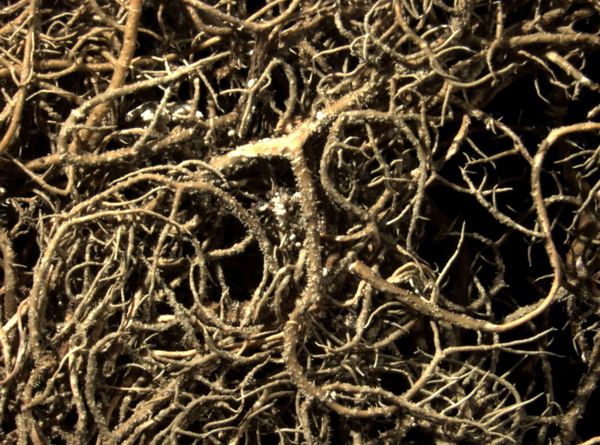
Usnea mutabilis Stirt.
Scottish Natur., 6: 107, 1881.
Synonyms: Usnea marocana Motyka
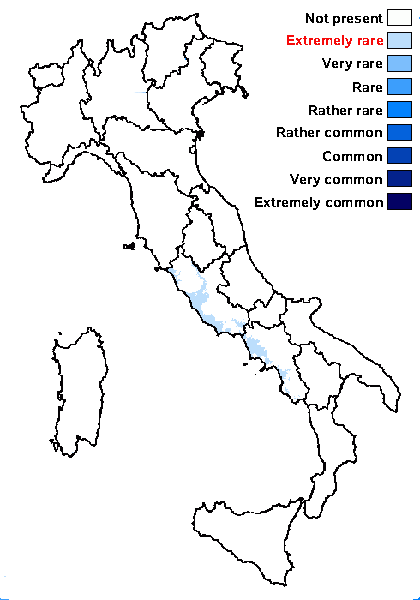
Distribution: C - Laz. S - Camp (CLU 17771).
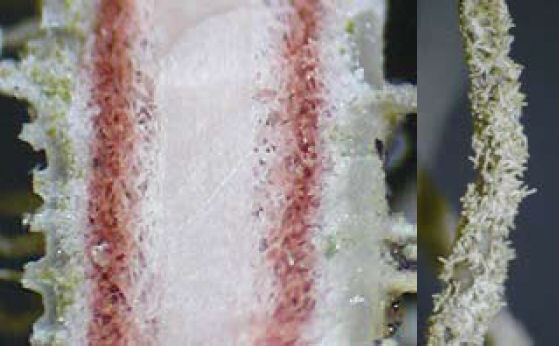
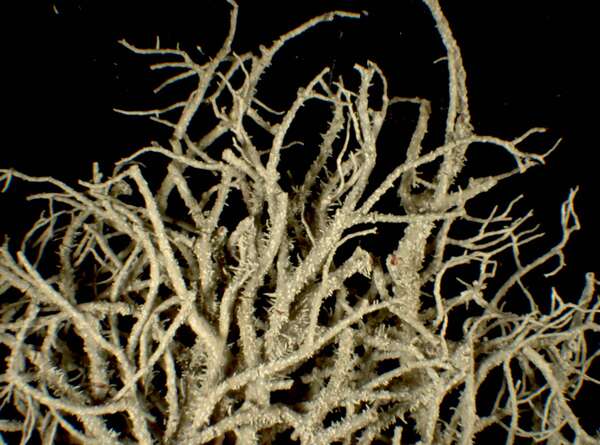
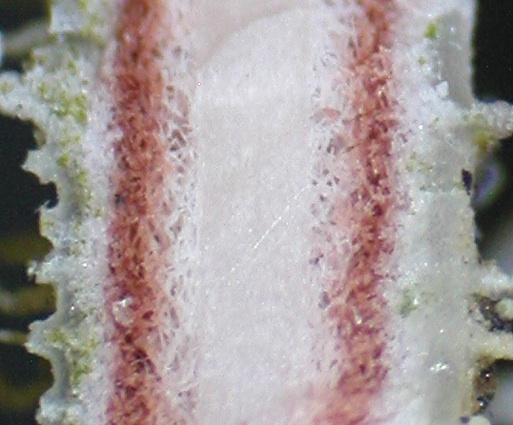
Description: Thallus fruticose-filamentous, greenish, shrubby, 3-7 cm long, rarely subpendulous and up to 14 cm long, branching mainly anisotomic-dichotomously with divergent branches. Main branches cylindrical, 0.5-1 mm thick, often foveolate or with transverse cracks especially toward the base, which is greenish to ochraceous. Lateral branches not constricted at attachment point, progressively tapering towards apices. Papillae and tubercles absent; fibrils mainly present on the main branches, spinulose, 1-2 mm long. Soralia punctiform, irregular, occupying less than half the diameter of the branch, originating from cortex on the lateral branches (in which case they are plane), or from fibercles on the main branches (and then slightly stipitate), finally confluent into large soralia which cover the entire branch; isidiomorphs numerous in the soralia, 0.1-0.3 mm long, giving the branches a spinulose appearance. Cortex shiny in longitudinal section, moderately thick (6-12% of total branch thickness); medulla heterogeneous, with a compact layer below the cortex, otherwise loose to compact, rather thin (21-26%), wine-red; central axis white to wine-red, of variable thickness (28-34%). Apothecia not observed in Italian material. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: cortex K-, C-, P-; medulla K-, C+ yellow-orange, KC+ yellow-orange, P-. Chemistry: cortex with usnic acid; medulla with eumitrin A2 and different fatty acids of the murolic acid complex.Note: a Mediterranean-Atlantic species, found on bark of ancient deciduous and evergreen, isolated trees in semi-natural, open forests subject to frequent humid winds, mostly in the Mediterranean belt. Known from Latium and Campania, it should be looked for elsewhere in Tyrrhenian Italy. It is included as “Critically Endangered” in the Italian red list of epiphytic lichens (Nascimbene & al. 2013c).
Growth form: Fruticose filamentous
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by soredia, or soredia-like structures (e.g. blastidia)
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia

P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14186)
2001/12/12
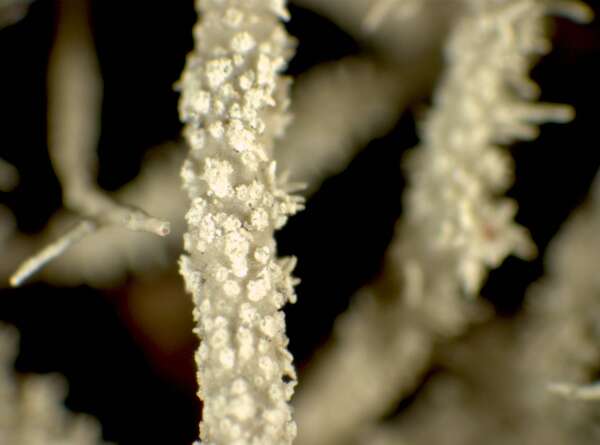


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14186)
2001/12/12
main branch
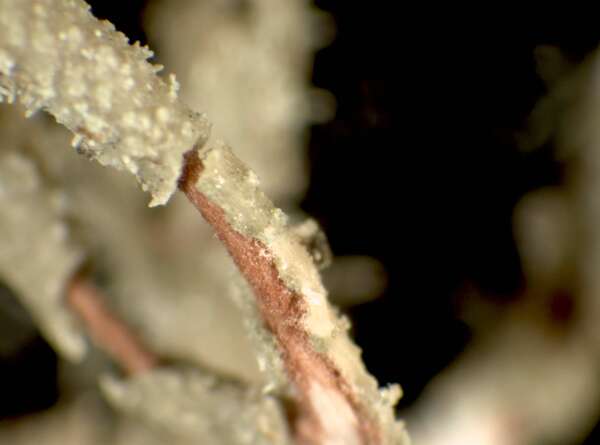


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14186)
2001/12/12
medullary axis
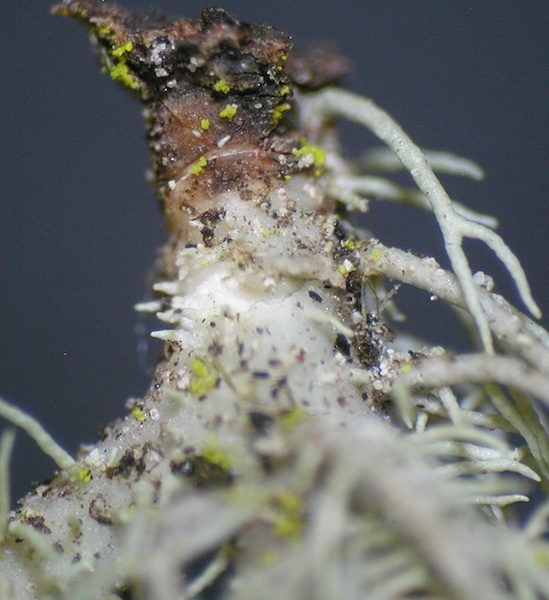

Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia

Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia
Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia
Growth form: Fruticose filamentous
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly asexual, by soredia, or soredia-like structures (e.g. blastidia)
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Oromediterranean belt: absent
Montane belt: absent
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: extremely rare
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |

Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14186)
2001/12/12


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14186)
2001/12/12
main branch


P.L. Nimis; Owner: Department of Life Sciences, University of Trieste
Herbarium: TSB (14186)
2001/12/12
medullary axis

Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia

Tiiu Tõrra; Owner: Tiiu Tõrra - Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences, University of Tartu, Estonia

 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF



