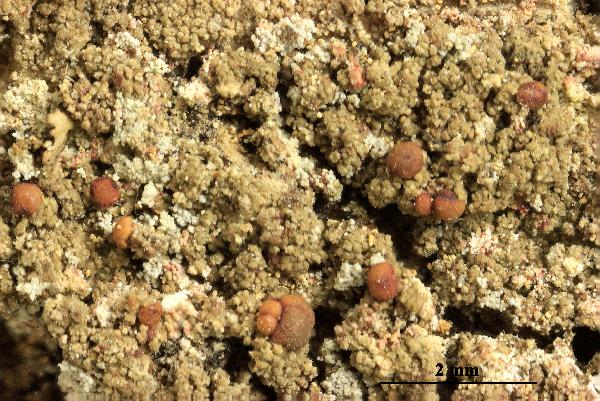
Biatora fallax Hepp
Flecht. Europ.: no. 505, 1860
Synonyms: Biatora vernalis (L) Fr. f. fallax (Hepp) Arnold; Biatorina fallax (Hepp) Hepp; Lecidea fallax (Hepp) Linds.
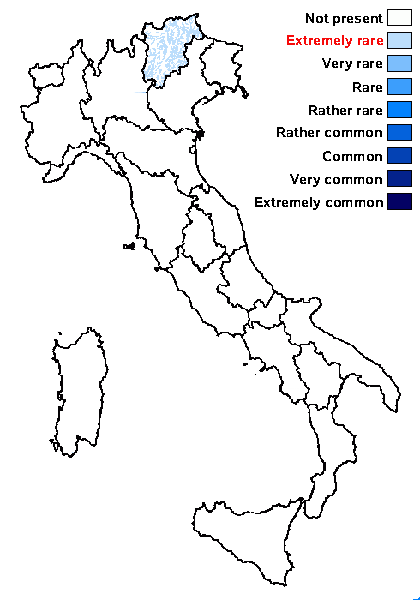
Distribution: N - TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2022).
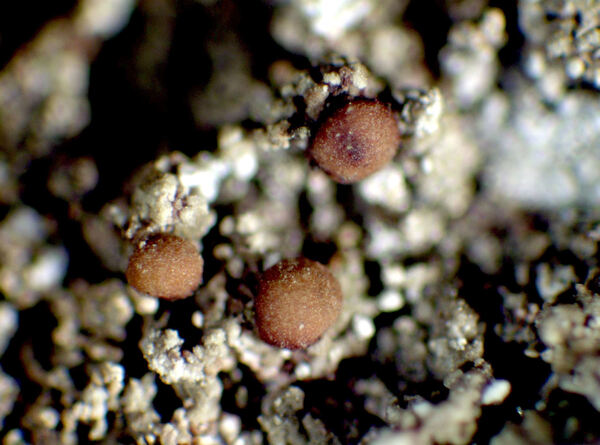
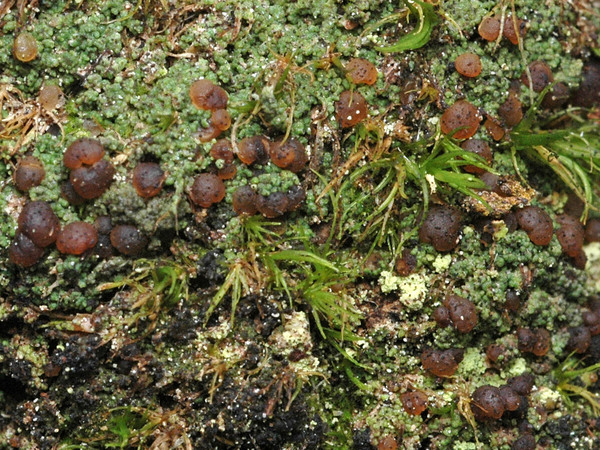
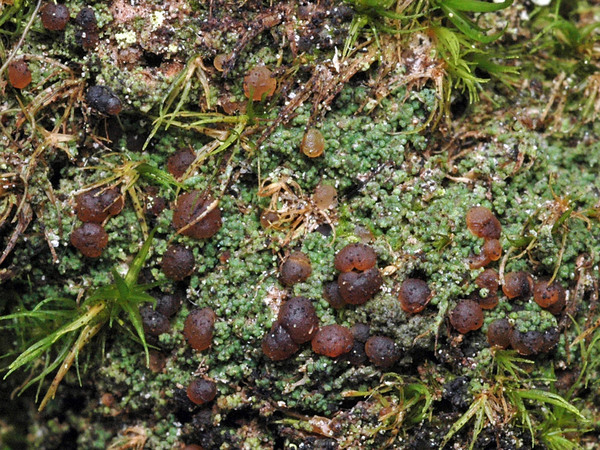
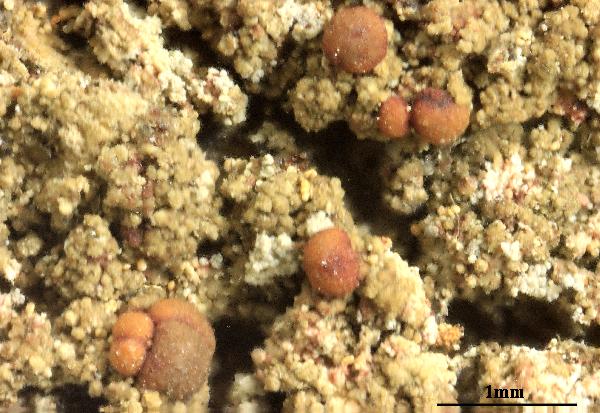
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, 0.2-0.4 mm thick, bright green to dark green (turning brownish in the herbarium), matt, granular-verrucose to minutely subsquamulose, forming up to 10 cm wide partches; verrucae/squamules small, 0.1-0.2(-0.3) mm in diam., convex, densely crowded and frequently overlapping, rarely finely dissected, dissolving into poorly delimited, 0.3-0.7 mm wide soralia, the soredia 20-40 μm across, sometimes gathered into 30-90 μm wide consoredia. Apothecia biatorine, rounded, sessile, strongly constricted at base, 0.3-0.7(-1.2) mm across, with a beige to reddish brown, strongly convex, epruinose disc, and an indistinct, slightly paler, soon excluded proper margin. Proper exciple colourless, 35-90 μm wide laterally, 100-280 μm wide basally, of radiating, weakly branched and anastomosing hyphae with cylindrical, 1-2.5 μm wide lumina, the lumina of apical cells up to 3 μm wide; epithecium scarcely differentiated from the hymenium; hymenium colourless or pale yellow, 40-55 μm high; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched and anastomosing, 1-1.5 μm thick at mid-level, the apical cells 1.5-3.5 μm wide; subhymenium distinct, colourless to yellowish brown, 50-95 µm high; hypothecium colourless to pale yellow-brown, 145-250 µm high. Asci 8-spored, clavate, with a K/I+ blue apical dome penetrated by a narrow, K/I- apical cushion surrounded by a narrow, deeply K/I+ blue zone, the wall K/I- but surrounded by an I+ red-brown, K/I+ blue outer layer, the ocular chamber relatively small, Biatora-type, 29-45 x 6-10 µm. Ascospores 1-celled or rarely 1-septate, hyaline, ellipsoid, (8.5-)11-14(-19.5) x (3-)3.7-4.5(-5.5) μm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus K-, C- or (especially the soralia) C+ fleeting pink, P+ orange-red. Chemistry: thallus with gyrophoric acid and argopsin (major), and norargopsin (traces). Note: on the base of coniferous trees near treeline; most records from the Alps are historical.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: bark and lignum
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
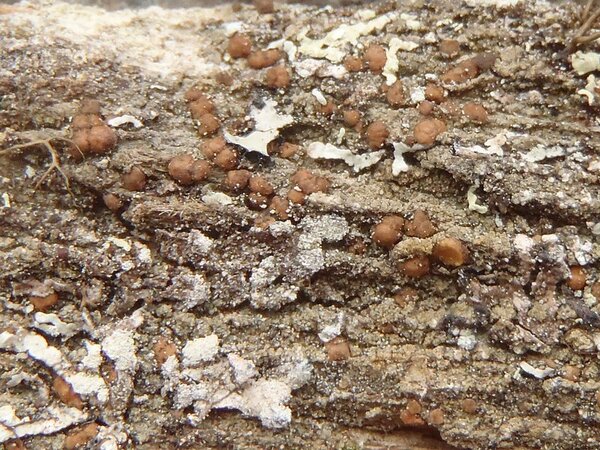


Curtis Randall Björk – CC BY-SA 4.0
British Columbia, Clearwater area, Raft Mountain Terricolous and at tree base, subalpine 2004-07-07
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: bark and lignum
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: extremely rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS






