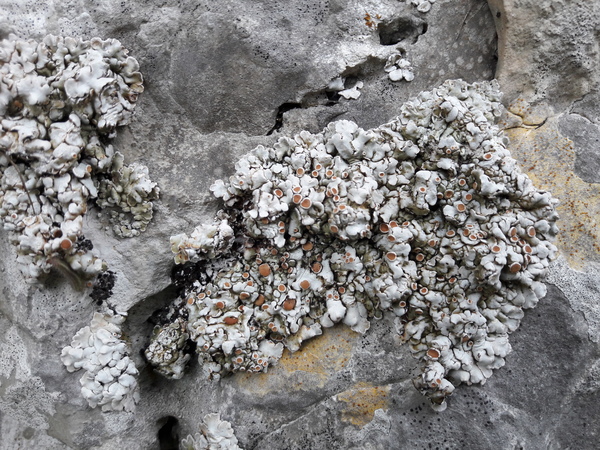
Squamarina confusa Cl. Roux & Poumarat
Bull. Soc. linn. Provence, 75: 105, 2024.
Synonyms:
Distribution: N - Ven (Herb Nascimbene).
Description: Thallus squamulose, the squamules imbricate, white to pale green when fresh, more or less pruinose, irregularly lobed (but young thalli forming regular rosettes), the margins of marginal squamules sometimes white, the lower surface pale in young squamules, then black, attached by numerous, concolorous rhizinoid hyphal strands. Upper cortex 30-85 µm thick, consisting of a 20-30 µm thick epinecral layer inspersed with crystals, and a 25-55 µm thick layer of mainly anticlinally arranged nyphae inspersed with crystals; medulla white (brownish in lower part), up to 0.5 mm thick. Apothecia frequent, lecanorine or weakly zeorine, 0.6-4.4 mm across, finally constricted at base, with a brownish, at first concave then flat to slightly convex disc and a 0.1-0.35 mm thick, whitish, smooth, finally often excluded thalline margin, the proper margin thin and poorly evident, somehow glossy, level with disc. Thalline exciple 175-260 μm wide, corticate; proper exciple 105-180 μm wide, filled with crystals, the hyphae slightly arranged in a fan-way; epithecium yellowish brown, granular, 10-25 µm high; hymenium colourless, 60-90 µm high, hemiamyloid; paraphyses coherent, mostly simple, 1-1.5 μm thick at mid-level, the apical cells 2-4 μm wide; hypothecium colourless, 55-65 μm high, prosoplectenchymatous, the upper part with large crystals soluble in K and insoluble in N, I- (the subhymenium is devoid of crystals). Asci 8-spored, elongate-clavate, with a thin, outer amyloid layer and a thickened, amyloid tholus devoid of an ocular chamber, penetrated by an axial tube the sides of which stain I+ deeper blue, approaching the Porpidia-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, long-ellipsoid to subfusiform, (10-)12-16.5(-18.5) x (3.5-)4.5-5.5(-6.5) µm, with more or less pointed ends. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC- or KC+ faintly yellow, P-; medulla P+ yellow. Chemistry: cortex with usnic and isousnic acids; medulla with psoromic and 2ʹ-O-demethylpsoromic acids.Note: a recently-described calcicolous species, easily confused with S. stella-petraea, probably more widespread in Italy, especially below the montane belt. For a more detailed description see Roux & Poumarat (2024).
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare
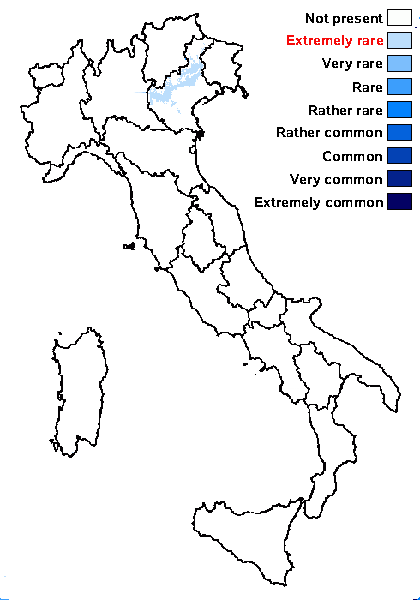
Predictive model
Growth form: Squamulose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare

Predictive model
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS



