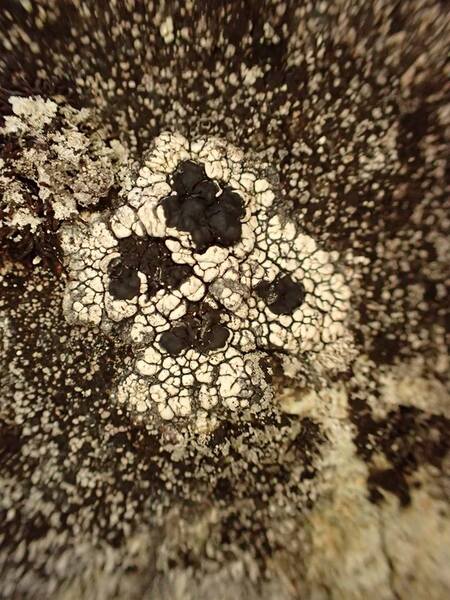
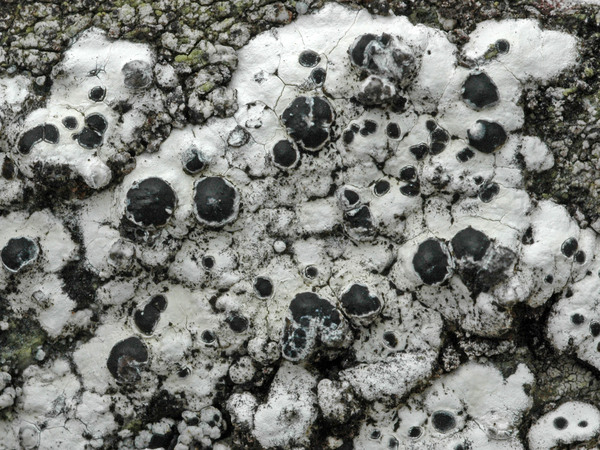
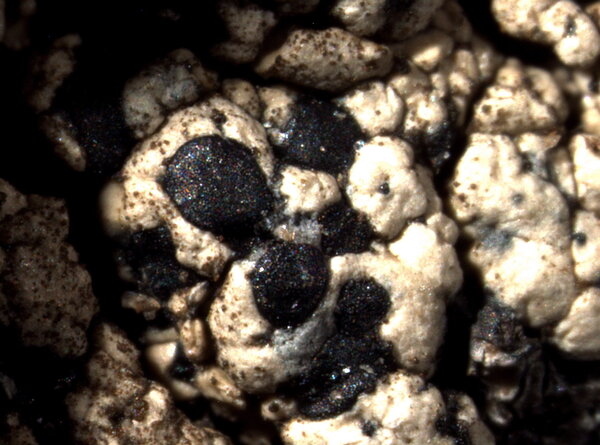
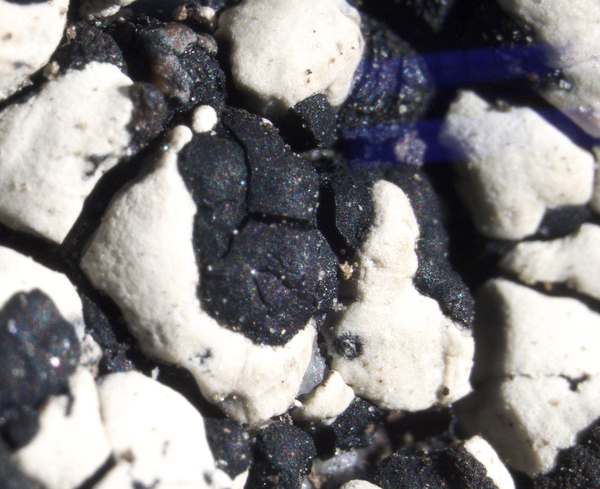
Calvitimela aglaea (Sommerf.) Hafellner
in Hafellner & Türk, Stapfia, 76: 151, 2001. Basionym: Lecidea aglaea Sommerf. - Suppl. Fl. Lapp.: 144, 1826.
Synonyms: Lecidea brunneri Nyl.; Lecidea relanderi Räsänen; Lecidella aglaea (Sommerf.) Körb.; Oedemocarpus aglaeus (Sommerf.) Trevis.; Tephromela aglaea (Sommerf.) Hertel & Rambold
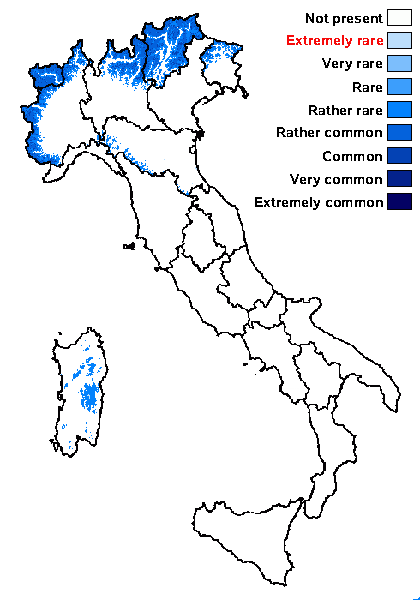
Distribution: N - Frl (Tretiach & Hafellner 2000), TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2022), Lomb, Piem (Haugan & Timdal 1994, Isocrono & al. 2004), VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999), Emil (Fariselli & al. 2020). C - Sar (Nöske 2000, Nöske & al. 2000).
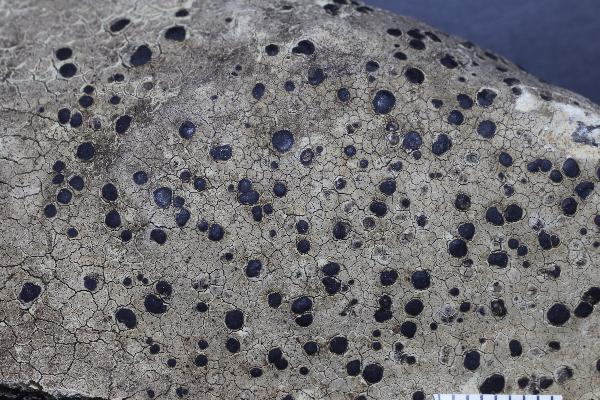
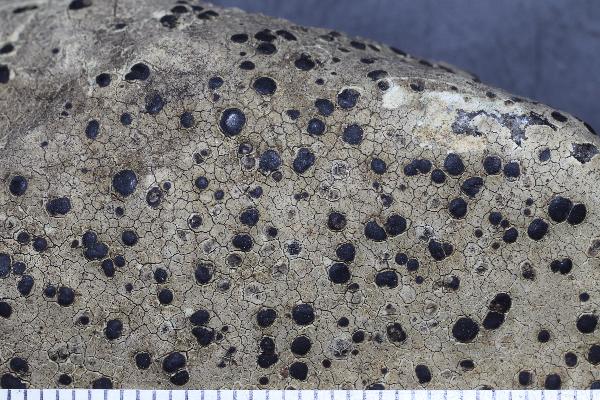
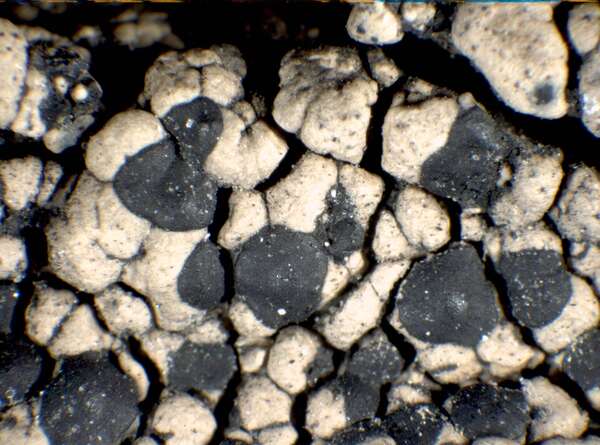
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, rather thick, warted-areolate, pale greenish yellow to yellowish brown, usually turning brown in the herbarium, forming up to 8(-10) cm wide patches, rarely delimited by a black prothallus. Areoles mostly contiguous, up to 2 mm wide, flat to convex. Cortex up to 60 µm thick, of thick-walled hyphae with cylindrical lumina, containing crystals dissolving in K; medulla white, of loosely interwoven, thin-walled hyphae, I-. Apothecia biatorine, black to brown-black, somehow shiny, 0.5-2(-3) mm across, with a flat to finally irregularly convex, epruinose disc, and a thin, poorly evident, soon excluded proper margin. Proper exciple poorly developed, with a dark brown to dark green-brown rim, paler brown within; epithecium bluish green-black, sometimes in part brown; hymenium colourless, 60-80 µm high, I+ blue; paraphyses coherent, sparingly branched and anastomosing, 3-4 µm thick in lower part, the apical cells to 8 µm wide, with a sharply delimited pigmented zone in the wall, covered by a green gel; hypothecium colourless in upper part, pale yellow-brown in lower part, I-. Asci 8-spored, clavate, the K/I+ blue tholus penetrated by a faintly amyloid apical cushion with parallel or diverging flanks, the wall K/I-, surrounded by a K/I+ blue outer layer, Lecanora-type. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, (7.5-)9-13.5(-16) x (4.5-)5-7.5(-8.5) µm. Pycnidia dark, immersed, the wall greenish around the ostiole. Conidia hyaline, short-bacilliform, straight, 6-9 x 1-2 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: cortex K+ yellow, C-, KC+ yellow, P-; medulla K+ yellow-orange, C+ yellow, KC-, P+ orange or rarely P-. Chemistry: Chemotype I: atranorin, usnic and bourgeanic acids (the most common in the Alps). Chemotype II: atranorin, usnic, bourgeanic, and stictic acids, Chemotype III: atranorin and bourgeanic acid, chemotype IV: atranorin only.Note: an arctic-alpine, circumpolar species found on inclined faces of hard siliceous rocks in upland areas.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather common
Subalpine belt: common
Oromediterranean belt: extremely rare
Montane belt: rather rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (9224)
2001/12/09
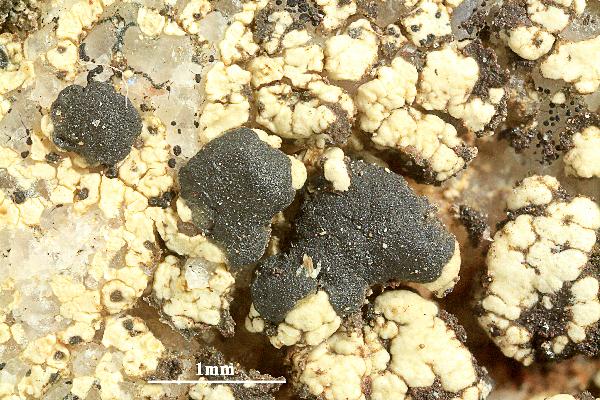


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL40626], Brazil, Bahia, Chapada Diamantina, Lençois Cachoeira
do Mosquito, 12°23' S, 41°22'40'' W, 450-500 m. On siliceous rock
along river. Leg. M. Cáceres & A. Aptroot (no 40626), 22.07.2017, det.
A. Aptroot, 2017. - Thallus UV+ pink; hypothecium brown; hymenium
not inspersed; spores simple, 11 x 6 μm.
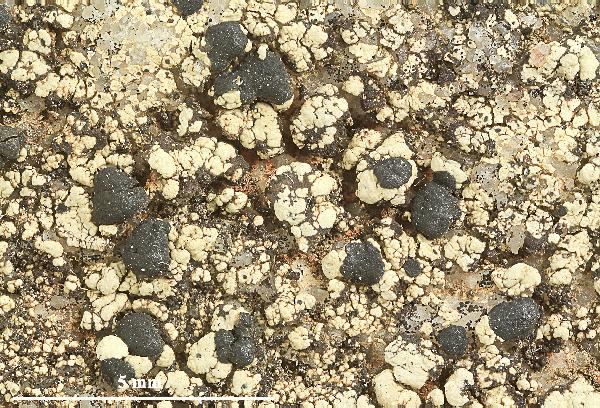


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL40626], Brazil, Bahia, Chapada Diamantina, Lençois Cachoeira
do Mosquito, 12°23' S, 41°22'40'' W, 450-500 m. On siliceous rock
along river. Leg. M. Cáceres & A. Aptroot (no 40626), 22.07.2017, det.
A. Aptroot, 2017. - Thallus UV+ pink; hypothecium brown; hymenium
not inspersed; spores simple, 11 x 6 μm.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather common
Subalpine belt: common
Oromediterranean belt: extremely rare
Montane belt: rather rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (9224)
2001/12/09


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[ABL40626], Brazil, Bahia, Chapada Diamantina, Lençois Cachoeira do Mosquito, 12°23' S, 41°22'40'' W, 450-500 m. On siliceous rock along river. Leg. M. Cáceres & A. Aptroot (no 40626), 22.07.2017, det. A. Aptroot, 2017. - Thallus UV+ pink; hypothecium brown; hymenium not inspersed; spores simple, 11 x 6 μm.


 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS








