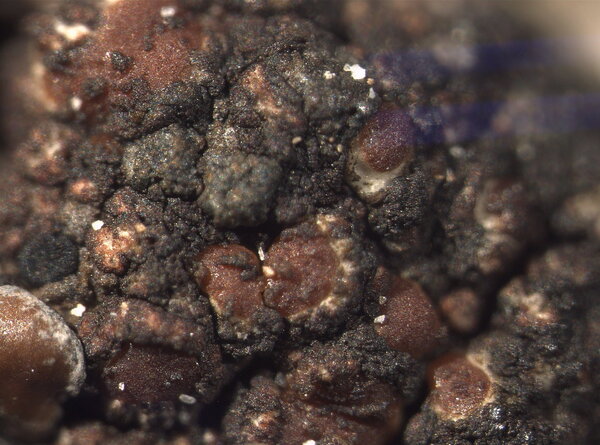
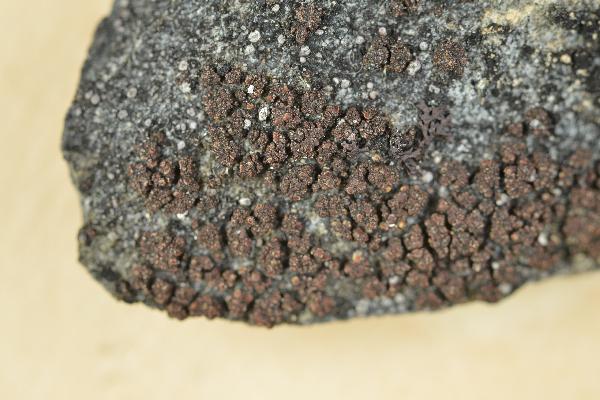
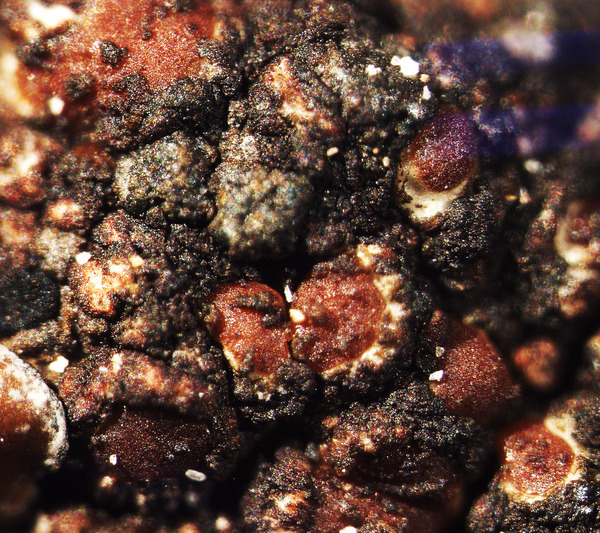
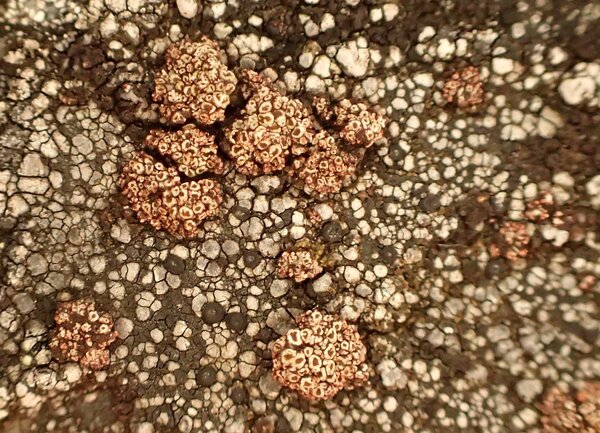
Euopsis granatina (Sommerf.) Nyl.
Flora, 58: 363, 1875. Basionym: Lecanora granatina Sommerf. - Suppl. Fl. Lapp.: 90, 1826.
Synonyms: Pyrenopsis granatina (Sommerf.) Nyl.; Pyrenopsis rufescens Nyl.
Distribution: N - TAA (S-F146882).
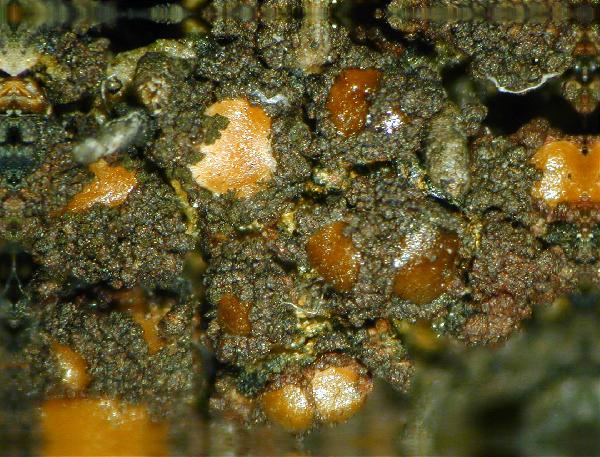
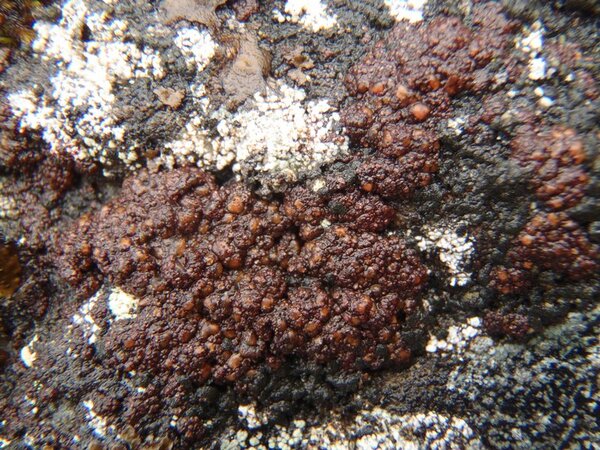
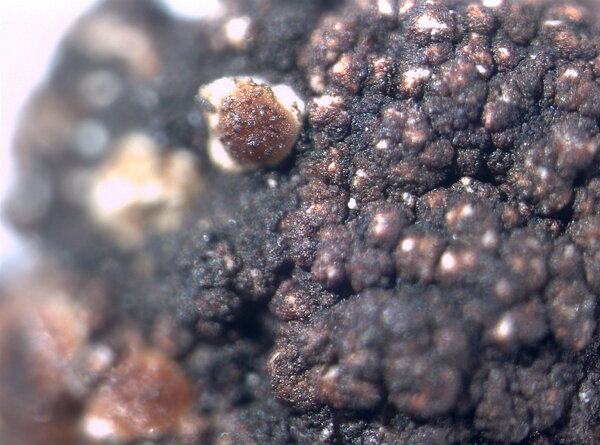
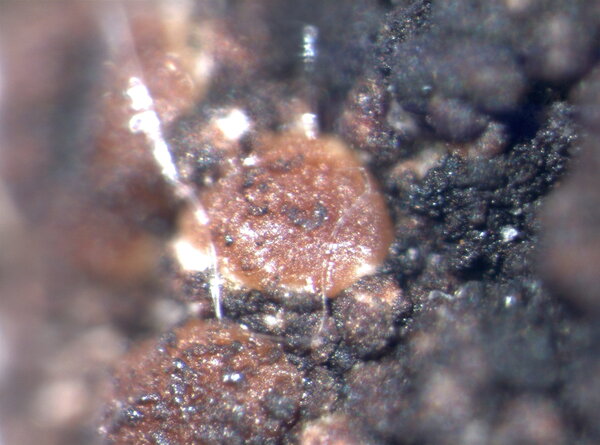
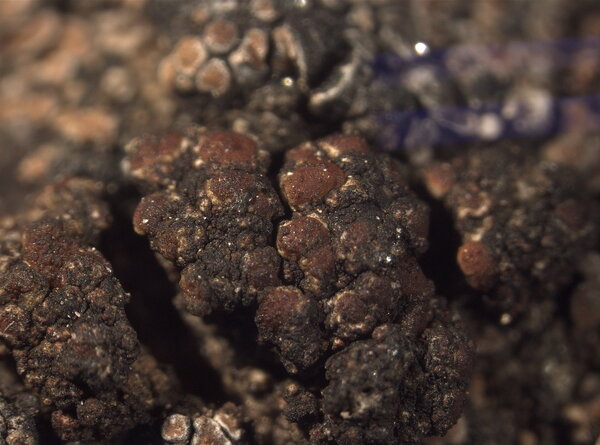
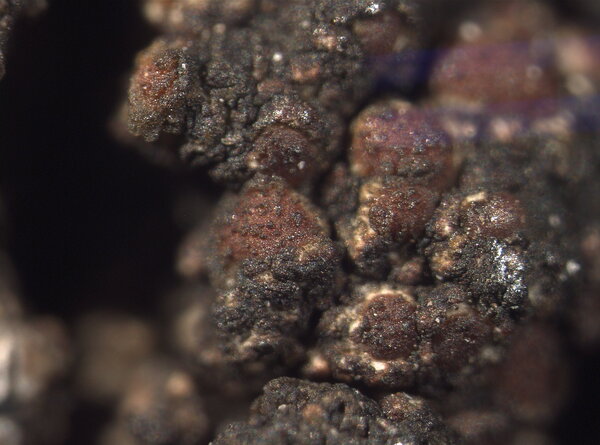
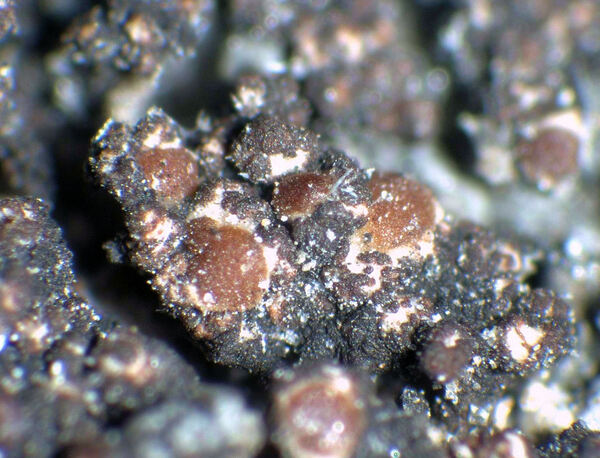
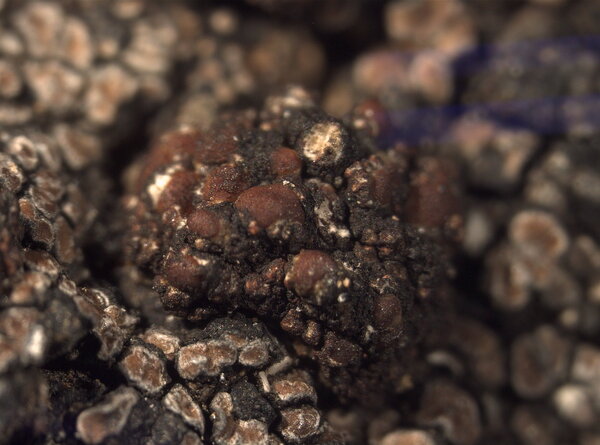
Description: Thallus crustose, homoiomerous, subgelatinous when wet, ecorticate, of granular, subumbilicate small warts, red-brown and white-spotted, to 0.2 mm thick. Thallus anatomy paraplectenchymatous, the hyphae forming a network around the photobiont cells. Apothecia formed in a tangle of generative hyphae. to 0.5 mm across, immersed to adnate, with a flat to convex, red-brown, glossy disc, and a whitish, irregular margin containing green algae. Thalline exciple thick, paraplectenchymatous; proper exciple thin, 10-20(-25) μm wide, of parallel hyphae; epithecium brownish; hymenium colourless, 70-100(-120) μm high, I-, K/I-; paraphyses slender, sparingly branched, septate, gelatinized, c. 2 μm thick, not swollen at tips; hypothecium brownish, 60-75 μm high. Asci 8-spored, cylindrical, unitunicate, the wall composed of an outer, non-expansible and an inner, expansible layer surrounding the protoplast as an amyloid collar, which expands during spore release into a long, tapering rostrum, the outer wall layer strongly amyloid, its upper part separated from the expanded amyloid rostrum by a non-amyloid zone. Ascospores 1-celled, hyaline, oblong to slightly curved, 9-13 x 4-7 μm. Pycnidia rare, immersed in warts. Conidia bacilliform, 4-5 x c. 1 μm. Photobiont cyanobacterial, chroococcoid (Gloeocapsa), surrounded by a reddish (in outer parts) to colourless (in inner parts) gelatinous sheath, with additional trebouxioid green algae in delimited areas, especially in the thalline margin of apothecia. Spot tests: thallus K-, C-, KC-, P-. Chemistry: without lichen substances.Note: a species with an areolate thallus, the granulose areoles being dark brown and spotted pale brown due to the presence of two photobionts, and with minute lecanorine apothecia recalling small garnets, found on periodically wet siliceous boulders and outcrops in sunny places, from the subalpine to the nival belt; widespread in the Holarctic region but altogether rare. The sample from South Tyrol was collected by Arnold near Predazzo (Margola) on syenitic rocks.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, coccaceous (e.g. Gloeocapsa)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
On otherwise dry surfaces with short periods of water seepage after rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: extremely rare
Subalpine belt: very rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
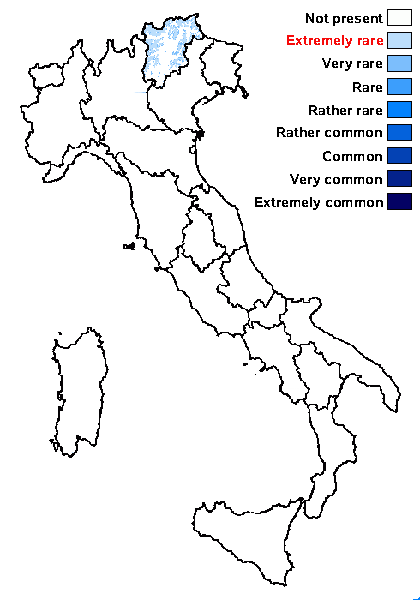
Predictive model
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, coccaceous (e.g. Gloeocapsa)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
On otherwise dry surfaces with short periods of water seepage after rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: extremely rare
Subalpine belt: very rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
 INDEX FUNGORUM
INDEX FUNGORUM
 GBIF
GBIF
 DOLICHENS
DOLICHENS