Acarospora badiofusca (Nyl.) Th. Fr.
N. Acta Reg. Soc. Sci. Upsal., ser. 3, 3: 190, 1861. Basionym: Lecanora badiofusca Nyl. - Herb. Mus. Fenn.: 110, 1859.
Synonyms: Acarospora anziana H. Magn.; Sarcogyne acarosporoides Anzi
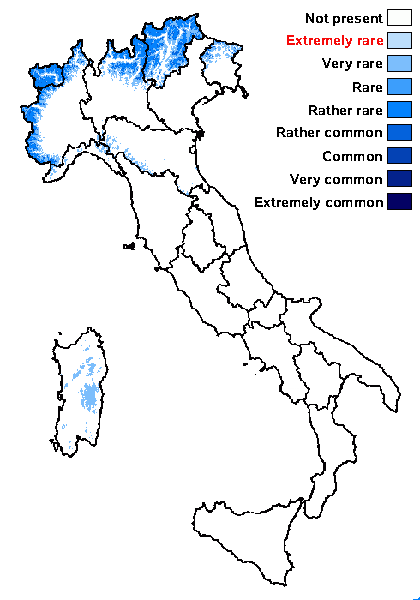
Distribution: N - Frl, TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2022), Lomb, Piem (TSB 33659), VA (Valcuvia 2000, Matteucci & al. 2015c), Emil (Fariselli & al. 2020), Lig (TSB 33438). C - Sar (Hafellner 1993, Rizzi & al. 2011, Cossu & al. 2015).
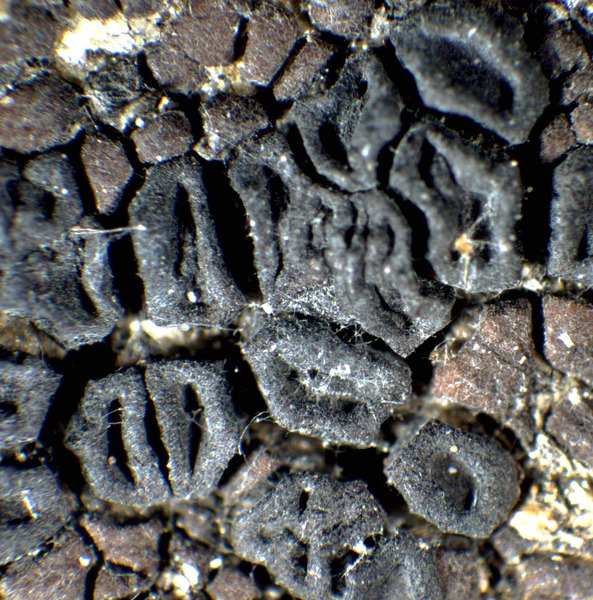
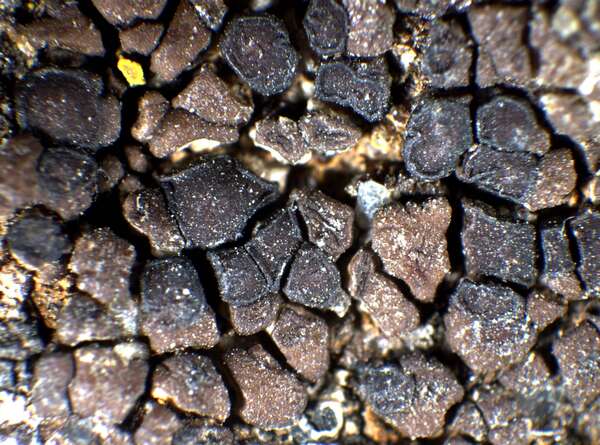
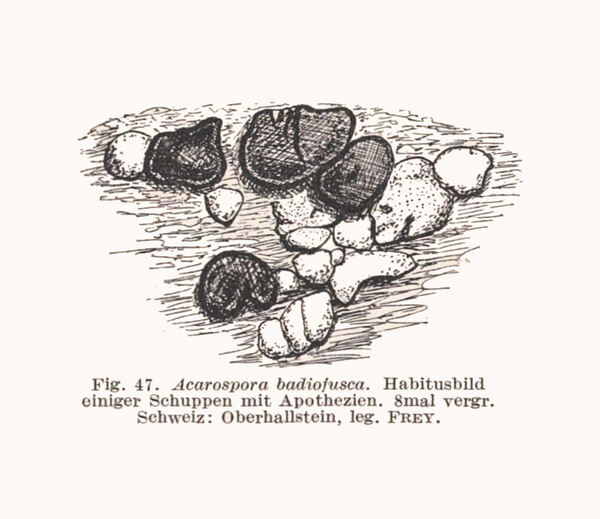
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, pale to dark chestnut brown, sometimes grey-brown, areolate (not subsquamulose), forming up to 8 cm wide patches, the areoles round or angular, sometimes indistinctly lobed, 0.7-3 mm across, up to 1 mm thick, contiguous to dispersed, flat to strongly convex, smooth or fissured and rugulose, epruinose; lower surface dark along the margins. Epicortex 10-20 µm thick, sometimes discontinuous; upper cortex paraplectenchymatous, the cells (3-)4-5(-6) µm wide, arranged in more or less vertical rows, the upper part reddish brown, the lower part colourless; algal layer continuous, 80-120 µm thick; medulla white, 100-300 µm thick (rarely more), continuous with the attaching hyphae, the hyphae thin-walled, ca. 2 µm thick. Apothecia 0.4-2(-3) mm across, 1(-4) per areole, when mature often larger than the corresponding areole, round to weakly angular, at first immersed, then subsessile, with an expanded, flat to slightly convex, smooth to rugose, black to dark reddish brown (turning reddish when wet), matt disc, and a prominent, concolorous proper margin. Proper exciple 15-20 µm wide, prosoplectenchymatous; epithecium yellowish brown, 10-15 µm high; hymenium colourless, 60-90(-100) µm high, the hymenial gel euamyloid, IKI+ persistently dark blue; paraphyses 2-3(-3.5) µm thick at base, the apical cells unexpanded or to c. 5 µm wide; subymenium to 75 µm high, colourless; hypothecium prosoplectenchymatous, 15-30 mm high. Asci c. 200-spored, clavate, the apical dome K/I-, c. 40-50 x 12-15 µm. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, broadly ellipsoid to ellipsoid, 3-6 x 1.5-2.5(-3) µm. Pycnidia globose, c. 80 x 80 µm, the conidiogenous cells ampulliform, c. 10 x 1 µm. Conidia c. 1.5-2 x 1 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: cortex and medulla K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-. Chemistry: without lichen substances. Note: an arctic-alpine to boreal-montane, circumpolar species of base-rich or lime-containing siliceous rocks, such as mica-schists and calciferous sandstone, on faces wetted by rain, incl. stones near the ground in grasslands. Frequent only in the Alps, with optimum in the subalpine belt. The species does not belong to Acarospora s.str. (Westberg & al. 2015).
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rather common
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
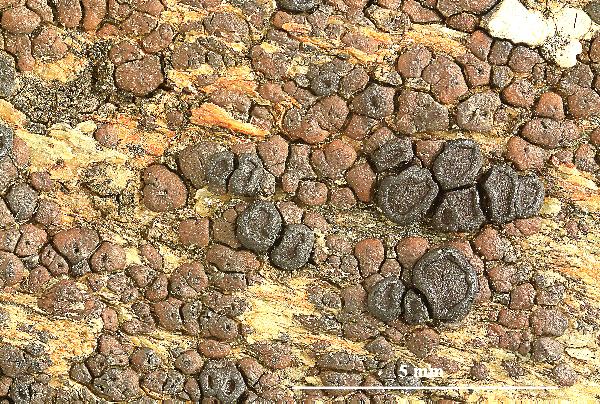


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1823], Austria, Salisburgia, Lungau, in alpibus "Radstädter Tauern",
in summo montis Speiereck dicti, alt. 2400 m. In rupibus calcareis.
Leg. P. Clerc & A. Vezda, 07.09.1981. - Ex A. VEZDA: LICHENES
SELECTI EXSICCATI Nr. 1823.
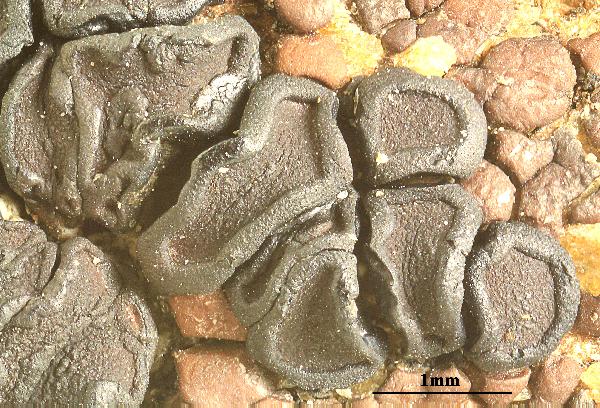


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1823], Austria, Salisburgia, Lungau, in alpibus "Radstädter Tauern",
in summo montis Speiereck dicti, alt. 2400 m. In rupibus calcareis.
Leg. P. Clerc & A. Vezda, 07.09.1981. - Ex A. VEZDA: LICHENES
SELECTI EXSICCATI Nr. 1823.
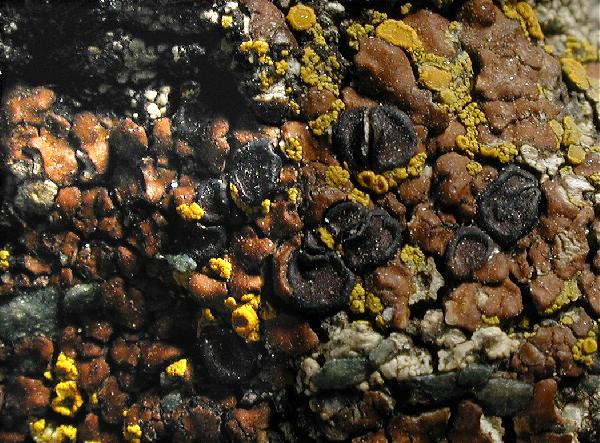

Ulrich Kirschbaum CC BY-SA 4.0 - Source: https://www.thm.de/lse/ulrich-kirschbaum/flechtenbilder
On rocks (gneiss).Austria: Alps.
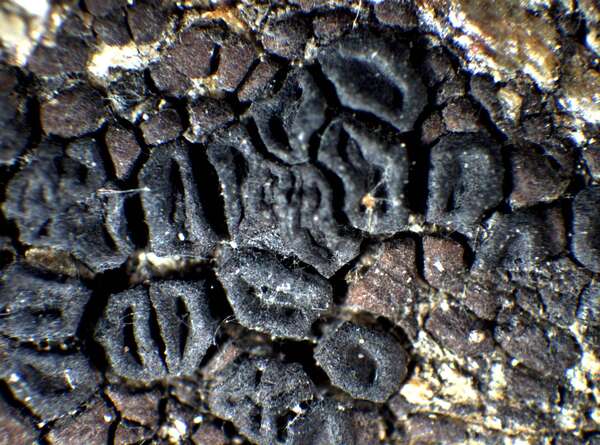


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (9189)
2001/11/20
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rather common
Oromediterranean belt: very rare
Montane belt: very rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1823], Austria, Salisburgia, Lungau, in alpibus "Radstädter Tauern", in summo montis Speiereck dicti, alt. 2400 m. In rupibus calcareis. Leg. P. Clerc & A. Vezda, 07.09.1981. - Ex A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI Nr. 1823.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[VZ1823], Austria, Salisburgia, Lungau, in alpibus "Radstädter Tauern", in summo montis Speiereck dicti, alt. 2400 m. In rupibus calcareis. Leg. P. Clerc & A. Vezda, 07.09.1981. - Ex A. VEZDA: LICHENES SELECTI EXSICCATI Nr. 1823.

Ulrich Kirschbaum CC BY-SA 4.0 - Source: https://www.thm.de/lse/ulrich-kirschbaum/flechtenbilder
On rocks (gneiss).Austria: Alps.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS




