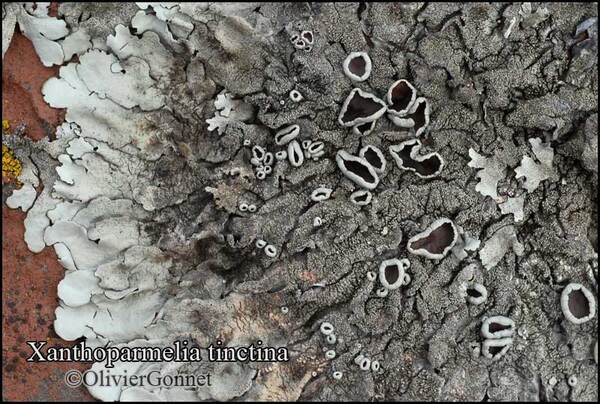

Courtesy Danièle et Olivier Gonnet - Source: https://www.afl-lichenologie.fr/Photos_AFL/Photos_AFL_X/Xanthoparmelia_tinctina.htm
France, session AFL 2010 - Hérault

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata
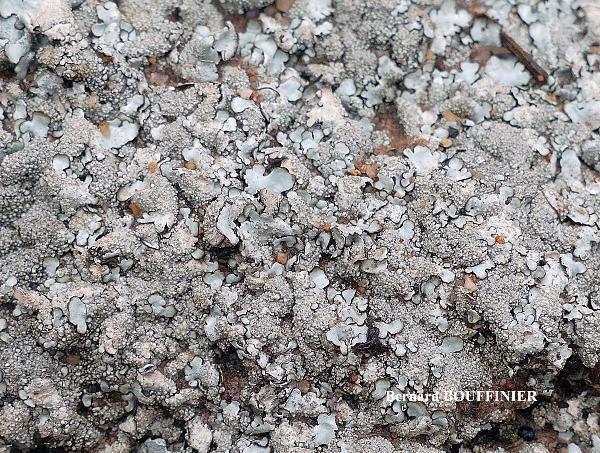

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata
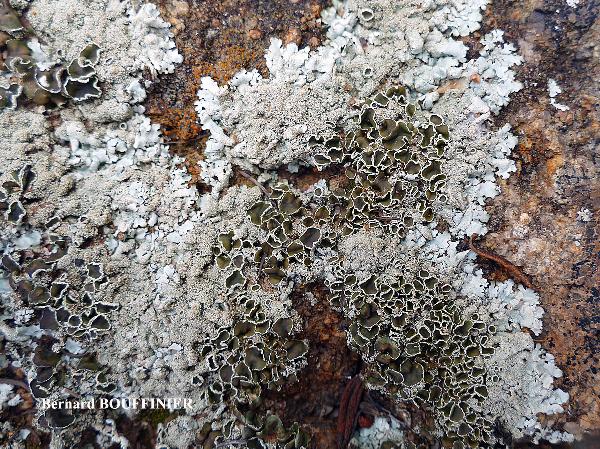

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by isidia, or isidia-like structures (e.g. schizidia)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: common
Humid mediterranean belt: very common
Dry mediterranean belt: rather common

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


G. Incerti; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (33895)
2001/11/26


Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017


Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017


Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017


Andrea Moro; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Italy, Lazio, Roma, Ruines of ancient Tusculum, above Frascati
18/03/2017


G. Incerti; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (33895)
2001/11/26
apothecia and isidia

Courtesy Danièle et Olivier Gonnet - Source: https://www.afl-lichenologie.fr/Photos_AFL/Photos_AFL_X/Xanthoparmelia_tinctina.htm
France, session AFL 2010 - Hérault

Courtesy Danièle et Olivier Gonnet - Source: https://www.afl-lichenologie.fr/Photos_AFL/Photos_AFL_X/Xanthoparmelia_tinctina.htm
France, session AFL 2010 - Hérault

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata

Bernard Bouffinier - Source: http://www.lichensmaritimes.org/index.php?task=fiche&lichen=1295&lang=en
France, Corse, Pointe de la Revellata

 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS