Lecanographa rinodinae (Vězda) R. Sant.
in Santesson & al., Lichen-Forming and Lichenicolous Fungi of Fennoscandia: 146, 2004. Basionym: Opegrapha rinodinae Vězda - Česká Mykol., 23, 2: 104, 1969.
Synonyms:
Distribution:
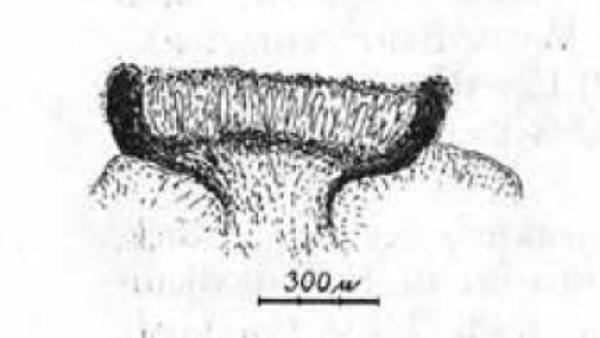
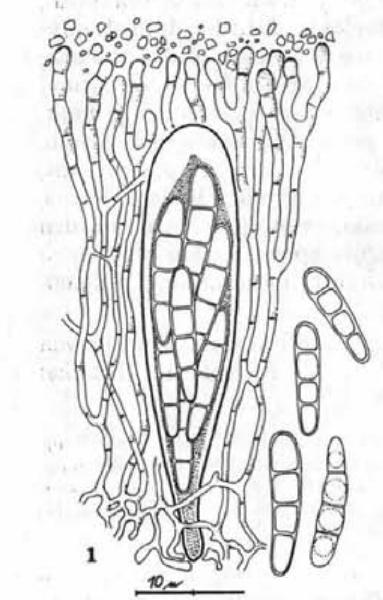
Description: Thallus inapparent, not lichenized, the hyphae developing inside the thalli of Phaeorrhiza nimbosa. Apothecia scattered or clustered, round to angular by mutual compression, brown-black but usually whitish-pruinose, at first immersed in the host thallus, then sessile, 0.4-1.2 mm across, 0.15-0.3 mm tall, with a flat disc and a relatively thick, raised, entire proper margin. Proper exciple black, carbonized, up to 60 µm thick, not extending below the hymenium; epithecium dark olive-brown, up to 20 µm high, the upper part with 1-2 µm wide granules; hymenium pale brown, 80-90 µm high, I+ blue soon turning red-brown; paraphyses branched and anastomosing, the lumina c. 1.5 µm wide, the terminal cells up to 5 µm wide; hypothecium olive-brown, I+ faintly blue. Asci (4-6-)8-spored, bitunicate, cylindrical-clavate, shortly stalked, the apex with a narrow, K/I± pale blue apical dome penetrated by a small ocular chamber surrounded by a small, K/I+ dark blue, ring-like zone, 50-70 x 13-15 µm. Ascospores 3(-4-5)-septate, hyaline, elongate-ellipsoid with rounded ends, 22-26 x 4-6 µm, surrounded by a thin gelatinous perispore. Photobiont absent. Spot tests: all negative. Chemistry: not known, but probably without lichen substances.Note: a rare, arctic-alpine lichenicolous fungus developing in the thalli of Phaeorrhiza nimbosa; described from the Carpathians and also known from Fennoscandia, arctic Russia and the Alps (Austria, Switzerland). To be looked for in the Italian Alps.
Growth form: Lichenicolous fungus
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Predictive model
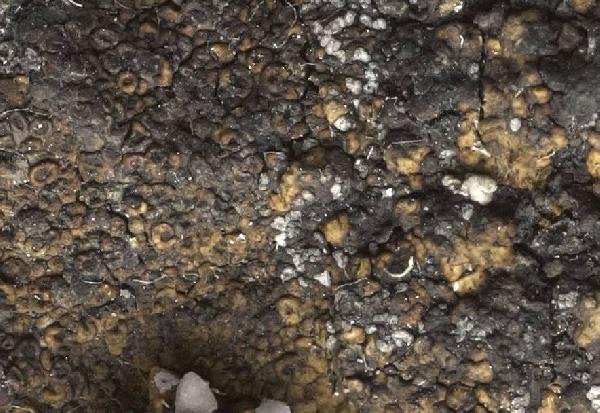

Detail from: https://gzu.jacq.org/GZU000289045 GZU000289045 - Vězda, A.: Lichenes Selecti Exsiccati 774 In thallo Rinodinae nimbosae (Fr.) Th. Fr. parasymbiontice vigens
Growth form: Lichenicolous fungus
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual

Predictive model