Buellia epigaea (Pers.) Tuck.
Gen. Lich.: 185, 1872. Basionym: Lichen epigaeus Pers. - Ann. Bot. (Usteri), 1: 25, 155, 1794.
Synonyms: Buellia epigaea var. intermedia (Schrad.) Anzi; Buellia nivea (Anzi) Zahlbr.; Catolechia epigaea (Pers.) Anzi; Diploicia epigaea (Pers.) A. Massal.; Diploicia epigaea var. intermedia (Schrad.) Körb.; Lecidea epigaea (Pers.) Schaer.; Psora epigaea (Pers.) Hoffm.; Rinodina nivea Anzi
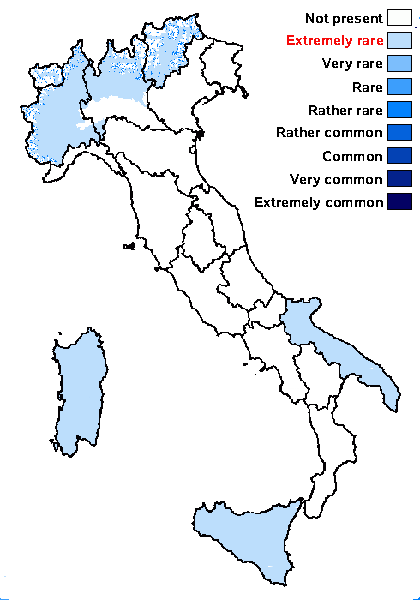
Distribution: N - TAA (Trinkaus & Mayrhofer 2000), Lomb, Piem (Matteucci & al. 2013), VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999, Piervittori & al. 2004). C - Sar (Trinkaus & Mayrhofer 2000). S - Pugl, Si.
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, 0.2-1 mm thick, chalky white to pale grey-white or cream-coloured, the surface often farinose to small-granulose, irregularly areolate to bullate, forming irregular, 1-1.5 cm wide patches, without a distinct prothallus. Phenocortex up to 150 µm thick; medulla white, filled with crystals of calcium-oxalates, I-. Apothecia lecideine, bluish black but usually slightly white-pruinose, (0.3-)0.5-1.5 mm across, immersed to sessile, often provided with a thin thalline rim when young. Proper exciple up to 50(-90) µm wide laterally, Aethalea-type, the inner hyphae hyaline, prosoplectenchymatous, the outer hyphae parallel and usually strongly brown-pigmented; epithecium brown, 5-10(-15) µm high; hymenium colourless, not inspersed with oil droplets, up to 130 µm high; paraphyses sparingly branched in upper part, 1.5-3 µm thick at mid-level, the apical cells 3-8 µm wide, with a dark cap; hypothecium colourless to pale brown, up to 100 µm high. Asci 8-spored, clavate to cylindrical-clavate, the apical dome K/I+ dark blue with a pale, conical-pointed apical cushion (axial mass), the wall I-, but the thin outer gel I+ blue, Bacidia-type. Ascospores 1-septate, slightly constricted at septum, brown, ellipsoid, (14-)15-22(-26) x (6-)7-10(-12) µm, Buellia-type, thin-walled throughout, the wall minutely areolate. Pycnidia rare, black, pear-shaped, immersed. Conidia bacilliform, 5-7 x c. 1 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-. Chemistry: without lichen substances.Note: widely distributed in Europe, from submediterranean regions to Scandinavia, on base-rich mineral soil, on weathered gypsum and gypsum soil. South Italian records (Nimis 1993: 138) should be checked: they could refer to B. asterella Poelt & Sulzer.
Growth form: Crustose placodiomorph
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: extremely rare
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
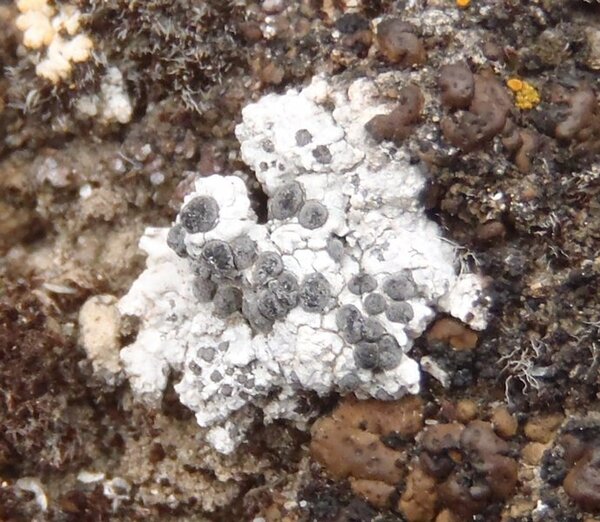


Curtis Randall Björk – CC BY-SA 4.0
Washington, Asotin County, Hells Canyon, Lime Hill Limestone cliffs in canyon grassland 2013-05-06
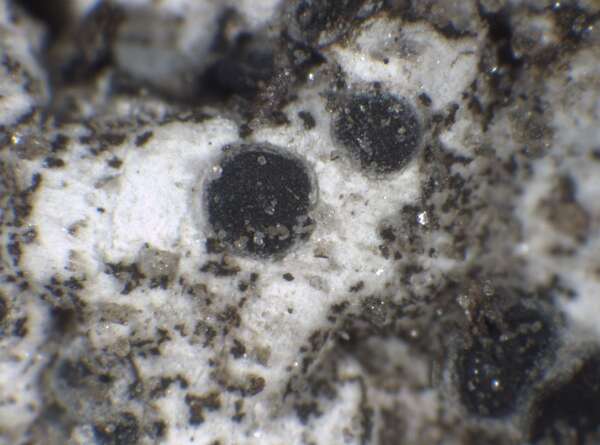


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (35347)
2003/03/06
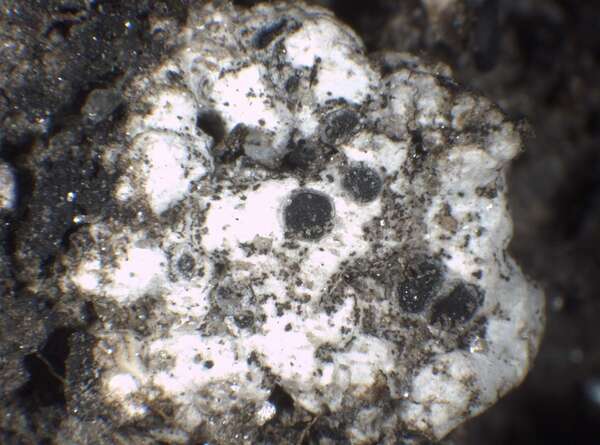


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (35347)
2003/03/06
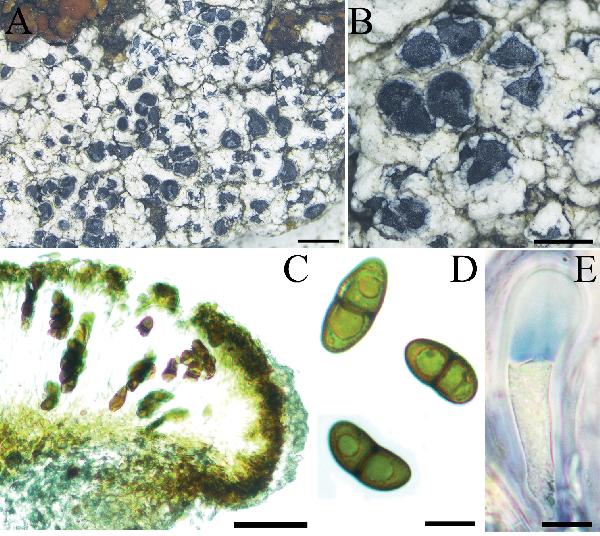
Source: Ai M, Li LJ, Worthy FR, Yin AC, Zhong QY, Wang SQ, Wang LS, Wang XY (2022) Taxonomy of Buellia epigaea-group (Caliciales, Caliciaceae), revealing a new species and two new records from China. MycoKeys 92: 45-62 - CC BY-4.0
Morphology of Buellia epigaea (XY19-2294 KUN) A thallus growing on the soil B lecideine apothecia with white pruina, surrounded by a thalline collar (pseudolecanorine) C the section of apothecium, exciple aethalea-type D ascospores with 1-septate, Callispora-type E ascus Bacidia-type. Scale bars: 2 mm (A); 1 mm (B); 50 µm (C); 10 µm (D, E).


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
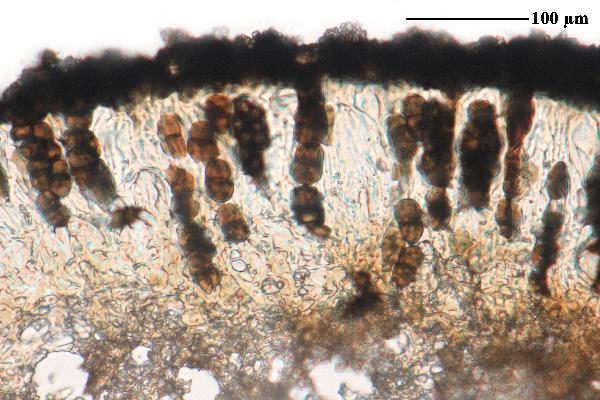
[VZ1338], Jugoslavia. Macedonia, Ohrid, supra lacum Ohridsko ezero,
prope vicum Elsani haud procul Peštani, 980 m. In rupibus calcareis,
supta terram et muscos emortuos. Leg. A. Vezda, 10.7.1975. EX A.
VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1338.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1338], Jugoslavia. Macedonia, Ohrid, supra lacum Ohridsko ezero,
prope vicum Elsani haud procul Peštani, 980 m. In rupibus calcareis,
supta terram et muscos emortuos. Leg. A. Vezda, 10.7.1975. EX A.
VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1338.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
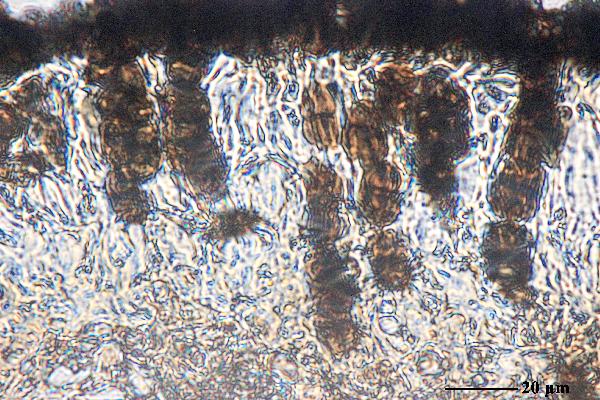
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan
dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200
m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A.
Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR.
1424


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan
dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200
m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A.
Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR.
1424

Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan
dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200
m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A.
Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR.
1424

Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan
dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200
m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A.
Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR.
1424
Growth form: Crustose placodiomorph
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: extremely rare
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: extremely rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


Curtis Randall Björk – CC BY-SA 4.0
Washington, Asotin County, Hells Canyon, Lime Hill Limestone cliffs in canyon grassland 2013-05-06


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (35347)
2003/03/06


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (35347)
2003/03/06

Source: Ai M, Li LJ, Worthy FR, Yin AC, Zhong QY, Wang SQ, Wang LS, Wang XY (2022) Taxonomy of Buellia epigaea-group (Caliciales, Caliciaceae), revealing a new species and two new records from China. MycoKeys 92: 45-62 - CC BY-4.0
Morphology of Buellia epigaea (XY19-2294 KUN) A thallus growing on the soil B lecideine apothecia with white pruina, surrounded by a thalline collar (pseudolecanorine) C the section of apothecium, exciple aethalea-type D ascospores with 1-septate, Callispora-type E ascus Bacidia-type. Scale bars: 2 mm (A); 1 mm (B); 50 µm (C); 10 µm (D, E).


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1338], Jugoslavia. Macedonia, Ohrid, supra lacum Ohridsko ezero, prope vicum Elsani haud procul Peštani, 980 m. In rupibus calcareis, supta terram et muscos emortuos. Leg. A. Vezda, 10.7.1975. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1338.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1338], Jugoslavia. Macedonia, Ohrid, supra lacum Ohridsko ezero, prope vicum Elsani haud procul Peštani, 980 m. In rupibus calcareis, supta terram et muscos emortuos. Leg. A. Vezda, 10.7.1975. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1338.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200 m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A. Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1424


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200 m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A. Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1424


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1424], URSS. Azerbajdzania. Distr. Baku, reservatum Kobistan dictum (in litore maris Caspii 60 km in austro-occidente a Baku), 200 m. Ad terram locis desertis in saxosis arenareis. Leg. E. Jelínková et A. Vezda, 15.5.1978. EX A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI NR. 1424


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS

