Calogaya arnoldiiconfusa (Gaya & Nav.-Ros.) Arup, Frödén & Søchting
in Arup & al., Nord. J. Bot., 31: 38, 2013. Basionym: Caloplaca arnoldiiconfusa Gaya & Nav.-Ros. in Gaya - Bibl. Lichenol., 101: 54, 2009.
Synonyms: Caloplaca arnoldii auct.ital. p.max.p.
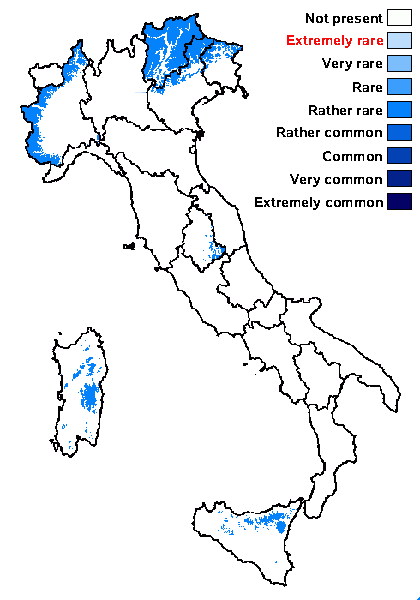
Distribution: N - Frl, Ven (Nascimbene & Caniglia 2000, 2003c, Nascimbene 2008c), TAA (Nascimbene & al. 2006, 2022, Nascimbene 2008b), Piem (TSB 33080). C - Umb (Ravera & al. 2011), Sar (ASU 235739). S - Si (Gaya 2009).
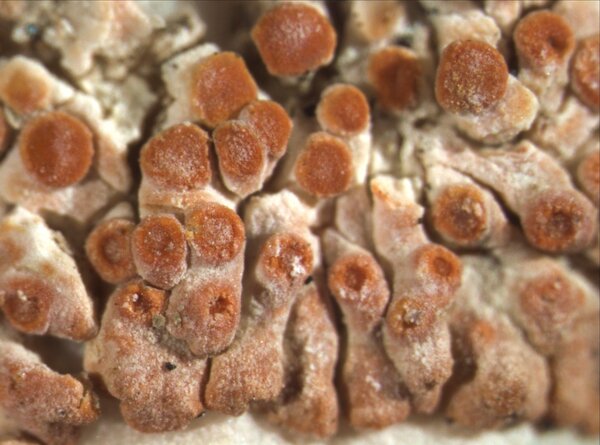
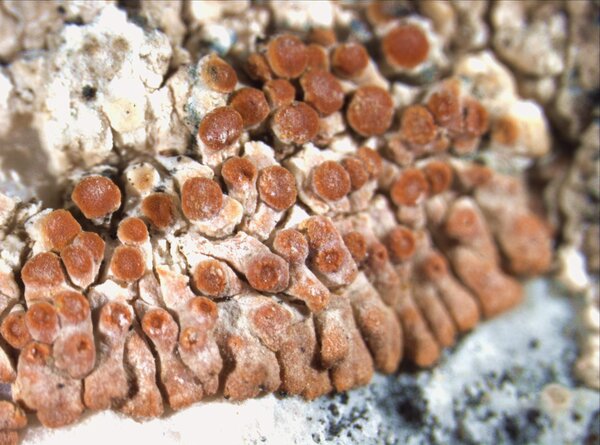
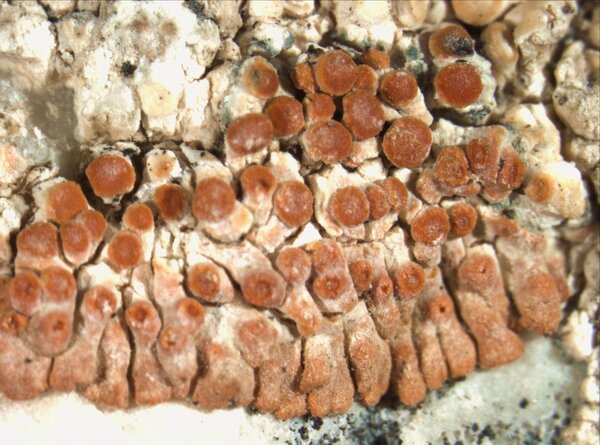
Description: Thallus crustose-placodioid, episubstratic, forming well-delimited, 5-11 mm wide rosettes, deep reddish-orange to almost red, mostly epruinose, the central parts often becoming necrotic and whitish. Areoles located in thallus center, polygonal or irregular, relatively flat, 0.4-1 mm in diam., covered with apothecia; marginal lobes deeply divided, convex, rarely slightly flattened toward tips, contiguous to rarely imbricate, 0.1-0.9(-1.5) mm long and 0.1-0.6(-0.9) mm wide at tips. Upper cortex thin, scleroplectenchymatous, with a yellowish-orange external part and a hyaline inner part, with scarce amounts of superficial crystals visible under polarized light; algal layer more or less continuous; medulla white, lax. Apothecia pseudolecanorine, 0.1-0.6(-0.8) mm across, dispersed or grouped on the areoles or lobe-bases, usually rounded or somewhat distorted, with a flat to convex, orange- brown to dull red, epruinose disc and a slightly paler, thin margin. Exciple of radially arranged hyphae, scleroplectenchymatous; epithecium brownish-orange, K+ purple-red; hymenium and hypothecium colourless; paraphyses septate, sparsely branched in upper part, 1.5-3(-3.5) µm wide at base, the apical cell swollen, up to 7(-8.5) µm wide. Asci 8-spored, clavate, functionally unitunicate, apically thickened with a broad internal beak, the inner part of apex and external cap I+ blue, Teloschistes-type. Ascospores 2-celled, polarilocular, hyaline, mostly broadly ellipsoid, (8.5-)10-13(-16) x (3.8-)5-6.5(-7.5) µm, the equatorial thickening (“septum”) (2.5-)3-4(-5) µm. Photobiont chlorococcoid. Spot tests: thallus and apothecia K+ purple-red, C-, KC-, P-. Chemistry: thallus and apothecia with parietin, fallacinal, emodin, and teloschistin.Note: in the past this species was confused with C. arnoldii, which substitutes in upland areas, on vertical to rain-sheltered surfaces of calcareous and dolomitic rocks. For further details see Gaya (2009) and Gaya & al. (2001).
Growth form: Crustose placodiomorph
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: rather rare
Montane belt: rather rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent
Predictive model
Herbarium samples
Growth form: Crustose placodiomorph
Substrata: rocks
Photobiont: green algae other than Trentepohlia
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
In underhangs rarely wetted by rain
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: rather rare
Subalpine belt: rather rare
Oromediterranean belt: rather rare
Montane belt: rather rare
Submediterranean belt: absent
Padanian area: absent
Humid submediterranean belt: absent
Humid mediterranean belt: absent
Dry mediterranean belt: absent

Predictive model
| Herbarium samples |
 Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
 GBIF
GBIF





