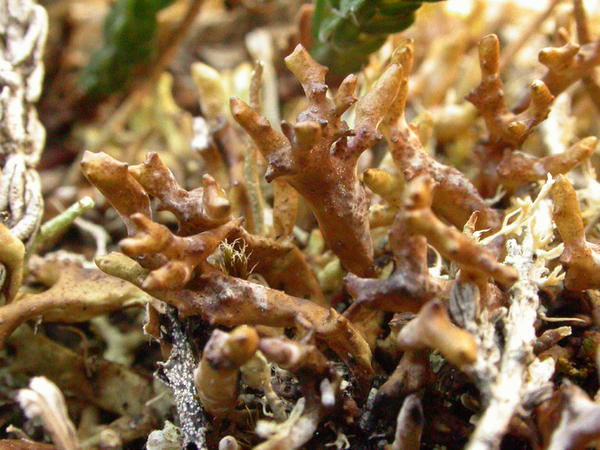
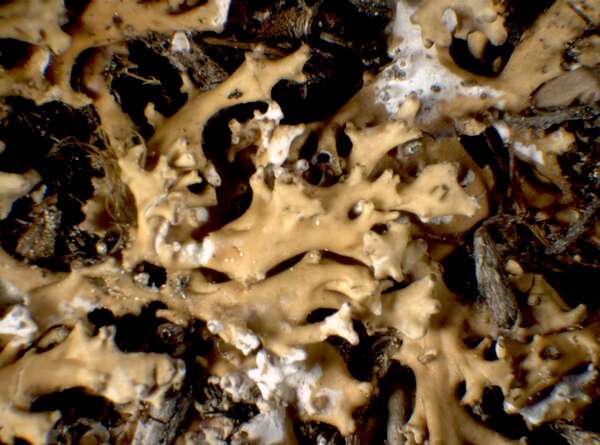
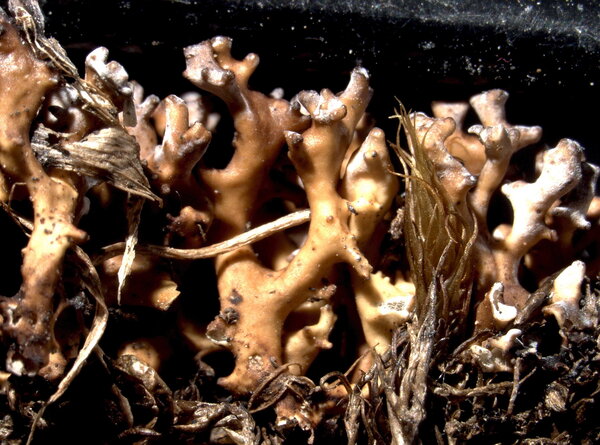
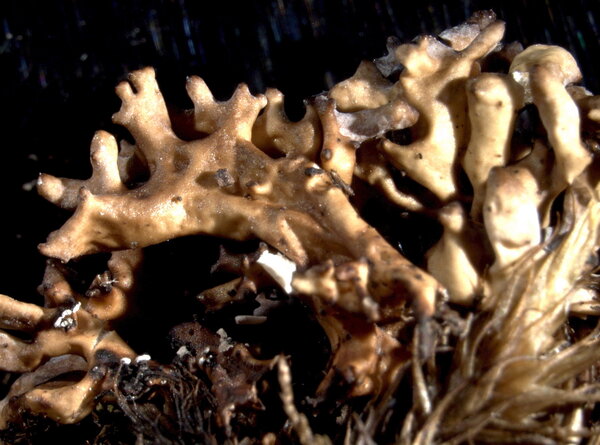
Dactylina ramulosa (Hook. f.) Tuck.
Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts Sc., 5: 397, 1862. Basionym: Dufourea ramulosa Hook. - Bot. Appendix Parry J. Sec. Voy.: 414, 1825.
Synonyms: Dufourea muricata Laurer
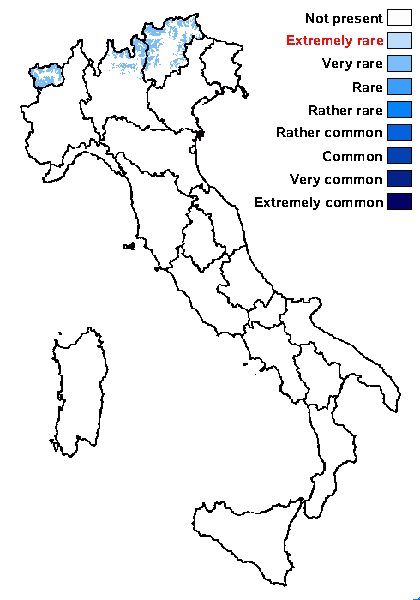
Distribution: N - TAA (Tretiach 1993), Lomb (Dalle Vedove & al. 2004), VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999).
Description: Thallus fruticose, loosely attached, straw-coloured spotted brownish yellow or pale violet-pruinose, shrubby. Branches to 2.5 cm tall, 1-2(-3) mm thick, erect to prostrate, subterete, fragile, dying at base, more or less sympodial with a few branches, but with many short, often black-tipped side branches, usually forming tufts. Epicortex c. 5 µm thick; cortex compact, 2-layered, the outer layer palisade plectenchymatous, c. 30 µm thick, composed of 3-4 layers of pachydermatous hyphae, the inner layer prosoplectenchymatous, 25-30 µm thick, the cells thick-walled, sharply distinguished from the arachnoid medullary hyphae; medulla hollow, with a few loosely arranged hyphae scattered in the cavity. Apothecia extremely rare (never found in Italian material), lecanorine, terminal on lateral branches, 1-3 mm across, with a brown disc and a crenulate thalline margin. Thalline exciple paraplectenchymatous, 2-layered; epithecium colourless or very pale brown; hymenium colourless, 50-60 µm high; paraphyses sparingly branched, 2.5-4 µm thick at mid-level, the apical cells 4-6 µm wide; hypothecium colourless. Asci 8-spored, broadly clavate, Lecanora-type, with biseriately arranged spores. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, globose, 4.5-6 µm in diam., thick-walled. Pycnidia rare, dark, knobby, globose, more frequent on lateral branches. Conidia oblong-citriform to almost bacilliform, straight, 5-7 x c. 1 µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC- or KC+ yellow to pink, P-; medulla K-, C-, KC+ red, P+ red or P-. Chemistry: usnic acid (cortex) and usually physodalic and physodic acids in the medulla (in which case it reacts P+ red).Note: an arctic-alpine, circumpolar species found on soil developing from calcareous schists above treeline; probably confined to the Alps in Italy.
Growth form: Fruticose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by thallus fragmentation
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: very rare
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Fruticose
Substrata: soil, terricolous mosses, and plant debris
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by thallus fragmentation
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: very rare
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS






