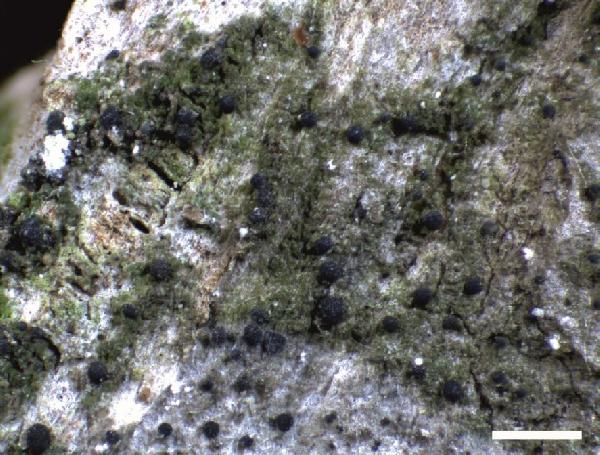
Micarea melanobola (Nyl.) Coppins
Bull. Br. Mus. nat. Hist., Bot., 11, 2: 156, 1983. Basionym: Lecidea melanobola Nyl. - Flora, 50, 24: 371, 1867.
Synonyms: Catillaria melanobola (Nyl.) Vain.; Lecidea prasinella Müll. Arg.
Distribution:
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, pale to dark green, sometimes olivaceous, composed of 14-35 µm wide goniocysts often coalescing into larger granules, which contain crystals soluble in K, visible under polarized licht, and are sometimes surrounded by an olivaceous, K+violet pigment. Apothecia numerous, micareoid, 0.15–0.4 mm across, hemispherical to subglobose, simple or tuberculate, dark grey to black, more rarely brown-black, K+ violet and C+ violet in cross-section. Epithecium grey, dark grey, blackish grey, sometimes brownish grey or greenish grey, K+ and C+ violet, withouit crystals; hymenium colourless, c. 30-55 µm high, often with crystals soluble in K and visible under polarized light; paraphyses richly branched, 0.5-1 µm thick; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, clavate, with a K/I+ pale blue apical dome with a dark blue tubular structure, 30-35 x 9-11 µm. Ascospores 0-1-septate, hyaline, oblong ellipsoid or obovoid, 7-11 x 2.5-3.5(-4) µm. Pycnidia mostly pigmented, grey to blackish grey, the wall K+ and C+ violet, of two types: a) mesopycnidia usually numerous, 30-90 µm wide, often immersed, globose or barrel-shaped with a gaping ostiole often extruding a white conidial mass, producing cylindrical or cylindrical-fusiform mesoconidia measuring 3.5-4.5 x 1-1.5 µm; b) micropycnidia small and inconspicuous, 40-90 µm wide, immersed or rarely sessile, globose, producing straight or sometimes curved, bacilliform or narrowly fusiform microconidia measuring 5-7(-7.5) x 0.5-1 µm. Photobiont micareoid, the cells 4.5-7 µm wide. Spot tests: thallus K- or K+ faintly violet, C- or C+ faintly violet, P-, UV-. Chemistry: micareic acid, variable amounts of the Sedifolia-grey pigment.Note: considered for a long time as a dark-fruited form of M. prasina, this species, mostly growing on the bark of conifers, more rarely on wood, is known from Northern and Central Europe, with a single, old record from Switzerland. To be looked for in the Italian Alps.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: bark and lignum
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Predictive model
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: bark and lignum
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual

Predictive model


