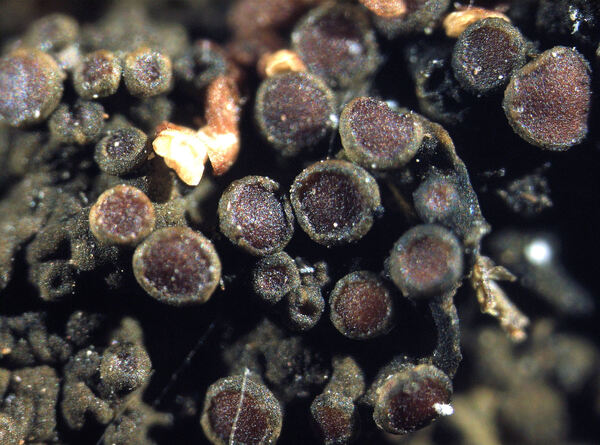
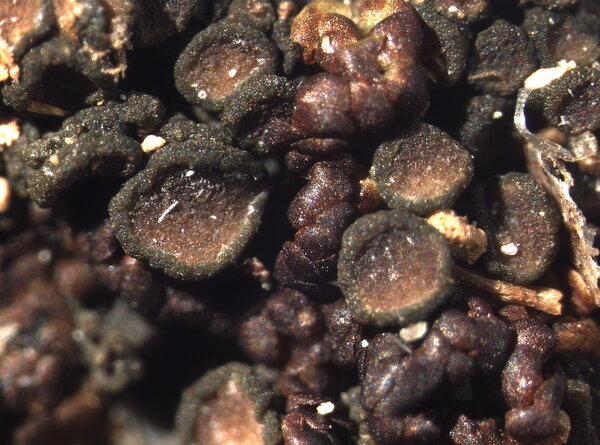
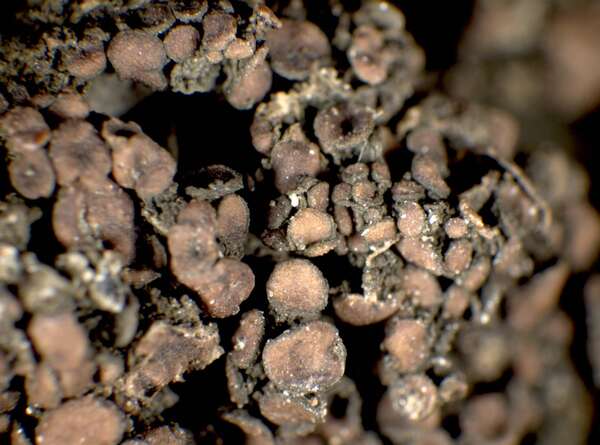
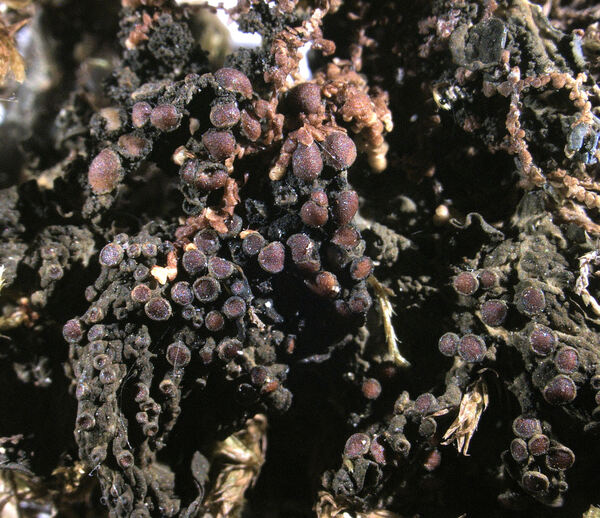
Gabura fascicularis (L.) P.M. Jørg.
Lichenologist, 46: 594, 2014. Basionym: Lichen fascicularis L. - Mantissa Pl., 1: 133, 1767.
Synonyms: Arctomia fascicularis (L.) Otálora & Wedin; Collema aggregatum sensu Sommerf.; Collema ascaridosporum (A. Massal.) Degel.; Collema dinaricum Zahlbr.; Collema fasciculare (L.) F.H. Wigg.; Lathagrium aggregatum (“Ach.”) M. Choisy; Lathagrium ascaridosporum A. Massal.; Parmelia nigrescens var. fascicularis (L.) Schaer.; Synechoblastus aggregatus (“Ach.”) Th. Fr.; Synechoblastus ascaridosporus (A. Massal.) Zwackh; Synechoblastus fascicularis (L.) A.L. Sm.; Synechoblastus labyrinthicus Anzi
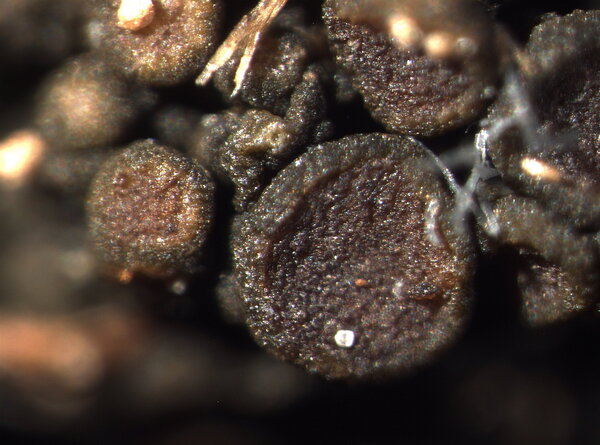
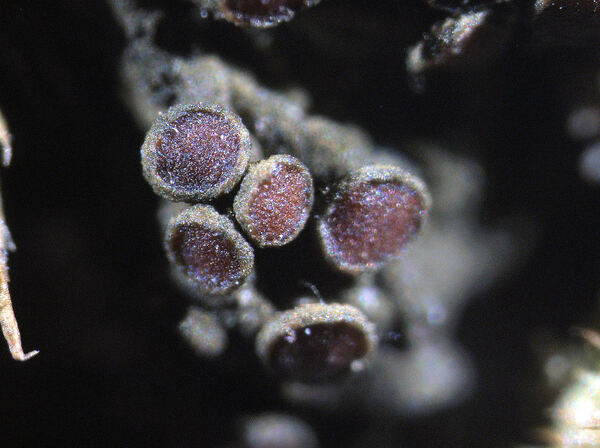
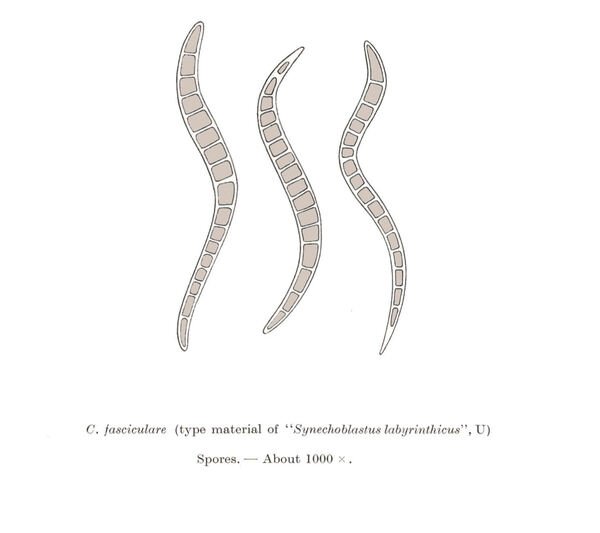
Description: Thallus subfoliose to subcrustose, homoiomerous, ecorticate, gelatinous and markedly swollen when wet, coarsely wrinkled and indistinctly lobed, dark olive-green to brown-black when dry, forming rounded, up to 2-3 cm wide and to 1 cm thick (when moist) pillows. Lobes not always developed, short, flattened, adpressed, sometimes with erect lobules developing from wrinkles. Apothecia common, lecanorine, numerous and crowded, 0.8-1.5(-2) mm across, sessile to rarely substipitate, with a flat, brown disc, and a thick to thin, more or less wrinkled thalline margin. Thalline exciple ecorticate; proper exciple thin, euthyplectenchymatous, of thin-walled, slightly pigmented hyphae; epithecium brownish; hymenium colourless, 85-130 µm high, I+ blue; paraphyses lax, thin and flexuose, branched, 1-1.5 µm thick at mid-level, distinctly brown-pigmented at the slightly swollen apices. Asci (6-)8-spored, clavate, with an I+ reddish to blue wall, the tholus lacking amyloid structures. Ascospores 9-16-septate, hyaline, worm-like and spirally arranged in ascus, often attenuated towards one or both ends, (50-)70-120(-170) x 4.5-5(-6) µm. Photobiont: cyanobacterial (Nostoc, the cells in long chains). Spot tests: all negative. Chemistry: without lichen substances.
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Dry submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
pH of the substrata:
1 2 3 4 5
Solar irradiation:
1 2 3 4 5
Aridity:
1 2 3 4 5
Eutrophication:
1 2 3 4 5
Poleotolerance:
0 1 2 3
Altitudinal distribution:
1 2 3 4 5 6
Rarity
absent
extremely rare
very rare
rare
rather rare
rather common
common
very common
extremely common
Loading data...
Occurrence data
Predictive map
Growth form: Foliose, broad lobed
Substrata: bark
Photobiont: cyanobacteria, filamentous (e.g. Nostoc, Scytonema)
Reproductive strategy: mainly sexual
Most common in areas with a humid-warm climate (e.g. most of Tyrrenian Italy)
Commonnes-rarity: (info)
Alpine belt: absent
Subalpine belt: absent
Montane belt: extremely rare
Dry submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Humid submediterranean belt: extremely rare
Padanian area: absent
pH of the substrata:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Solar irradiation:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Aridity:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Eutrophication:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Poleotolerance:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Altitudinal distribution:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Rarity
absent
extremely rare
very rare
rare
rather rare
rather common
common
very common
extremely common
Loading data...
Occurrence data
Predictive map