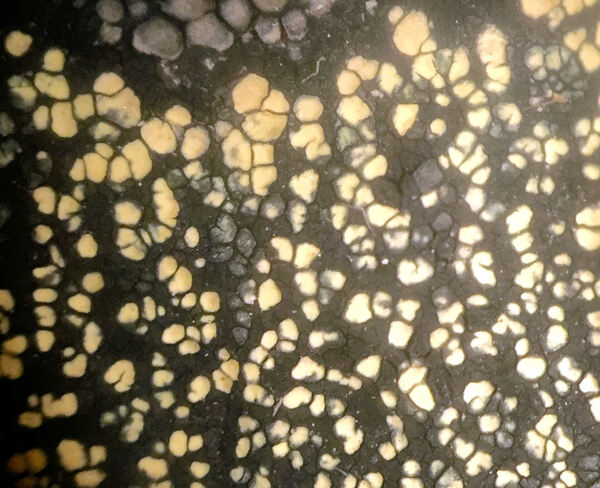
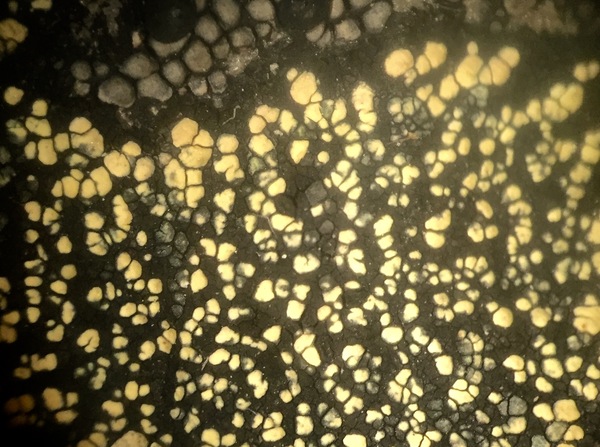
Rhizocarpon geographicum subsp. frigidum (Räsänen) Hertel
in Hertel & Ullrich, Mitt. bot. Staatss. München, 12: 483, 1976. Basionym: Rhizocarpon frigidum Räsänen - Ann. Bot. Soc. Zool.-Bot. Fenn. Vanamo, 19: 9, 1944.
Synonyms: Rhizocarpon tinei subsp. frigidum (Räsänen) Runemark
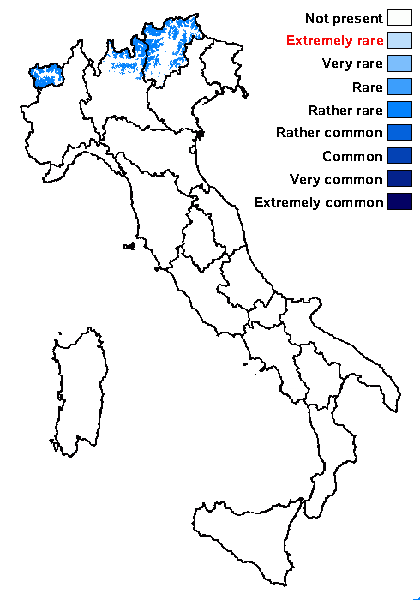
Distribution: N - TAA, Lomb, VA (Piervittori & Isocrono 1999).
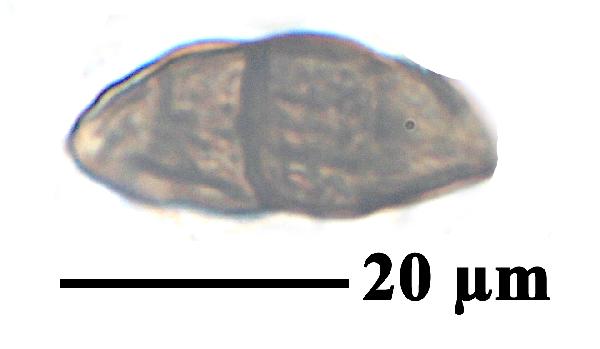
Description: Thallus crustose, bright yellow-green, areolate, forming patches 1-5 cm in diam., delimited by a black prothallus which is often visible also as a hypothallus between areoles. Areoles angular, 0.3-1 mm wide, dispersed or contiguous, flat to slightly convex, smooth, epruinose, usually glossy. Cortex 30-60 µm thick, without distinct structure; medulla white, I+ blue. Apothecia frequent and numerous, lecideine, arising between the areoles, angular, 0.3-0.9 mm across, 0.2-0.6 µm thick, with a black, flat, epruinose disc, and a thin, usually persistent proper margin. Proper exciple pale brown to brownish red; epithecium reddish brown to reddish violet, K+ distinctly red; hymenium 110-160 µm thick, colourless to greenish, K/I+blue; paraphysoids strongly conglutinate, richly branched and anastomosing, clavate; hypothecium dark brown, K-. Asci 8-spored, clavate, fissitunicate, with a well-developed tholus, lacking an ocular chamber, Rhizocarpon-type. Ascospores muriform, with a few septa, soon becoming dark green to brown, ellipsoid, 20-32 x 10-14 µm, halonate. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: medulla K-, C-, KC-, P+ yellow. Chemistry: cortex with rhizocarpic acid; medulla with psoromic acid; epithecium with gyrophoric acid. Note: an arctic-alpine lichen found on steeply inclined to rqain-sheltered surfaces of siliceous rock above treeline; restricted to the Alps, where it can reach the nival belt.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.

Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.
Growth form: Crustose
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rare
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


Felix Schumm - CC BY-SA 4.0
[2921], Spanien, Kanarische Inseln, La Gomera: stellenweise großflächigan lichtoffenen, kühlgetönten, in regelmäßigen Abständen nebelfeuchtenKulm- und Stirnflächen glatten grauen Ergußgesteins imUmbilicarietum cylindricae, 1200 m, pH 6.5, Nordostabbruch derHochfläche der Fortaleza im Zentralmassiv der Insel. Leg. G. Follmann& Sánchez-Pinto & S.Scholz, 03.1980, det. Tassilo Feuerer, 02.1982.Ex G. Follmann: Lichenes Exsiccati Selecti A Museo Historiae CasselensiEditi Nr. 376.


 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF