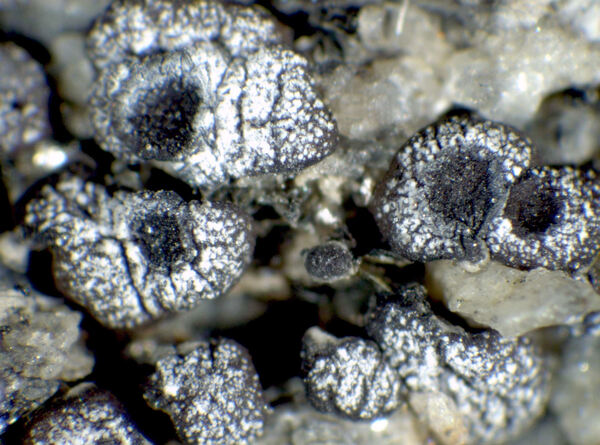
Acarospora versicolor Bagl. & Carestia
Comm. Soc. Critt. Ital., 1, 5: 440, 1864.
Synonyms: Acarospora cineracea (Nyl.) Hue; Acarospora miskolensis H. Magn.
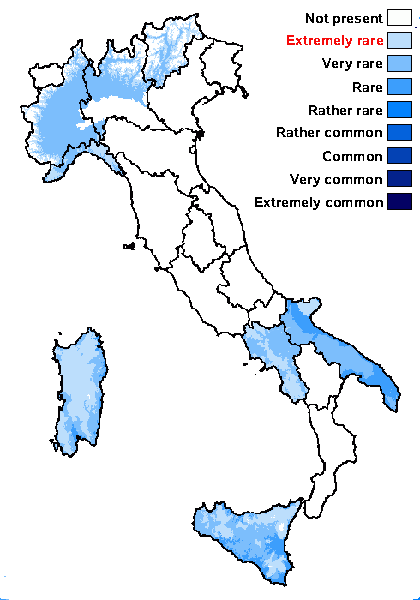
Distribution: N - TAA, Lomb (Nascimbene 2006), Piem (Isocrono & al. 2003), Lig. C - Sar (Knudsen & al. 2015). S - Camp (Jatta 1909-1911), Pugl (Jatta 1909-1911), Si (Grillo 1998, Poli & al. 1998).
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, areolate, the areoles 0.5-1(-2) mm wide, 0.3-0.5 mm thick, usually flat, smooth, dispersed or contiguous, grey to brown, partially bluish white-pruinose, the margins most often brown. Epicortex thin or lacking; cortex 20-40 µm thick, the cells mostly 3-4 µm wide; algal layer continuous, 70-150 µm thick; medulla white, up to 0.3 µm thick, I-. Apothecia immersed, 0.1-0.4 mm across, with a black (brown when wet), concave disc, and a thin thalline margin. Proper exciple prosoplectenchymatous, I-, 5–20 µm wide or widening around the disc up to 70 µm, forming a black excipular ring around the disc; epithecium brown, c. 10 µm high; hymenium colourless, 100-120 µm high, the hymenial gel hemiamyloid, K/I+ light blue fading to light red; paraphyses 1.5-2 µm thick at mid-level, the apical cells hardly swollen or sometimes up to 4-5 µm wide; subhymenium 20-60 µm high, colourless or faintly golden yellow, I+ blue; hypothecium narrow, usually c. 10 µm high. Asci 100-200-spored, cylindrical to narrowly clavate, the apical dome K/I-, 70–100 x 10–20(x30) µm. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, ellipsoid, 3-5 x 1.5-2 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: cortex and medulla K-, C-, KC-, P-, UV-. Chemistry: without lichen substances. Note: on basic siliceous rocks in the Mediterranean belt, but also on walls in Alpine villages, and on thin soil layers, probably more widespread in Tyrrhenian Italy and in dry-warm Alpine valleys below the montane belt. For further details see Knudsen & al. (2015).
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: very rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare
Predictive model
Herbarium samples

Source: Westberg M, Timdal E, Asplund J, Bendiksby M, Haugan R, Jonsson F, Larsson P, Odelvik G, Wedin M, Millanes AM (2015) New records of lichenized and lichenicolous fungi in Scandinavia. MycoKeys 11: 33-61. - CC BY-4.0
NORWAY. Buskerud: Hole, west side of the island Storøya, 60,04685°N, 10,2376°E. 8 June 2008, Westberg 08-092 (S F268460)
Scale: 1 mm.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Subcontinental: restricted to areas with a dry-subcontinental climate (e.g. dry Alpine valleys, parts of Mediterranean Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: very rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid mediterranean belt: very rare
Dry mediterranean belt: rare

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |

 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS




