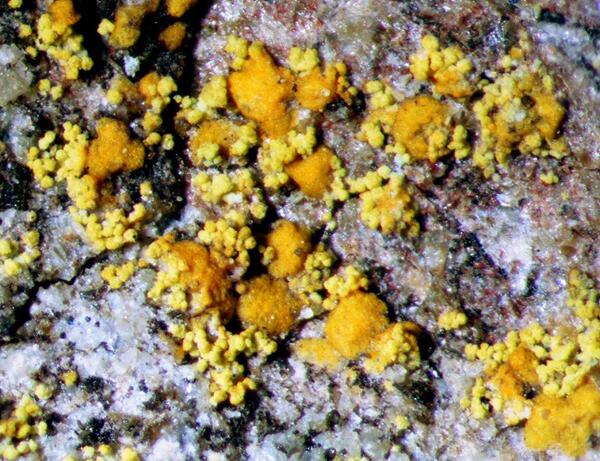
Flavoplaca confusa (Vondrák, Ríha, Arup & Søchting) Arup, Søchting & Frödén
Nord. J. Bot., 31: 45, 2013. Basionym: Caloplaca confusa Vondrák - Ríha, Arup & Søchting, Lichenologist, 41: 593, 2009.
Synonyms:
Distribution: S - Si (Vondrák & al. 2009).
Description: Thallus crustose, episubstratic, yellow to yellow-orange, continuous or of dispersed areoles/squamules which are (80-)95-150(-180) μm thick and (0.2-)0.3-0.9(-1.4) mm wide, flat, smooth or covered with blastidia/soredia of three types: ‘confusa-type’ (blastidia at first marginal, labriform soralia developing after the blastidia have eroded); ‘flavocitrina-type’ (soredia produced directly in well-delimited labriform soralia); ‘limonia-type’ (blastidia laminal, true soredia produced after the blastidia have eroded); soredia (18-)22-40(-43) μm in diam., sometimes gathered into small consoredia. Cortex and medulla poorly developed. Apothecia rare, biatorine/zeorine, yellow-orange, 0.4-1 mm across, with a more or less flat disc and a usually paler margin. Exciple 50-110 μm wide; proper exciple filling the whole exciple width in young apothecia, the thalline exciple being hidden below the true one; epithecium orange, granular, K+ purple-red; hymenium colourless, 70-80 μm high; paraphyses simple or sparingly branched, the apical cells (3.5-)4-5(-5.5) μm wide; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, cylindrical-clavate, functionally unitunicate, apically thickened with a broad internal beak, the inner part of apex and external cap I+ blue, Teloschistes-type. Ascospores 2-celled, polarilocular, hyaline, ellipsoid, 10-13 x 4.5-7 μm, the equatorial thickening (“septum”) 3.5-7 μm (c. 40 % of spore length). Pycnidia yellow-orange. Conidia 3-3.5 x 1-1.5 μm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus and apothecia K+ purple-red, C-, KC-, P-. Chemistry: thallus and apothecia with parietin (major), fallacinal, emodin, teloschistin and parietinic acid (minor), corresponding with chemosyndrome A of Søchting (1997). Note: on hard siliceous, mainly volcanic sea shore cliffs in the supralittoral zone, from c. 2 m upwards in sheltered shores and 5-18 m on exposed shores; probably more widespread in Italy. The species is morphologically very similar to F. flavocitrina and earlier records might be under F. citrina s.lat.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by soredia, or soredia-like structures (e.g. blastidia)
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Taxon bound to maritime-coastal situations
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: very rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: very rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
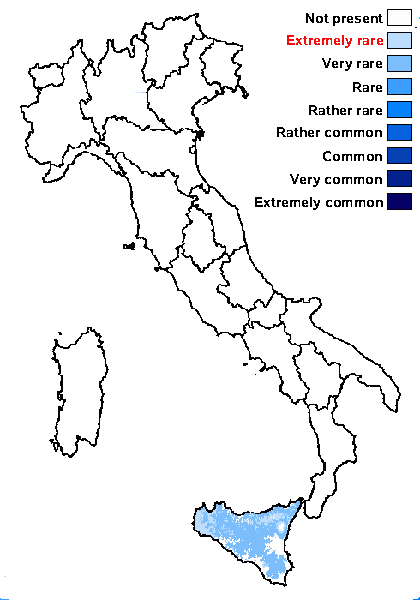
Predictive model
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by soredia, or soredia-like structures (e.g. blastidia)
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Taxon bound to maritime-coastal situations
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Submediterranean belt: very rare
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: very rare
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF


